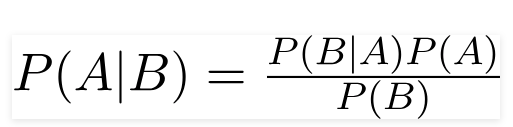The threat of abuse and harassment online prevent many people from expressing themselves and make them give up on seeking different opinions. In the meantime, platforms struggle to effectively facilitate conversations, leading many communities to limit or completely shut down user comments. Therefore, Kaggle started this competition with the Conversation AI team, a research initiative founded by Jigsaw and Google. The competition could be found here: https://www.kaggle.com/c/jigsaw-toxic-comment-classification-challenge
- Dataset Overview
- Data Preprocessing and EDA
- Models used
- Results
The dataset we are using consists of comments from Wikipedia’s talk page edits. These comments have been labeled by human raters for toxic behavior. The types of toxicity are:
- toxic
- severe_toxic
- obscene
- threat
- insult
- identity_hate
The training dataset consists of 159k training samples and the test set consists of 153k samples.
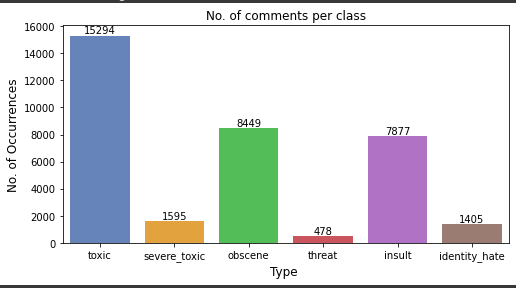
On analyzing the dataset I found that most of the comments are completely clean ,i.e., there is no toxicity present in them. Out of all the comments in the training dataset, on counting the number of comments that fall under each class turn out to be the following:
Plotting the same as a bar-chart:
For preprocessing the data we did the following:
- Firstly, we remove the English Stopwords from every comment using the nltk library.
- Remove all numbers with letters attached to them.
- .lower() - convert all strings to lowercase.
- Remove all '\n' in the string and replace it with a space.
- Remove all non-ascii characters.
Useful to show the words which occur most frequently for each category. Warning: Profanity ahead.
TF-IDF stands for “Term Frequency — Inverse Document Frequency”. This is a technique to quantify words in a set of documents. We generally compute a score for each word to signify its importance in the document and corpus. It is one of the most important techniques used for information retrieval to represent how important a specific word or phrase is to a given document. TF-IDF = Term Frequency (TF) * Inverse Document Frequency (IDF) Term Frequency - This measures the frequency of a word in a document. This highly depends on the length of the document and the generality of the word, IDF - It is the inverse of the document frequency which measures the informativeness of term t. When we calculate IDF, it will be very low for the most occurring words such as stop words (because they are present in almost all of the documents, and N/df will give a very low value to that word). This finally gives what we want, a relative weightage.
Logistic Regression : Logistic Regression is a Supervised statistical technique to find the probability of dependent variable(Classes present in the variable). Logistic regression uses functions called the logit functions,that helps derive a relationship between the dependent variable and independent variables by predicting the probabilities or chances of occurrence. The logistic functions (also known as the sigmoid functions) convert the probabilities into binary values which could be further used for predictions.
KNN : The k-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm is a simple, supervised machine learning algorithm that can be used to solve both classification and regression problems. It’s easy to implement and understand, but has a major drawback of becoming significantly slows as the size of that data in use grows. KNN works by finding the distances between a query and all the examples in the data, selecting the specified number examples (K) closest to the query, then votes for the most frequent label (in the case of classification) or averages the labels (in the case of regression).
Multinomial Naive Bayes : A Naive Bayes classifier is a probabilistic machine learning model that’s used for classification task. The crux of the classifier is based on the Bayes theorem. Using Bayes theorem, we can find the probability of A happening, given that B has occurred. Here, B is the evidence and A is the hypothesis. The assumption made here is that the predictors/features are independent. That is presence of one particular feature does not affect the other. Hence it is called naive.
Types of Naive Bayes Classifier:
Multinomial Naive Bayes : This is mostly used for document classification problem, i.e whether a document belongs to the category of sports, politics, technology etc. The features/predictors used by the classifier are the frequency of the words present in the document.
Bernoulli Naive Bayes : This is similar to the multinomial naive bayes but the predictors are boolean variables. The parameters that we use to predict the class variable take up only values yes or no, for example if a word occurs in the text or not. Naive Bayes algorithms are mostly used in sentiment analysis, spam filtering, recommendation systems etc. They are fast and easy to implement but their biggest disadvantage is that the requirement of predictors to be independent. In most of the real life cases, the predictors are dependent, this hinders the performance of the classifier.
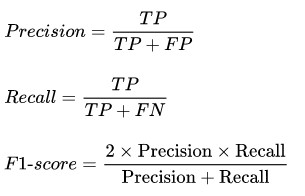
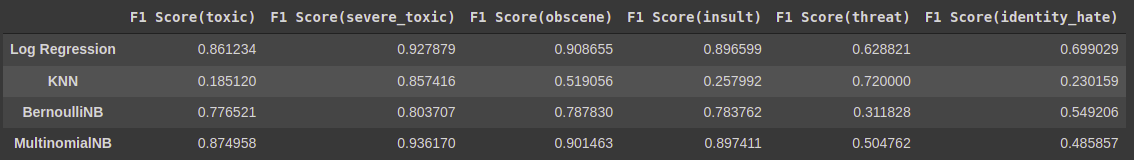
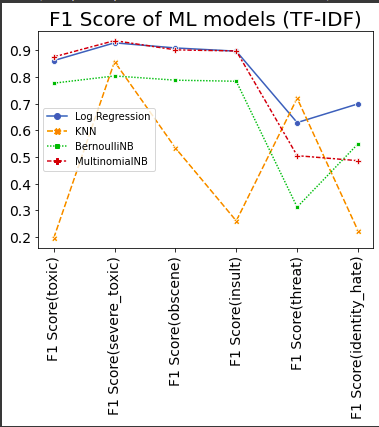
The F-score or F-measure is a measure of a test's accuracy. It is calculated from the precision and recall of the test, where the precision is the number of true positive results divided by the number of all positive results, including those not identified correctly, and the recall is the number of true positive results divided by the number of all samples that should have been identified as positive. Precision is also known as positive predictive value, and recall is also known as sensitivity in diagnostic binary classification.