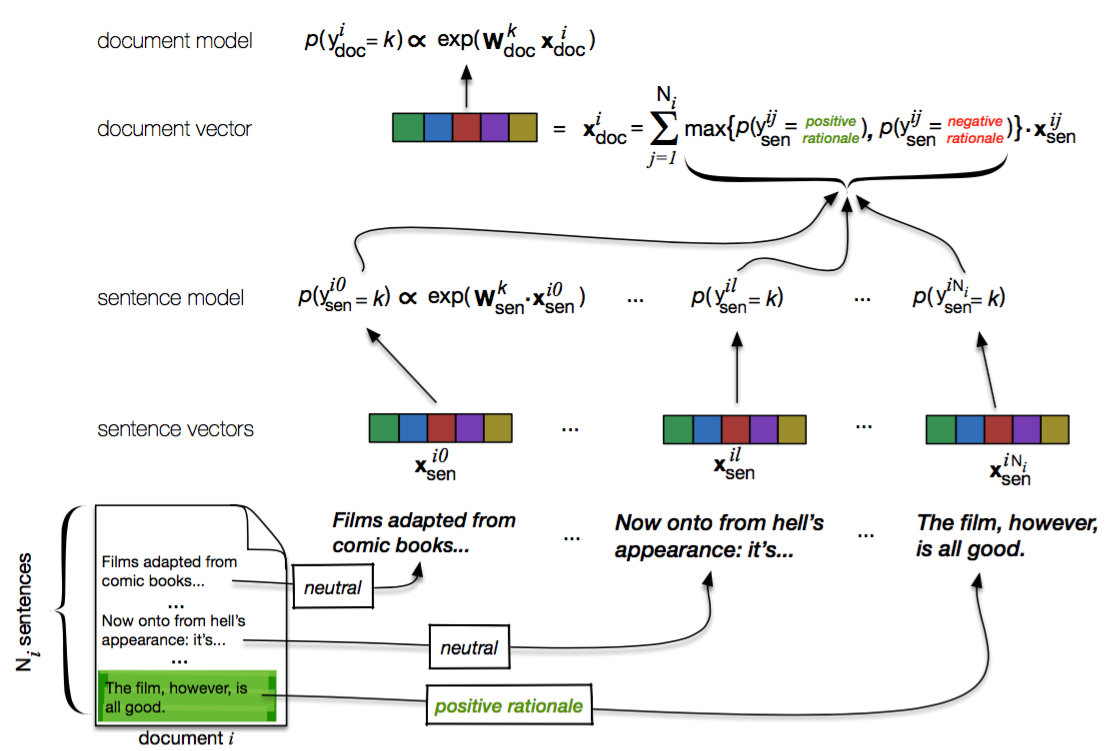
A Keras implementation of our CNNs with "rationales". Reference article: https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.04469. Citation:
Ye Zhang, Iain J. Marshall and Byron C. Wallace Rationale-Augmented Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification, EMNLP, 2016.
We note that the results reported in our paper are from a Theano implementation of the model, which is available upon request (contact Ye Zhang [email protected]).
This should run fine in Python 2.7 or 3.x. Requires the usual stack of numpy/scipy/pandas, plus an up-to-date version of Keras; we developed and test on 1.0.5.
Your data should be formatted as a CSV with no headers. Each row is expected to have the following format:
doc_id, doc_lbl, sentence_number, sentence, sentence_lbl
Where doc_id is an arbitrary unique document identifier; doc_lbl is a (binary) label on the document; sentence_number is the index of the sentence within a document (each document starting at sentence 0); and sentence_lbl encodes whether the sentence is a rationale (1) or not (-1). The movies.txt file under the `data' directory provides a concrete example.
You will need to create a simple config.ini file, which points to your data. In particular, it should look like this:
[paths]
data_path=/Path/to/data.txt
word_vectors_path=/Path/to/embeddings.bin
The embeddings should contain the pre-trained word vectors to use for initialization (these will be tuned).
As an example, we distribute the movies dataset, which is from Zaidan's original work on rationales. To run this, create a movies_config.ini file, with the above two entries. We suggest using the standard Google news trained word2vec embeddings.
THEANO_FLAGS=mode=FAST_RUN,device=gpu,floatX=float32 python train_RA_CNN.py --inifile=/path/to/movies_config.ini --sentence-epochs=15 --batch-size=50 --document-epochs=200 --dropout-document=0.5 --dropout-sentence=0.7 --name=movies --mf=25000 --max-doc-length=40 --max-sent-length=20 --shuffle --val-split=.1 --num-filters=20
Obviously, the inifile path needs to be changed accordingly. Note that in practice, one needs to tune the sentence dropout on the train set, because the model is rather sensitive to this hyper-parameter.
For explanations regarding all possible arguments, use:
python train_RA_CNN.py -h
In addition to the command line interface, you can of course instantiate the model directly (as in train_RA_CNN.py). To do this, you'll want to create a Preprocessor instance
from rationale_CNN import Preprocessor
p = Preprocessor(MAX_FEATURES, MAX_SENT_LEN)
And then you'll need to instantiate Document instances for each of the items to be classified -- see read_data in train_RA_CNN.py for an example of this, or simply inspect the simple Document class. Document instances accept Preprocessor objects to generate sequences that constitute inputs to RA-CNN.
You'll next want to instantiate the model, like so:
r_CNN = rationale_CNN.RationaleCNN(p)
Note that many hyper-parameters can be set here (e.g., filter sizes, dropout rates, etc.). Next we train the sentence model, ignoring the document level model for now:
r_CNN.build_sentence_model()
r_CNN.train_sentence_model(documents, nb_epoch=nb_epoch_sentences)
And once that's through, construct the full model, which will be initialized using sentence-level parameters as estimated in the previous step.
r_CNN.build_RA_CNN_model()
Assemble X and y tensors; in particular, X should have dimensions (NUM_INSTANCES, MAX_DOC_LEN, MAX_SENT_LEN). This can be done by building up a list of sentence sequence vectors; again, see train_RA_CNN.py for a concrete example. Finally, you can train the document level model as usual:
r_CNN.doc_model.fit(X_doc, y_doc)
To make predictions for a new instance, first again create a Document instance, new_doc. Then you can call:
pred, rationales = r_CNN.predict_and_rank_sentences_for_doc(new_doc, num_rationales=3)
Here, pred will be a scalar and rationales a list of extracted snippets supporting this.
This work is part of the RobotReviewer project, and is generously supported by the National Institutes of Health (under the National Library of Medicine), grant R01-LM012086-01A1.