Baremetal environment for "System programming lab" class in Dept. of Information Science, The University of Tokyo. (originated from sykwer/utokyo_syspro_baremetal and pflab-ut/utokyo_syspro_baremetal_2021)
The bootloader is implemented referencing UEFI Specification Version 2.8 (PDF) and UEFI Platform Initialization Specification (PDF). The following tools need to be installed by users to build the bootloader, the kernel and the apps.
- x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc : Cross-compiler for building UEFI bootloader
- qemu-system-x86_64 : Emulator
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt upgrade
$ sudo apt install -y mingw-w64 qemu-system-x86 unzip git make gcc ovmf
The bootloader can be built on any environment if the cross-compiler x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc is installed. The kernel and the apps have to be built on x86_64 Linux (in order to use -T option of ld command). I do not assume some specific
version of gcc, but the gcc version on writer's test environment is shown below.
$ gcc --version
gcc (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0
First, clone this repo with the following commands.
$ git clone https://github.com/pflab-ut/utokyo_syspro_baremetal_2023
$ cd utokyo_syspro_baremetal_2023
This repository provides the official build environment using Docker. Run the following commands after installing Docker on your system.
$ make docker-build # Only the first time
$ make docker-make
$ make qemu
After installing x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc and qemu-system-x86_64, do the following commands.
$ make local
$ make qemu
The kernel will paint all the part of the window in ayame color.
Booting from USB is supported on UEFI-boot suppored systems. The writer tested USB boot on the following machines.
- HP ZBook 15v G5
- MacBookPro 2014
- MacBookPro 2019
To boot from USB, follow the instructions below.
- Format Partition1 of USB drive in FAT32
- Run 'make' command in the top directory
- Copy all the files under 'fs/' directory to USB
- Boot from USB on your real machine
// Find usb device file
$ sudo fdisk -l
// Assume this prints `/dev/sdc` here
// Start fdisk session
$ sudo fdisk /dev/sdc
Command (m for help): d
Selected partition 1
Partition 1 has been deleted.
Command (m for help): o
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x190598a4.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-61439999, default 2048):
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-61439999, default 61439999):
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 29.3 GiB.
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list all codes): b
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'W95 FAT32'.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
// FAT32 format
$ sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 /dev/sdc1
// Mount USB
$ sudo mount /dev/sdc1 /path/to/mount-point
// Prepare files under fs directory
$ cd /path/to/utokyo_syspro_baremetal_2022
$ make
// Copy file system
$ sudo cp -R /path/to/utokyo_syspro_baremetal_2022/fs/* /path/to/mount-point/
// Unmount
$ sudo umount /path/to/mount-point
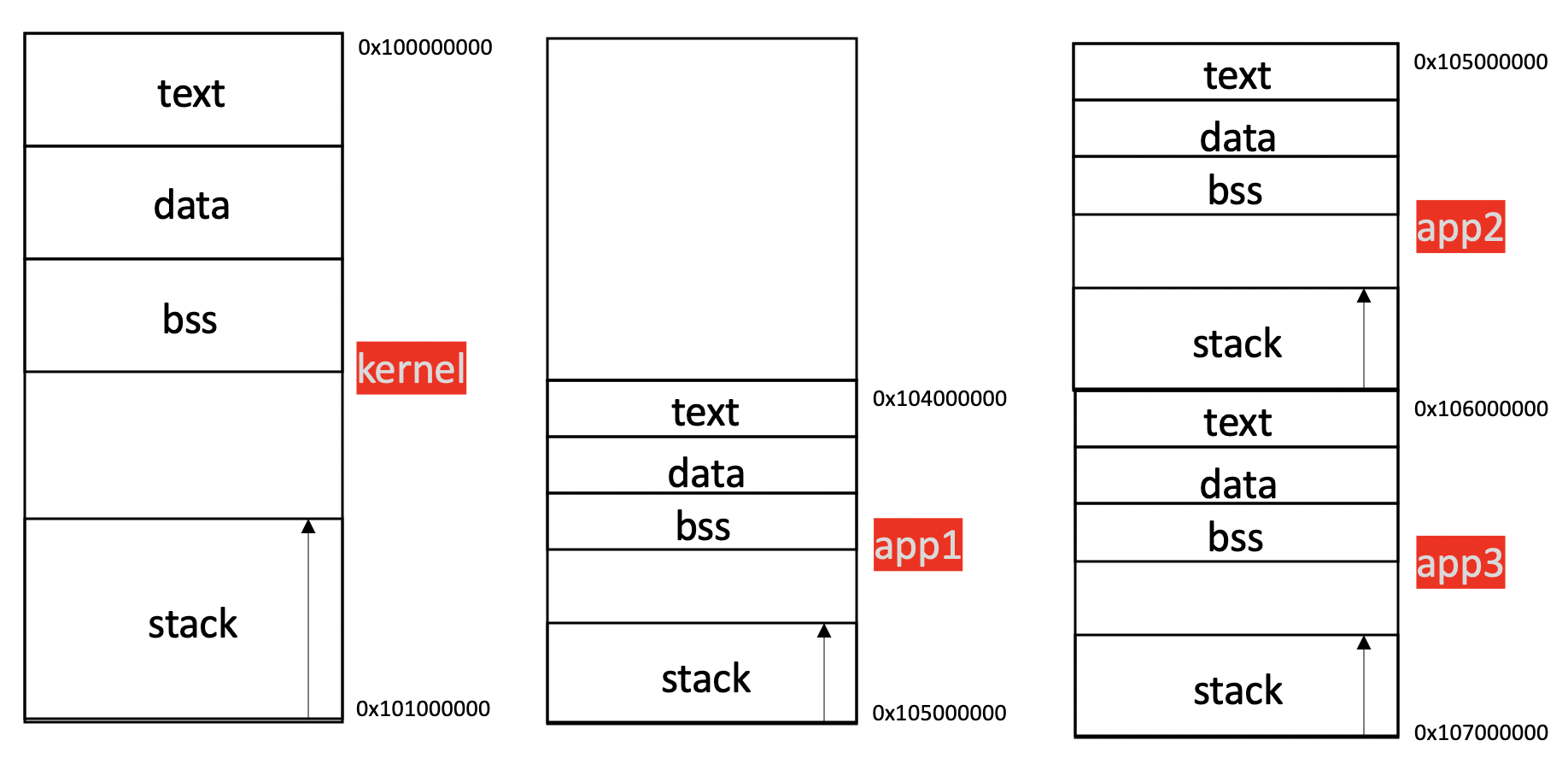
The built images of the kernel and the apps are loaded by the bootloader to the physical addresses dipicted in the figure below.
- kernel : origin=0x100000000, length=16MiB
- app1 : origin=0x104000000, length=16MiB
- app2 : origin=0x105000000, length=16MiB
- app3 : origin=0x106000000, length=16MiB