Enable Erlang connection among distributed dockers (docker containers on different hosts) by reimplementing the distributed connection protocol of net_kernel.
Erlang nodes need connect with each other to work together, so they are usually used in one subnet. However, dockers on different hosts are in different subnets (one subnet per host). So it's difficult to build Erlang cluster on distributed docker cluster.
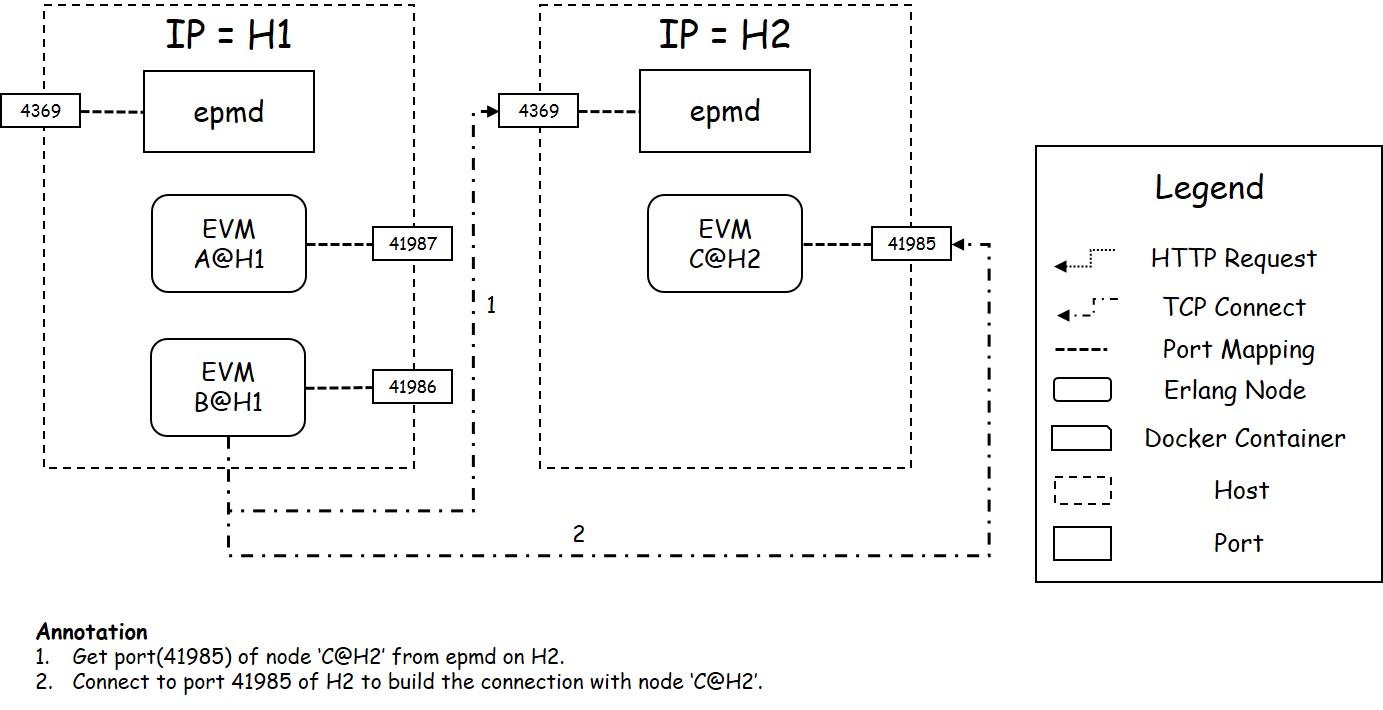
When an Erlang node attempts to connect another node, it must create a tcp connection to the node. Because different Erlang nodes listen on different ports, there should be a naming service with a known port which can tell us the port of a Erlang node. That's epmd.
The following figure shows the connection buiding process of Erlang nodes:
It is difficult to connect nodes among distributed dockers, because:
- Dockers on different hosts are in different subnets. If a process in a docker wants to communicate with a process on another docker, it should access the host IP and published host port of the target process.
- It is difficult to publish ports used by Erlang node. It is because the port which an Erlang node listens on is allocated dynamically when the node starts.
- It is hard to get the published port of an Erlang node. If we use
-Por-p xxx:xxxto fix the port mapping, we can start only one docker with Erlang on one host because of port conflict. If we use-p xxxto map the port to an arbitrary host port, we can only get the published port from the docker daemon.
In this project, we implement a new connection protocol module eid_tcp_dist.erl instead of inet_tcp_dist.erl. The following figure shows the new protocol of Erlang connection.
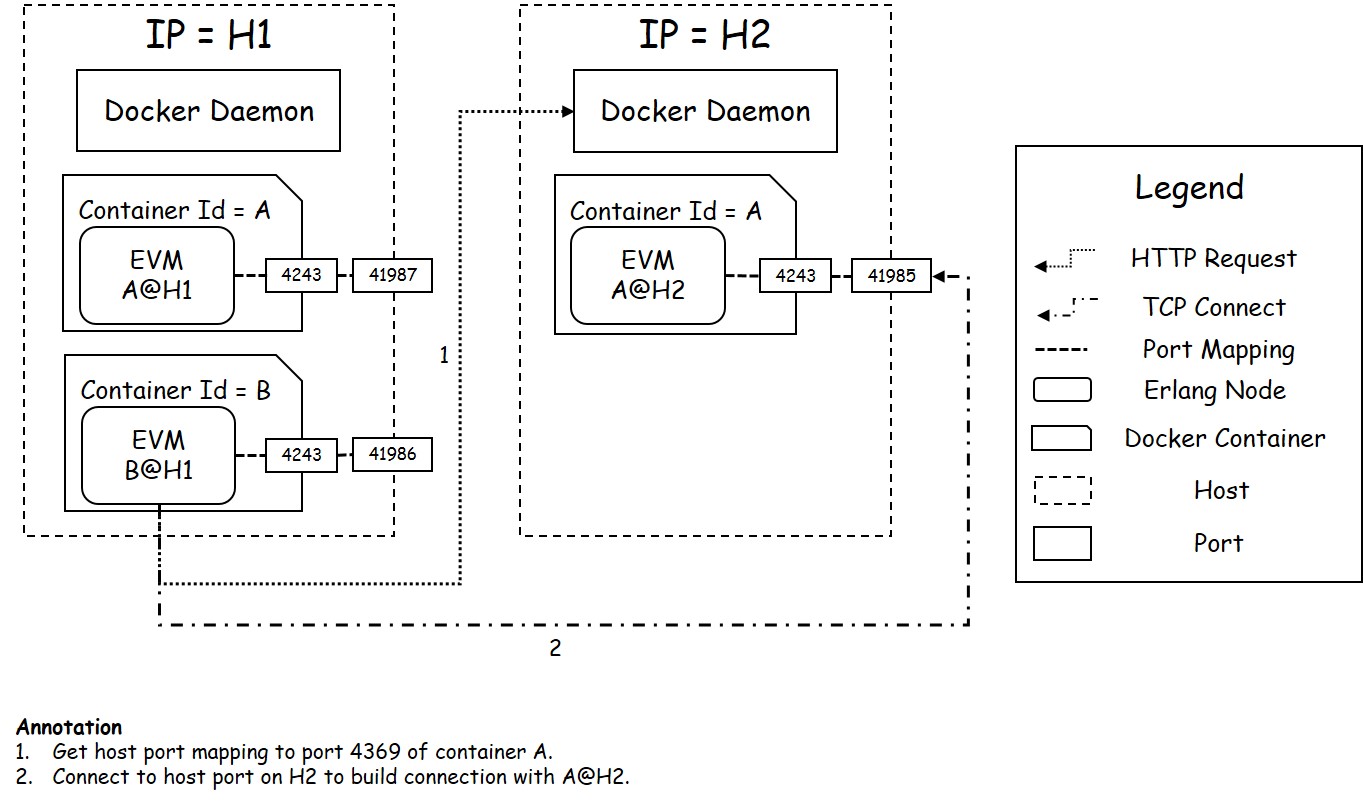 We mainly did the following modifications on the connection protocol:
We mainly did the following modifications on the connection protocol:
- Limit that each docker can only hold one Erlang node.
- Rule that the Erlang node name should be
DockerContainerID@HostIP. - Fix the port used by Erlang. (Default 12345)
- Use Docker Remote API to get the published port of Erlang node.
Docker Remote API should be enabled by following steps:
- add
DOCKER_OPTS="-H tcp://0.0.0.0:4243"in/etc/default/docker.ioor/etc/default/docker. - Restart docker daemon by
sudo service docker restart.
PS:
4243is the default port used by docker HTTP API. It can also be set to some other value such as4321, but eid should be configured the same docker port value by adding-kernel docker_dameon_port 4321when starting Erlang VM.
You must ensure you have an erlang environment on your computer.
You can compile and install Erlang-In-Docker with the simple command ./build %target_path%, for example:
./build /usr/lib/erlangAfter the installation, a complete Erlang environment with eid started automatically is installed to %target_path%.
- You should install Erlang-In-Docker in your docker image, and use new erlang environment installed by Erlang-In-Docker instead of the old one.
- When starting docker, you should add argument
-p 12345to export and publish the port used by Erlang node. - When starting Erlang node, you should add argument
-proto_dist eid_tcpto enableeid_tcp_distinstead ofinet_tcp_dist.
PS:
12345is the default port used by Erlang node. It can also be set to some other value such as1234, but eid should be configured the same erlang port value by adding-kernel erlang_port 1234when starting Erlang VM.
For example, the command should be like this:
sudo docker run -i -t -p 12345 %image_name% /bin/bash
%target_path%/erl -proto_dist eid_tcp -name [email protected] -setcookie taotaotheripperPS:
asd134fczcvis the container ID,192.168.4.231is the IP of the host.
As is mentioned before, when starting Erlang node, you can use kernel envrionment value docker_daemon_port to specify the docker HTTP port Erlang-In-Docker will request, erlang_port to specify the port Erlang node will use in docker. For example:
# DOCKER_OPTS="-H tcp://0.0.0.0:4321
sudo docker run -i -t -p 1234 %image_name% /bin/bash
%target_path%/erl -proto_dist eid_tcp -name [email protected] -setcookie taotaotheripper -kernel docker_daemon_port 4321 erlang_port 1234