This repository contains code for "N-Best-ASR-Transformer: Enhancing SLU Performance using Multiple ASR Hypotheses." The paper has been accepted in ACL-IJCNLP 2021.
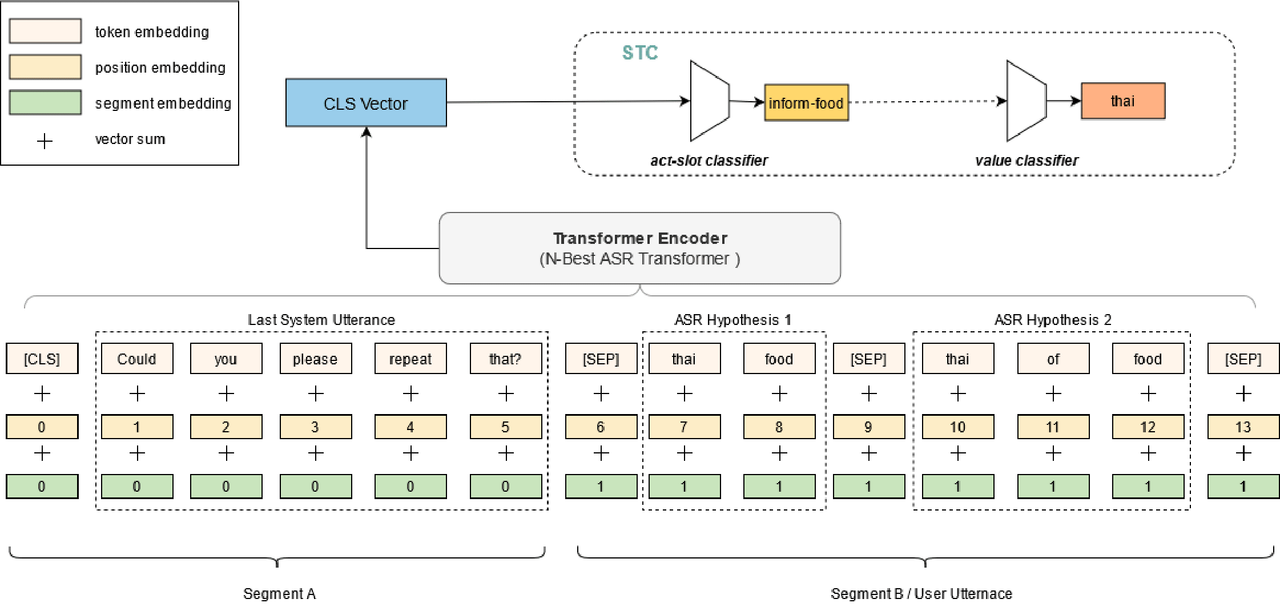
Spoken Language Understanding (SLU) systems parse speech into semantic structures like dialog acts and slots. This involves the use of an Automatic Speech Recognizer (ASR) to transcribe speech into multiple text alternatives (hypotheses). Transcription errors, common in ASRs, impact downstream SLU performance negatively. Approaches to mitigate such errors involve using richer information from the ASR, either in form of N-best hypotheses or word-lattices. We hypothesize that transformer models learn better with a simpler utterance representation using the concatenation of the N-best ASR alternatives, where each alternative is separated by a special delimiter [SEP]. In our work, we test our hypothesis by using concatenated N-best ASR alternatives as the input to transformer encoder models, namely BERT and XLM-RoBERTa, and achieve performance equivalent to the prior state-of-the-art model on DSTC2 dataset. We also show that our approach significantly outperforms the prior state-of-the-art when subjected to the low data regime. Additionally, this methodology is accessible to users of third-party ASR APIs which do not provide word-lattice information.
We conduct our experiments on a benchmark SLU dataset which ASR alternatives, DSTC2. Origin data can be obtained here.
- Data preprocessing:
Note that you should replace the <input_dir> with the original DSTC2 data, and replace the <output_dir> with your own output directory.
python helpers/process_dstc2_with_SEP.py \ --data_dir <input_dir> \ --out_dir <output_dir>
The data is preprocessed and saved in dstc2_data/processed_data/*, where each line is a data sample in the form of:
[SYS] Hello you are here to book a table [USR] yes want a to book a table [SEP] yes book table
We build our experiments keeping this repository as our base code.
The data preprocessing step mentioned above converts the DSTC2 data into the desired input format.
We build two classifiers, the first one for act-slot pairs and the second one for value.
Run command:
./run/train_eval_N_Best_ASR_Transformer_STC.shParameters:
--pre_trained_model : pre-trained model name to use among `"bert"`,`"roberta"`,`"xlm-roberta"`
--add_l2_loss: Flag used to set usage of MSE loss between asr and transcript hidden state.
--tod_pre_trained_model: Path to TOD pre-trained checkpoint Note: This will override pre_trained_model value if passed.
--add_segment_ids : Flag to decide to add segment ids.
--without_system_act: Flag to remove previous system act [In our case this is previous system utterance]
Parameter to perform Sample Complexity related Experiments:
--coverage: Based on coverage percentage stratified data samples will be picked as a training set. Coverage = (0,1], where, coverage = 1 means you are including the whole data set for training, and, coverage < 1 refers to the percentage of samples you want to consider for training your model. For our work we test our model for sample complexity coverage of {0.05, 0.10, 0.20, 0.50}.
Results of Multi-Seq ASR BERT:
| Model | F1 score (%) | Acc. (%) |
|---|---|---|
| N-Best-ASR ASR BERT | 87.4 | 81.9 |
| N-Best-ASR ASR XLM-R | 87.8 | 81.8 |
Results are average after 5 runs on the dataset, each having a unique random seed.
If you use our work, please cite
@inproceedings{ganesan-etal-2021-n,
title = "N-Best {ASR} Transformer: Enhancing {SLU} Performance using Multiple {ASR} Hypotheses",
author = "Ganesan, Karthik and
Bamdev, Pakhi and
B, Jaivarsan and
Venugopal, Amresh and
Tushar, Abhinav",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 2: Short Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-short.14",
doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.acl-short.14",
pages = "93--98",
}