The secure manager for your WireGuard clients
- Purpose
- Usage
- Configuration
- API settings
- Blazor settings
- SSL
- Database
- Authentication
- docker-compose
- License
Tunnel is a secure manager for your WireGuard clients' configuration. It is not meant to manage your server's and your clients' private keys. Your server's private key should be stored securely on your server and your clients' private keys should be stored on their devices only. Tunnel does not automatically update your WireGuard configuration on the file system nor does it manage the WireGuard services.
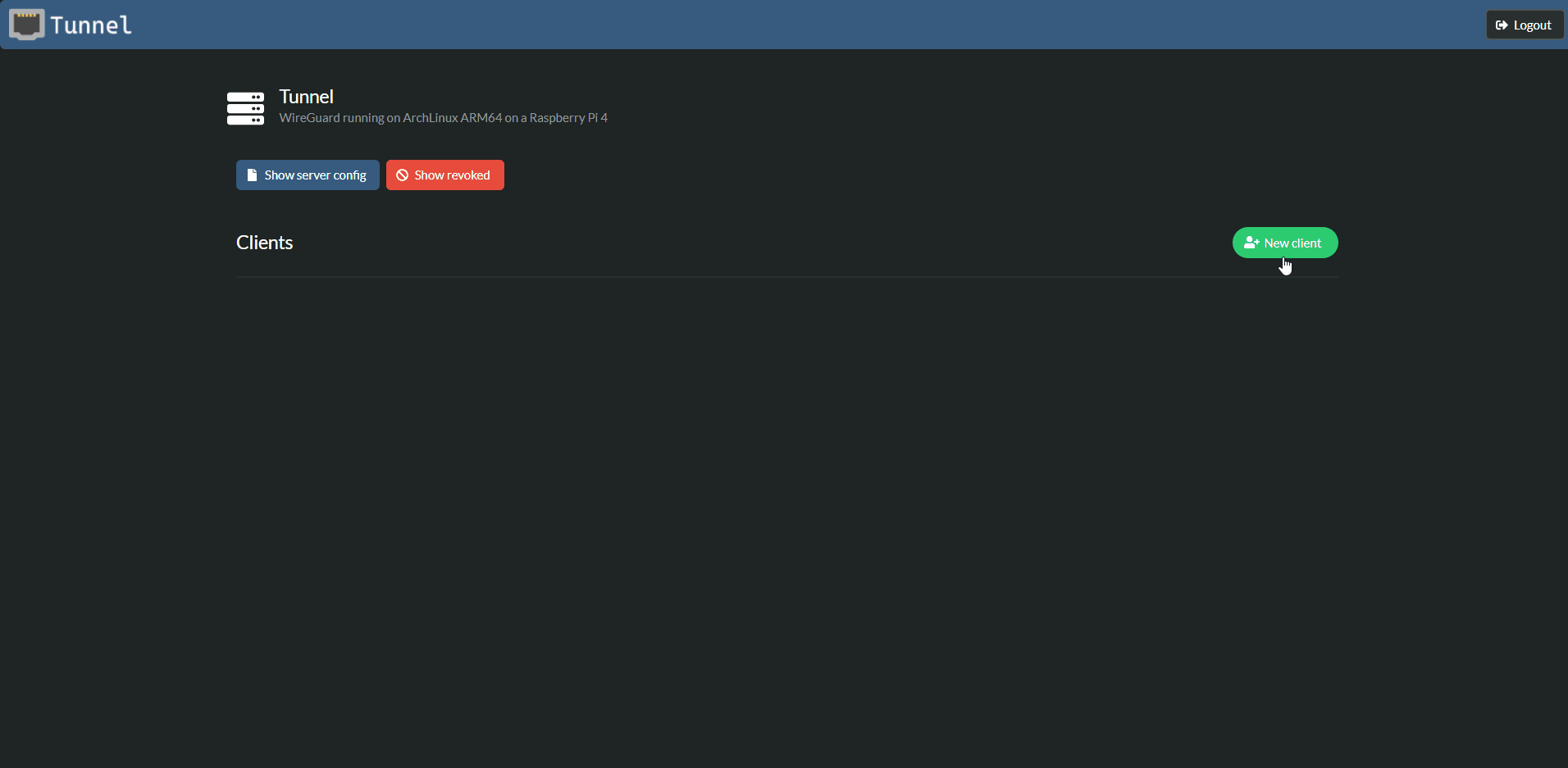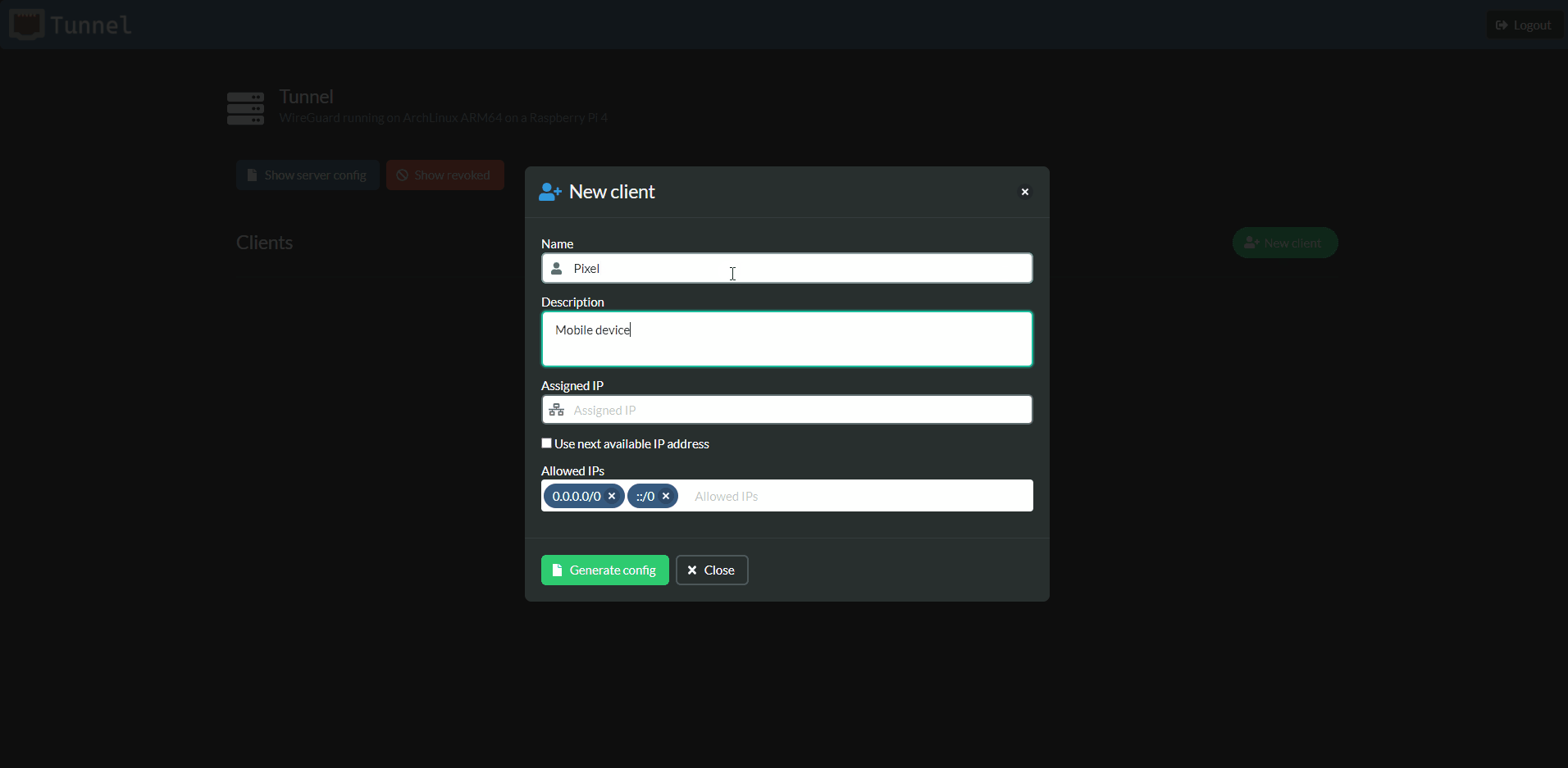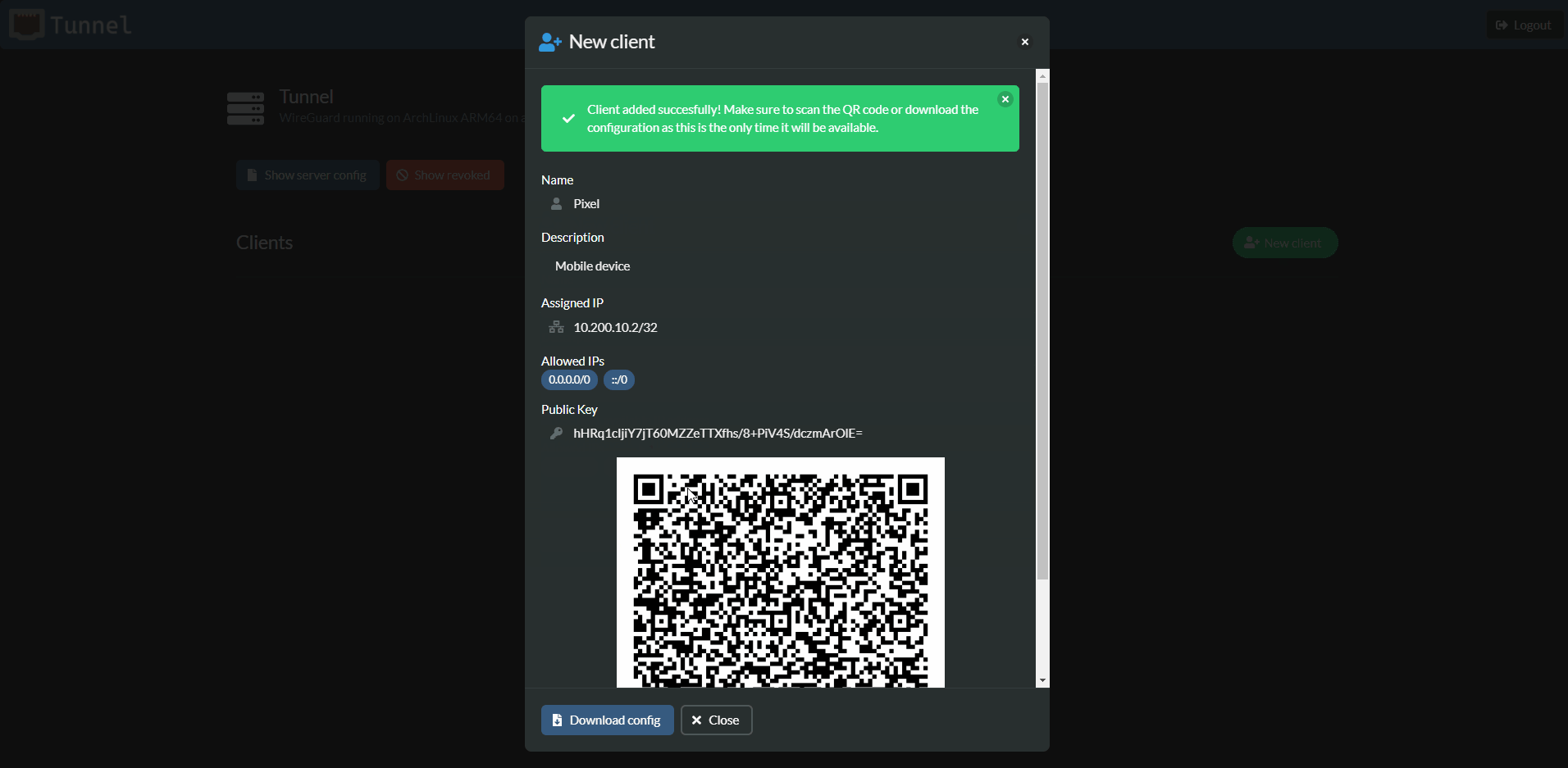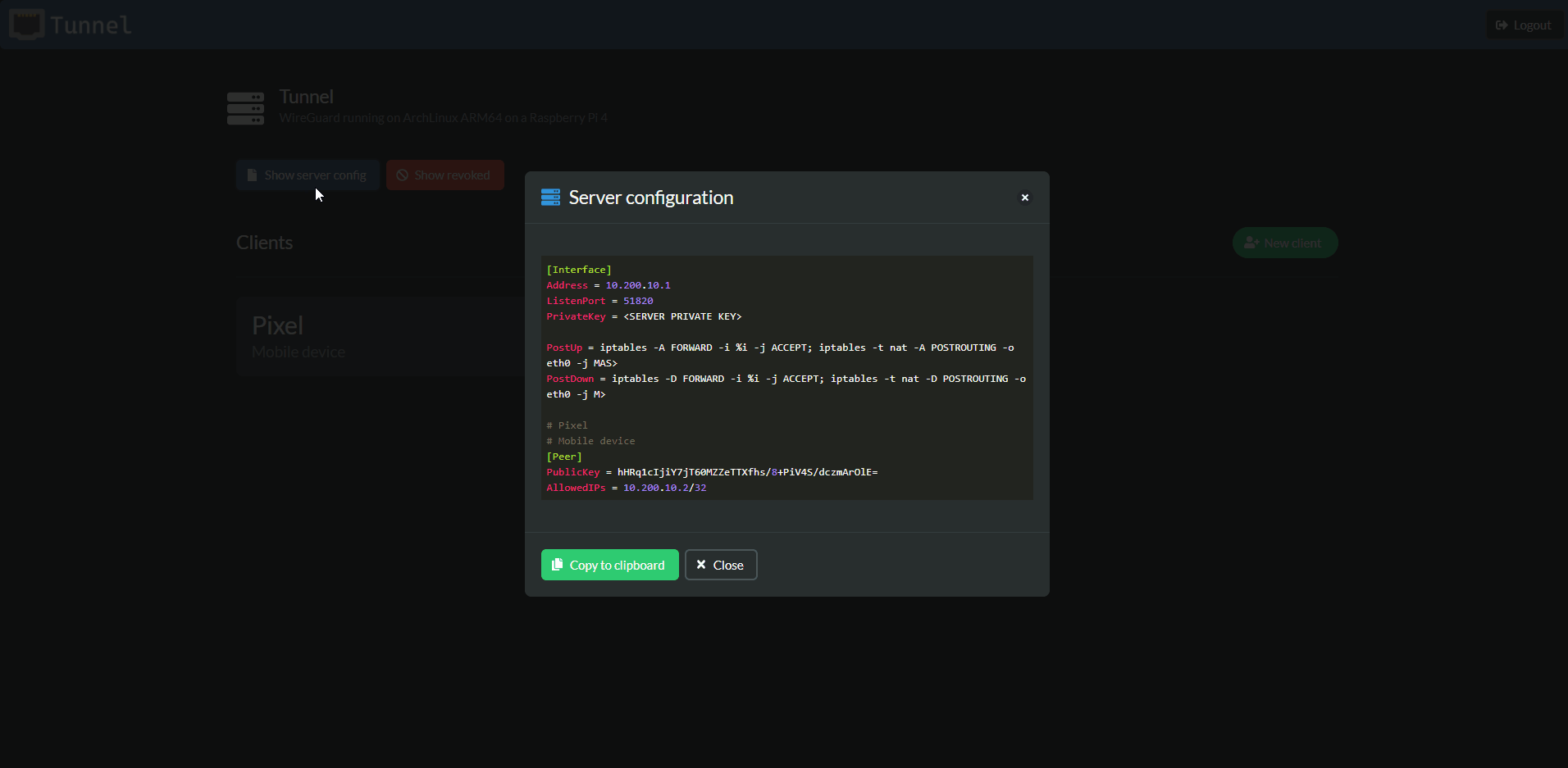
Tunnel offers an easy way to add new clients. Their keys are generated in the browser (using C# running on WebAssembly) and only the public key is sent to the server. Your private key is never sent. The relevant peer section can then be copied from the server configuration and added to your WireGuard config file on your server.
The QR Code and WireGuard config file are only available when you first add the client. They are gone after you close the dialog and can never be generated by Tunnel again (again the private key is not stored). You can always revoke an exisiting client and generate a new key pair by creating a new client.
The simplest way to get started is to use the docker image.
docker run -it --rm -p "5800:5800" whyvra/tunnelYou should now be able to access tunnel via http://localhost:5800/
By default, the docker image exposes port 5800 where it serves its content using HTTP. The data is stored in a SQLite database saved in /data. A 7-day rotating log is also kept under /data/logs.
The docker image configuration can be tweaked in a number of different ways using appsettings.json files and/or environment variables.
The appsettings.json files hold all the base settings for the Tunnel app. There's one for the API and one for Blazor frontend located in /srv/dotnet and /srv/www respectively.
The default API settings can be overwritten by mounting a custom appsettings.json file and pointing the DOTNET_CUSTOM_APPSETTINGS environment variable to it. Please note if a setting is not overwritten in the custom appsettings.json file, the base setting will still be read.
docker run -it --rm -p "5800:5800" \
-e "DOTNET_CUSTOM_APPSETTINGS=/run/secrets/appsettings.json" \
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)",target=/run/secrets \
whyvra/tunnelThe API settings can also be overwritten using environment variables. Each element in the hierarchy is separated by a double underscore.
For example, if you wanted to override the TunnelContext connection string, the environment variable would be called ConnectionStrings__TunnelContext.
docker run -it --rm -p "5800:5800" \
-e "ConnectionStrings__TunnelContext=Data Source=/data/tunnel_db.sqlite3;" \
whyvra/tunnelThe Blazor frontend settings can only be modified by overwriting the appsetting.json file in /srv/www as shown below.
docker run -it --rm -p "5800:5800" \
-v "$(pwd)/appsettings.json":/srv/www/appsettings.json \
whyvra/tunnelThe default Blazor frontend settings are shown below. These are the minimal required settings for the frontend. If you overwrite the Blazor appsettings.json file, you should at least include those.
{
"api": {
"url": "/api"
},
"auth": {
"enabled": false
}
}See the Authentication section below for more info on the auth parameters.
To use HTTPS instead of HTTP, use the SSL_CERT and SSL_KEY environment variables to point to the location of the mounted certificate and key files.
docker run -it --rm -p "5800:5800" \
-e "SSL_CERT=/run/secrets/cert.pem" \
-e "SSL_KEY=/run/secrets/key.pem" \
--mount type=bind,source="$(pwd)"/ssl,target=/run/secrets \
whyvra/tunnelPlease note that SSL_CERT should point to the chained version of your SSL certificate.
Tunnel supports SQLite and PostgreSQL. The relevant settings in the API appsettings.json are as follows:
{
...
"database": {
"type": "sqlite",
"automaticMigrations": true
},
"ConnectionStrings": {
"TunnelContext": "Data Source=/data/tunnel.sqlite3;"
}
}For PostgreSQL, set database.type to postgres and update the TunnelContext connection string.
You can also use the following environment variables:
database__typedatabase__automaticMigrationsConnectionStrings__TunnelContext
Authentication can be added by using an OpenID Connect server like Keycloak. In order to configure authentication, you'll need to update both the API and Blazor settings. The API settings can be tweaked using environment variables but you will need to update the /srv/www/appsettings.json file for the Blazor settings.
Add the following auth parameters to appsettings.json
{
...
"auth": {
"authority": "https://example.keycloak.com/auth/realms/apps",
"clientId": "wg.tunnel",
"enabled": true,
"requiredRole": "wg_admin",
"responseType": "code"
}
}The requiredRole parameter is optional. If provided, it will require the logged-in user to have the provided role under the roles claim in the JWT issued by the Open ID Connect server.
The responseType parameter is only required for the Blazor settings. It will default to code if omitted. Should it be provided to the API settings, it will just be ignored.
Please note that if you have an SSL certificate issued by a custom or internal CA on your Open ID connect server, you will need to add or mount the root CA certificate under /etc/ssl/certs.
Detailed below is a docker-compose example making use of PostgreSQL as the backend database and Keycloak (Open ID Connect server) for authentication. This example has been tested using docker stack.
.
├── appsettings.json
├── data (data folder for tunnel)
├── docker-compose.yml
├── init_script.sql
├── pgdata (folder for postgres data)
└── ssl
├── tls.crt
└── tls.key
The tls.crt and tls.key can be generated with the following commands. Please note that the certificate should answer to keycloak.lan or whatever hostname you choose to replace it with.
$ openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -pkeyopt rsa_keygen_bits:4096 -out tls.key
$ openssl req -key tls.key -x509 -new -days 720 -out tls.crt# docker-compose.yml
version: '3.5'
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:13-alpine
hostname: postgres
environment:
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
- PGDATA=/var/lib/postgresql/data/pgdata
volumes:
- ./pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data/pgdata
- ./init_script.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init_script.sql
keycloak:
image: jboss/keycloak:latest
hostname: keycloak
depends_on:
- postgres
environment:
- DB_VENDOR=postgres
- DB_ADDR=postgres
- DB_PORT=5432
- DB_USER=postgres
- DB_PASSWORD=postgres
- KEYCLOAK_USER=admin
- KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD=admin
- KEYCLOAK_LOGLEVEL=WARN
- ROOT_LOGLEVEL=WARN
volumes:
- ./ssl:/etc/x509/https
ports:
- "8443:8443"
tunnel:
image: whyvra/tunnel:0.1
hostname: wg-tunnel
depends_on:
- postgres
- keycloak
environment:
- database__type=postgres
- ConnectionStrings__TunnelContext=Host=postgres;Database=tunnel;Username=postgres;Password=postgres;
- auth__enabled=true
- auth__authority=https://keycloak.lan:8443/auth/realms/apps
- auth__clientId=wg_tunnel
- auth__requiredRole=wg_admin
volumes:
- ./data:/data:rw
- ./appsettings.json:/srv/www/appsettings.json
- ./ssl/tls.crt:/etc/ssl/certs/tls.crt
ports:
- "5800:5800"// appsettings.json
{
"api": {
"url": "/api"
},
"auth": {
"authority": "https://keycloak.lan:8443/auth/realms/apps",
"clientId": "wg_tunnel",
"enabled": true,
"requiredRole": "wg_admin"
}
}# init_script.sql
CREATE DATABASE keycloak;
CREATE DATABASE tunnel;Released under the MIT License.