An interactive phishing simulation that utilizes LLMs for generating messages, adapted to specific users and environments, and for coaching users. The simulation requires the setup of an LLM-API to a local LLM via Ollama or the "llm" library. By default, the qwen 2.5 7B LLM is configured via Ollama.
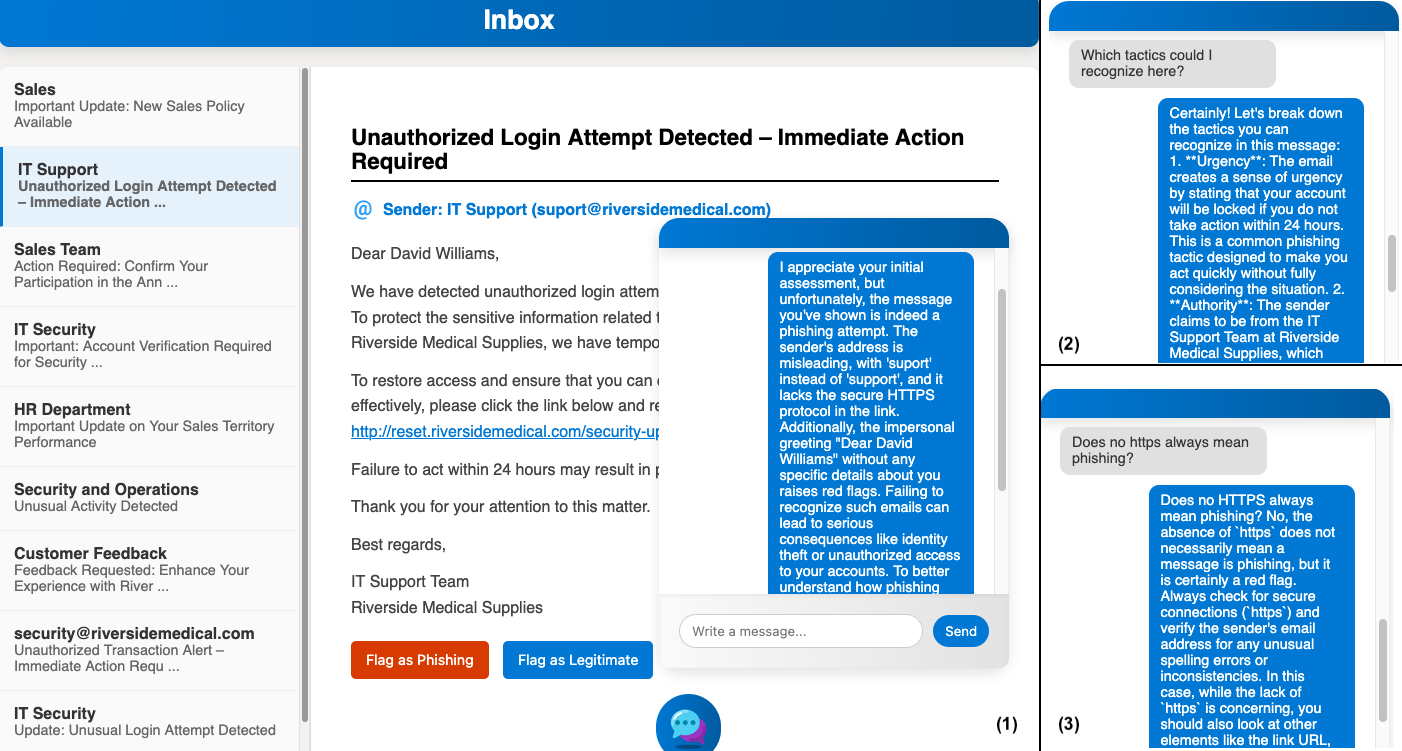
Example: After flagging a phishing message as a legitimate message, the behavior of the LLM can be observed, giving feedback (1) and answering questions (2, 3). Qwen 2.5 7B is used in the example. A video is available on YouTube.
Credits: initial version by Kapischan Sriganthan, extension for LLMs by Felix Härer.
The prototype is implemented in Python 3.13 using the modules flask, flask-cors, ollama, llm, and openai. Parts of the HTML/JS/CSS code are derived from the chatbot-deployment project.
- Python 3.13 or later is required
- Setup of a virtual environment in the project directory:
- macOS/Linux:
python3 -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate - Windows:
python -m venv .venv .venv\Scripts\Activate
- macOS/Linux:
- Installation of required libraries:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- LLM
- Start Ollama or configure another LLM-API in llm_api.py
- By default, the qwen 2.5 7B LLM is set
- Model download:
ollama pull qwen2.5:7b
- Start the application:
python app.py
- By default, the web-based UI is available at http://127.0.0.1:8081/.
Messages are customized to users and environments that are specified in prompting/message_generation_context.json using sample messages specified in prompting/message_samples.json. On most machines, this process might take 30 - 60 seconds, depending on the system's hardware and the selected LLM.
The inbox of a message environment appears with a welcome page. It contains instructions to browse through messages and flag them as spam or legitimate messages. Throughout the process, a chat-based coach is present in the lower right corner. The coach will answer questions and provide guidance if needed. Prompt templates located at prompting/prompt_templates.json are used to construct prompts together with additional context from prompting/message_generation_context.json.
In response to user choices and the correct or incorrect flagging of messages, the coach explains why the flagging might be correct or incorrect, points out phishing tactics of the message that are relevant and could have been recognized, and answers questions about phishing tactics in the message and in general. Prompts are constructed from the prompt templates prompting/prompt_templates.json with additional context such as the message and data from prompting/message_generation_context.json.
adaptive-phishing-awareness-training
│
├── app.py - Initializes the LLM components and controller classes and starts the Flask-based training application when executed as the main module.
├── interaction_controller.py - Implements the interaction state machine, manages phase transitions (initialization, message generation, user engagement, coaching), and generates coaching prompts in response to user decisions and queries.
├── llm_api.py - Provides an abstraction layer for LLM backends (Ollama, llm library, OpenAI), manages conversation state per model, and loads prompt templates from a JSON file.
├── message_generator.py - Loads sample messages and contextual data, constructs LLM prompts using templates, generates contextualized phishing and non‑phishing messages in batches, and maintains the list of generated messages.
├── requirements.txt - Specifies the Python package dependencies required to run the prototype.
├── training_environment_ui.py - Defines the Flask-based web user interface, including routes for loading the main page, generating messages, flagging decisions, showing messages, and handling chat queries.
│
├── prompting - JSON files for prompting.
│ ├── message_generation_context.json - Stores structured descriptions of environments and users that supply contextual information for generated messages.
│ ├── message_samples.json - Contains a collection of labeled sample messages, including phishing annotations, that serve as the basis for generating training messages.
│ └── prompt_templates.json - Defines prompt templates and instructions for message generation, coaching for different outcomes, and conversation handling in the interaction
│
├── static - Client-side website static files.
│ ├── app.js - Client-side logic for chat and inbox interaction, including sending queries and flagging actions to the backend and updating the displayed messages and chat transcript.
│ ├── icon*.png - Client-side website icons.
│ ├── LICENSE - Software license for HTML/JS/CSS chat code from https://github.com/patrickloeber/chatbot-deployment.
│ └── style.js - Client-side website style file.
│
└── templates - Client-side website HTML template.
└── base.html - Provides the HTML layout for the training interface, including the inbox view, email display area, and instructional content for the simulation.