npm install compromise
 compromise tries its best.
compromise tries its best.
Welcome to v12! - Release Notes here 👍
compromise makes it simple to interpret and match text:
let doc = nlp(entireNovel)
doc.if('the #Adjective of times').text()
// "it was the blurst of times??"if (doc.has('simon says #Verb')) {
return true
}conjugate and negate verbs in any tense:
let doc = nlp('she sells seashells by the seashore.')
doc.verbs().toPastTense()
doc.text()
// 'she sold seashells by the seashore.'transform nouns to plural and possessive forms:
let doc = nlp('the purple dinosaur')
doc.nouns().toPlural()
doc.text()
// 'the purple dinosaurs'interpret plaintext numbers
nlp.extend(require('compromise-numbers'))
let doc = nlp('ninety five thousand and fifty two')
doc.numbers().add(2)
doc.text()
// 'ninety five thousand and fifty four'grab subjects in a text:
let doc = nlp(buddyHolly)
doc
.people()
.if('mary')
.json()
// [{text:'Mary Tyler Moore'}]
let doc = nlp(freshPrince)
doc
.places()
.first()
.text()
// 'West Phillidelphia'
doc = nlp('the opera about richard nixon visiting china')
doc.topics().json()
// [
// { text: 'richard nixon' },
// { text: 'china' }
// ]work with contracted and implicit words:
let doc = nlp("we're not gonna take it, no we ain't gonna take it.")
// match an implicit term
doc.has('going') // true
// transform
doc.contractions().expand()
dox.text()
// 'we are not going to take it, no we are not going to take it.'Use it on the client-side:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/compromise"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/compromise-numbers"></script>
<script>
nlp.extend(compromiseNumbers)
var doc = nlp('two bottles of beer')
doc.numbers().minus(1)
document.body.innerHTML = doc.text()
// 'one bottle of beer'
</script>or as an es-module:
import nlp from 'compromise'
var doc = nlp('London is calling')
doc.verbs().toNegative()
// 'London is not calling'or if you don't care about POS-tagging, you can use the tokenize-only build: (90kb!)
<script src="https://unpkg.com/compromise/builds/compromise-tokenize.js"></script>
<script>
var doc = nlp('No, my son is also named Bort.')
//you can see the text has no tags
console.log(doc.has('#Noun')) //false
//but the whole api still works
console.log(doc.has('my .* is .? named /^b[oa]rt/')) //true
</script>compromise is 170kb (minified):
it's pretty fast. It can run on keypress:
it works mainly by conjugating many forms of a basic word list.
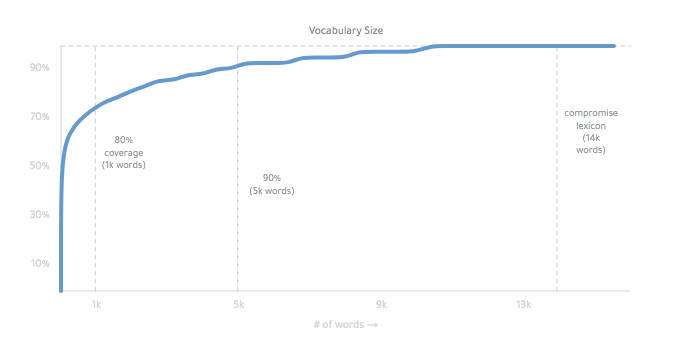
The final lexicon is ~14,000 words:
you can read more about how it works, here.
set a custom interpretation of your own words:
let myWords = {
kermit: 'FirstName',
fozzie: 'FirstName',
}
let doc = nlp(muppetText, myWords)or make more changes with a compromise-plugin.
const nlp = require('compromise')
nlp.extend((Doc, world) => {
// add new tags
world.addTags({
Character: {
isA: 'Person',
notA: 'Adjective',
},
})
// add or change words in the lexicon
world.addWords({
kermit: 'Character',
gonzo: 'Character',
})
// add methods to run after the tagger
world.postProcess(doc => {
doc.match('light the lights').tag('#Verb . #Plural')
})
// add a whole new method
Doc.prototype.kermitVoice = function() {
this.sentences().prepend('well,')
this.match('i [(am|was)]').prepend('um,')
return this
}
})(these methods are on the nlp object)
- .tokenize() - parse text without running POS-tagging
- .extend() - mix in a compromise-plugin
- .fromJSON() - load a compromise object from
.json()result - .verbose() - log our decision-making for debugging
- .version() - current semver version of the library
- .world() - grab all current linguistic data
- .all() - return the whole original document ('zoom out')
- .found [getter] - is this document empty?
- .parent() - return the previous result
- .parents() - return all of the previous results
- .tagger() - (re-)run the part-of-speech tagger on this document
- .wordCount() - count the # of terms in the document
- .length [getter] - count the # of characters in the document (string length)
- .clone() - deep-copy the document, so that no references remain
- .cache({}) - freeze the current state of the document, for speed-purposes
- .uncache() - un-freezes the current state of the document, so it may be transformed
- .first(n) - use only the first result(s)
- .last(n) - use only the last result(s)
- .slice(n,n) - grab a subset of the results
- .eq(n) - use only the nth result
- .terms() - split-up results by each individual term
- .firstTerms() - get the first word in each match
- .lastTerms() - get the end word in each match
- .sentences() - get the whole sentence for each match
- .termList() - return a flat list of all Term objects in match
- .groups('') - grab any named capture-groups from a match
(all match methods use the match-syntax.)
- .match('') - return a new Doc, with this one as a parent
- .not('') - return all results except for this
- .matchOne('') - return only the first match
- .if('') - return each current phrase, only if it contains this match ('only')
- .ifNo('') - Filter-out any current phrases that have this match ('notIf')
- .has('') - Return a boolean if this match exists
- .lookBehind('') - search through earlier terms, in the sentence
- .lookAhead('') - search through following terms, in the sentence
- .before('') - return all terms before a match, in each phrase
- .after('') - return all terms after a match, in each phrase
- .lookup([]) - quick find for an array of string matches
- .toLowerCase() - turn every letter of every term to lower-cse
- .toUpperCase() - turn every letter of every term to upper case
- .toTitleCase() - upper-case the first letter of each term
- .toCamelCase() - remove whitespace and title-case each term
- .pre('') - add this punctuation or whitespace before each match
- .post('') - add this punctuation or whitespace after each match
- .trim() - remove start and end whitespace
- .hyphenate() - connect words with hyphen, and remove whitespace
- .dehyphenate() - remove hyphens between words, and set whitespace
- .toQuotations() - add quotation marks around these matches
- .toParentheses() - add brackets around these matches
- .tag('') - Give all terms the given tag
- .tagSafe('') - Only apply tag to terms if it is consistent with current tags
- .unTag('') - Remove this term from the given terms
- .canBe('') - return only the terms that can be this tag
- .map(fn) - run each phrase through a function, and create a new document
- .forEach(fn) - run a function on each phrase, as an individual document
- .filter(fn) - return only the phrases that return true
- .find(fn) - return a document with only the first phrase that matches
- .some(fn) - return true or false if there is one matching phrase
- .random(fn) - sample a subset of the results
- .replace(match, replace) - search and replace match with new content
- .replaceWith(replace) - substitute-in new text
- .delete() - fully remove these terms from the document
- .append(str) - add these new terms to the end (insertAfter)
- .prepend(str) - add these new terms to the front (insertBefore)
- .concat() - add these new things to the end
- .sort('method') - re-arrange the order of the matches (in place)
- .reverse() - reverse the order of the matches, but not the words
- .normalize({}) - clean-up the text in various ways
- .unique() - remove any duplicate matches
- .split('') - return a Document with three parts for every match ('splitOn')
- .splitBefore('') - partition a phrase before each matching segment
- .splitAfter('') - partition a phrase after each matching segment
- .segment({}) - split a document into labeled sections
- .join('') - make all phrases into one phrase
- .text('method') - return the document as text
- .json({}) - pull out desired metadata from the document
- .out('array|offset|terms') - some named output formats (deprecated)
- .debug() - pretty-print the current document and its tags
- .clauses() - split-up sentences into multi-term phrases
- .hyphenated() - all terms connected with a hyphen or dash like
'wash-out' - .phoneNumbers() - things like
'(939) 555-0113' - .hashTags() - things like
'#nlp' - .emails() - things like
'hi@compromise.cool' - .emoticons() - things like
:) - .emojis() - things like
💋 - .atMentions() - things like
'@nlp_compromise' - .urls() - things like
'compromise.cool' - .adverbs() - things like
'quickly' - .pronouns() - things like
'he' - .conjunctions() - things like
'but' - .prepositions() - things like
'of' - .abbreviations() - things like
'Mrs.' - .people() - names like 'John F. Kennedy'
- .places() - like 'Paris, France'
- .organizations() - like 'Google, Inc'
- .topics() -
people()+places()+ `organizations
- .contractions() - things like "didn't"
- .contractions().expand() - things like "didn't"
- .contract() -
"she would"->"she'd" - .parentheses() - return anything inside (parentheses)
- .possessives() - things like
"Spencer's" - .quotations() - return any terms inside quotation marks
- .acronyms() - things like
'FBI' - .lists() - things like
'eats, shoots, and leaves'- .lists().items() - return the partitioned things in the list
- .lists().add() - put a new item in the list
- .nouns() - return any subsequent terms tagged as a Noun
- .nouns().json() - overloaded output with noun metadata
- .nouns().adjectives() - get any adjectives describing this noun
- .nouns().toPlural() -
'football captain' → 'football captains' - .nouns().toSingular() -
'turnovers' → 'turnover' - .nouns().isPlural() - return only plural nouns
- .nouns().isSingular() - return only singular nouns
- .nouns().hasPlural() - return only nouns that can be inflected as plural
- .nouns().toPossessive() - add a
'sto the end, in a safe manner.
- .verbs() - return any subsequent terms tagged as a Verb
- .verbs().json() - overloaded output with verb metadata
- .verbs().conjugate() - return all forms of these verbs
- .verbs().toPastTense() -
'will go' → 'went' - .verbs().toPresentTense() -
'walked' → 'walks' - .verbs().toFutureTense() -
'walked' → 'will walk' - .verbs().toInfinitive() -
'walks' → 'walk' - .verbs().toGerund() -
'walks' → 'walking' - .verbs().toNegative() -
'went' → 'did not go' - .verbs().toPositive() -
"didn't study" → 'studied' - .verbs().isNegative() - return verbs with 'not'
- .verbs().isPositive() - only verbs without 'not'
- .verbs().isPlural() - return plural verbs like 'we walk'
- .verbs().isSingular() - return singular verbs like 'spencer walks'
- .verbs().adverbs() - return the adverbs describing this verb.
These are some helpful extensions:
npm install compromise-adjectives
- .adjectives() - like
quick- .adjectives().json() - overloaded output with adjective metadata
- .adjectives().conjugate() - return all conjugated forms of this adjective
- .adjectives().toSuperlative() - convert
quicktoquickest - .adjectives().toComparative() - convert
quicktoquicker - .adjectives().toAdverb() - convert
quicktoquickly - .adjectives().toVerb() - convert
quicktoquicken - .adjectives().toNoun() - convert
quicktoquickness
npm install compromise-dates
- .dates() - find dates like
June 8thor03/03/18- .dates().json() - overloaded output with date metadata
- .dates().format('') - convert the dates to specific formats
- .dates().toShortForm() - convert 'Wednesday' to 'Wed', etc
- .dates().toLongForm() - convert 'Feb' to 'February', etc
npm install compromise-numbers
- .numbers() - grab all written and numeric values
- .numbers().json() - overloaded output with number metadata
- .numbers().units() - grab 'kilos' from
25 kilos' - .numbers().fractions() - things like
1/3rd - .numbers().toText() - convert number to
fiveorfifth - .numbers().toNumber() - convert number to
5or5th - .numbers().toOrdinal() - convert number to
fifthor5th - .numbers().toCardinal() - convert number to
fiveor5 - .numbers().set(n) - set number to n
- .numbers().add(n) - increase number by n
- .numbers().subtract(n) - decrease number by n
- .numbers().increment() - increase number by 1
- .numbers().decrement() - decrease number by 1
- .numbers().isEqual(n) - return numbers with this value
- .numbers().greaterThan(min) - return numbers bigger than n
- .numbers().lessThan(max) - return numbers smaller than n
- .numbers().between(min, max) - return numbers between min and max
- .numbers().isOrdinal() - return only ordinal numbers
- .numbers().isCardinal() - return only cardinal numbers
- .numbers().toLocaleString() - add commas, or nicer formatting for numbers
- .money() - things like
'$2.50'
npm install compromise-export
- .export() - store a parsed document for later use
- nlp.load() - re-generate a Doc object from .export() results
npm install compromise-html
- .html({}) - generate sanitized html from the document
npm install compromise-hash
- .hash() - generate an md5 hash from the document+tags
- .isEqual(doc) - compare the hash of two documents for semantic-equality
npm install compromise-keypress
- nlp.keypress('') - generate an md5 hash from the document+tags
- nlp.clear('') - clean-up any cached sentences from memory
npm install compromise-ngrams
- .ngrams({}) - list all repeating sub-phrases, by word-count
- .unigrams() - n-grams with one word
- .bigrams() - n-grams with two words
- .trigrams() - n-grams with three words
- .startgrams() - n-grams including the first term of a phrase
- .endgrams() - n-grams including the last term of a phrase
- .edgegrams() - n-grams including the first or last term of a phrase
npm install compromise-paragraphs
this plugin creates a wrapper around the default sentence objects.
- .paragraphs() - return groups of sentences
- .paragraphs().json() - output metadata for each paragraph
- .paragraphs().sentences() - go back to a regular Doc object
- .paragraphs().terms() - return all individual terms
- .paragraphs().eq() - get the nth paragraph
- .paragraphs().first() - get the first n paragraphs
- .paragraphs().last() - get the last n paragraphs
- .paragraphs().match() -
- .paragraphs().not() -
- .paragraphs().if() -
- .paragraphs().ifNo() -
- .paragraphs().has() -
- .paragraphs().forEach() -
- .paragraphs().map() -
- .paragraphs().filter() -
npm install compromise-sentences
- .sentences() - return a sentence class with additional methods
- .sentences().json() - overloaded output with sentence metadata
- .sentences().subjects() - return the main noun of each sentence
- .sentences().toPastTense() -
he walks->he walked - .sentences().toPresentTense() -
he walked->he walks - .sentences().toFutureTense() --
he walks->he will walk - .sentences().toNegative() - -
he walks->he didn't walk - .sentences().toPositive() -
he doesn't walk->he walks - .sentences().isPassive() - return only sentences with a passive-voice
- .sentences().isQuestion() - return questions with a
? - .sentences().isExclamation() - return sentences with a
! - .sentences().isStatement() - return sentences without
?or! - .sentences().prepend() - smarter prepend that repairs whitespace + titlecasing
- .sentences().append() - smarter append that repairs sentence punctuation
- .sentences().toExclamation() - end sentence with a
! - .sentences().toQuestion() - end sentence with a
? - .sentences().toStatement() - end sentence with a
.
npm install compromise-syllables
- .syllables() - split each term by its typical pronounciation
Typescript support is still a work in progress. So far support for plugins has been mostly complete, and can be used to type-safely extend NLP.
import nlp from 'compromise'
import ngrams from 'compromise-ngrams'
import numbers from 'compromise-numbers'
// .extend() can be chained
const nlpEx = nlp.extend(ngrams).extend(numbers)
nlpEx('This is type safe!').ngrams({ min: 1 })
nlpEx('This is type safe!').numbers()The .extend() function returns an nlp type with updated Document and World types (Phrase, Term and Pool are not currently supported). While the global nlp also recieves the plugin from a runtime perspective; it's type will not be updated - this is a limitation of Typescript.
Typesafe plugins can be created by using the nlp.Plugin type:
interface myExtendedDoc {
sayHello(): string
}
interface myExtendedWorld {
hello: string
}
const myPlugin: nlp.Plugin<myExtendedDoc, myExtendedWorld> = (Doc, world) => {
world.hello = 'Hello world!'
Doc.prototype.sayHello = () => world.hello
}
const _nlp = nlp.extend(myPlugin)
const doc = _nlp('This is safe!')
doc.sayHello()
doc.world.hello = 'Hello again!'compromise_1.default is not a function- This is a problem with yourtsconfig.jsonit can be solved by adding"esModuleInterop": true. Make sure to runtsc --initwhen starting a new Typescript project.
- Tutorial #1 - Input → output
- Tutorial #2 - Match & transform
- Tutorial #3 - Making a chat-bot
- Geocoding Social Conversations with NLP and JavaScript - by Microsoft
- Microservice Recipe - by Eventn
- **Adventure Game Sentence Parsing with Compromise
- Building Text-Based Games - by Matt Eland
- Fun with javascript in BigQuery - by Felipe Hoffa
- Natural Language Processing... in the Browser??? - by Charles Landau
- Language as an Interface - by Spencer Kelly
- Coding Chat Bots - by KahWee Teng
- Chat dialogue framework - by Rob Ellis
- Automated Bechdel Test - by The Guardian
- Story generation framework - by Jose Phrocca
- Tumbler blog of lists - horse-ebooks-like lists - by Michael Paulukonis
- Video Editing from Transcription - by New Theory
- Browser extension Fact-checking - by Alexander Kidd
- Siri shortcut - by Michael Byrns
- Amazon skill - by Tajddin Maghni
- Tasking Slack-bot - by Kevin Suh
-
slash-support: We currently split slashes up as different words, like we do for hyphens. so things like this don't work:
nlp('the koala eats/shoots/leaves').has('koala leaves') //false -
inter-sentence match: By default, sentences are the top-level abstraction. Inter-sentence, or multi-sentence matches aren't supported:
nlp("that's it. Back to Winnipeg!").has('it back')//false -
nested match syntax: the
dangerbeauty of regex is that you can recurse indefinitely. Our match syntax is much weaker. Things like this are not (yet) possible:doc.match('(modern (major|minor))? general')complex matches must be achieved with successive .match() statements. -
dependency parsing: Proper sentence transformation requires understanding the syntax tree of a sentence, which we don't currently do. We should! Help wanted with this.
☂️ Isn't javascript too...
💃 Can it run on my arduino-watch?
-
Only if it's water-proof!
Read quick start for running compromise in workers, mobile apps, and all sorts of funny environments.
🌎 Compromise in other Languages?
✨ Partial builds?
-
we do offer a [compromise-tokenize](./builds/compromise-tokenize.js) build, which has the POS-tagger pulled-out.
but otherwise, compromise isn't easily tree-shaken.
the tagging methods are competitive, and greedy, so it's not recommended to pull things out.
Note that without a full POS-tagging, the contraction-parser won't work perfectly. ((spencer's cool) vs. (spencer's house))
It's recommended to run the library fully.
- naturalNode - fancier statistical nlp in javascript
- superScript - clever conversation engine in js
- nodeBox linguistics - conjugation, inflection in javascript
- reText - very impressive text utilities in javascript
- jsPos - javascript build of the time-tested Brill-tagger
- spaCy - speedy, multilingual tagger in C/python
- Prose - quick tagger in Go by Joseph Kato
MIT