-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 70
eclipse plugin_development
The Eclipse plugin is where all the other plugins (JavaPlugin, XMLPlugin, PropertyPlugin, TextMerger and the core) are loaded.
Activator class is the start point of the plugin. Activator class is loaded initially and it extends the AbstractUIPlugin, which tells the Eclipse Run-time that this Plugin is someway related to the Eclipse Platform UI.
An ID for the plugin is defined for configuration at Plugin.xml needs.
/**
* The plug-in ID
*/
public static final String PLUGIN_ID = "com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin"; //$NON-NLS-1$The overrode start() method starts the plugin and loads all the sub-plugins using the PluginRegistry from the core for each plug-in:
PluginRegistry.loadPlugin(PluginActivator.class);|
Note
|
How the |
The activator has the listener `ConfigurationProjectListener.java` from the workbenchcontrol package that checks continuously changes on the templates project
Plugin.xml file is used to initialize plugin. Here are defined the commands and the handler for each command, and also in which views should be shown the plugin menu with the commands.
The command configuration:
<extension point="org.eclipse.ui.commands">
<command
id="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.generate"
name="Generate">
</command>
<command
id="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.healthy_check"
name="Healthy Check">
</command>
</extension>
<extension point="org.eclipse.ui.handlers">
<handler
class="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipse.workbenchcontrol.handler.GenerateHandler"
commandId="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.generate">
</handler>
<handler
class="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipse.workbenchcontrol.handler.HealthCheckHandler"
commandId="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.health_check">
</handler>
</extension>As can be seen, to define the commands, the PLUGIN_ID defined at the Activator.java is used followed of the name of the command. Then, a handler from workbenchcontrol.handler package is assigned for each command.
After that, is defined the views where we want to show the CobiGen menu as Popup menu. (e.g. Project Explorer view)
<extension point="org.eclipse.ui.menus">
<menuContribution
allPopups="false"
locationURI="popup:org.eclipse.ui.navigator.ProjectExplorer#PopupMenu">
<separator
name="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.separator3"
visible="true">
</separator>
<menu label="CobiGen">
<command
commandId="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.generate"
label="Generate..."
style="push">
</command>
<command
commandId="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.health_check"
label="Health Check..."
style="push">
</command>
</menu>
<separator
name="com.capgemini.cobigen.eclipseplugin.separator4"
visible="true">
</separator>
</menuContribution>
</extension>The workbenchcontrol package provides to the plugin the listener regarding to the templates project, the listener for logging needs and the handler for the two main use cases (Generate and HealthCheck).
Update Template: Select Entity file and right click, then select CobiGen Update Templates after that click on download then download successfully will be come.
Adapt Template: Select Entity file and right click then select CobiGen Adapt Template .If CobiGen template jar not available then it download automatically. If CobiGen templates is already then it will override existing template in workspace and click on OK then imported template successfully message will come.
The wizard launching is the responsibility of the generate handler (`GenerateHandler.java`). In case of Generate action and depending of the input provided for that, the handler will create a JavaGeneratorWrapper or XMlGeneratorWrapper object.
For JavaGeneratorWrapper, if the input is a package or a selection of multiple entity files, the wizard will be launched in batch mode calling the `GenerateBatchWizard.java` from the wizard.generate package. But if the input is a single entity java class file, it will be launched in normal mode calling the `GenerateWizard.java` from the same package.
|
Note
|
For both Wrapper objects, the inputs will be converted to valid inputs for FreeMarker using the `Xml/JavaInputConverter.java` from the |
For XmlGeneratorWrapper, the input must be a single valid XML file. As only has a single file as input, the `GenerateWizard.java` will be called.
In summary, this will be the process for the Generate Action before calling the wizard:
At the case of Health Check action, a success/error dialog is shown instead of a wizard itself. The `HealtchCheckHandler.java` will call the execute method of `HealthCheck.java` from the healthcheck package. That class will test first if the templates project exists at the workspace opening and error dialog if not by throwing and handling the custom exception `GeneratorProjectNotExistentException.java` from the common.exceptions package.
try {
// check configuration project existence
//That method will throw GeneratorProjectNotExistentException
generatorConfProj = ResourcesPluginUtil.getGeneratorConfigurationProject();
...
..
.
} catch (GeneratorProjectNotExistentException e) {
LOG.warn("Configuration project not found!", e);
healthyCheckMessage = firstStep + "NOT FOUND!\n"
+ "=> Please import the configuration project into your workspace as stated in the "
+ "documentation of CobiGen or in the one of your project.";
PlatformUIUtil.openErrorDialog(HEALTH_CHECK_DIALOG_TITLE, healthyCheckMessage, null);
}If the project exists, HealthCheck will test if the context.xml file is valid. In case of invalid, HealthCheck will throw and handle the InvalidConfigurationException from the core and check if it is possible to upgrade the version of the XML file, showing an UPGRADE button at the dialog. If the upgrade is not possible, will show a dialog message telling the user to check the context.xml file for errors.
try {
//The CobiGen constructor will throw the InvalidConfigurationException
new CobiGen(generatorConfProj.getLocationURI());
...
..
.
} catch (InvalidConfigurationException e) {
healthyCheckMessage = firstStep + "OK.";
healthyCheckMessage += secondStep + "INVALID!";
if (generatorConfProj != null) {
Path configurationProject = Paths.get(generatorConfProj.getLocationURI());
ContextConfigurationVersion currentVersion = new ContextConfigurationUpgrader()
.resolveLatestCompatibleSchemaVersion(configurationProject);
if (currentVersion != null) {
// upgrade possible
healthyCheckMessage += "\n\nAutomatic upgrade of the context configuration available.\n" + "Detected: "
+ currentVersion + " / Currently Supported: "
+ ContextConfigurationVersion.getLatest();
boolean upgraded = openErrorDialogWithContextUpgrade(healthyCheckMessage, configurationProject);
if (upgraded) {
// re-run Health Check
Display.getCurrent().asyncExec(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
execute();
}
});
}
return;
} else {
healthyCheckMessage += "\n\nNo automatic upgrade of the context configuration possible. "
+ "Maybe just a mistake in the context configuration?";
healthyCheckMessage += "\n\n=> " + e.getLocalizedMessage();
}
}At this point, if all is correct, the user can choose to finish the HealtCheck process or run the Advance Health Check running the `AdvancedHealthCheck.java` to check the the validity of template configurations. That check has three steps:
-
Get configuration resources
Will get the template configuration file from the template folder corresponding to the input of the plugin provided by the triggers defined at thecontext.xmlfile for that input. -
Determine current state
Will check if the template configuration file exists, if it is accessible and if the version is up-to-date allowing upgrading if not. -
Show current status to the user
Will call the `AdvancedHealthCheckDialog.java` showing a dialog with the current state of each configuration template, showing an UPGRADE button if the configuration version can be upgraded.
To open a wizard, use the WizardDialog class from the org.eclipse.jface.wizard package.
The plugin does that at `GenerateHandler.java` as previously explained here:
if (((IStructuredSelection) sel).size() > 1 || (((IStructuredSelection) sel).size() == 1)
&& ((IStructuredSelection) sel).getFirstElement() instanceof IPackageFragment) {
WizardDialog wiz = new WizardDialog(HandlerUtil.getActiveShell(event),
new GenerateBatchWizard(generator));
wiz.setPageSize(new Point(800, 500));
wiz.open();
LOG.info("Generate Wizard (Batchmode) opened.");
} else if (((IStructuredSelection) sel).size() == 1) {
WizardDialog wiz = new WizardDialog(HandlerUtil.getActiveShell(event), new GenerateWizard(generator));
wiz.setPageSize(new Point(800, 500));
wiz.open();
LOG.info("Generate Wizard opened.");
}Adapt Template: Select Entity file and right click then select CobiGen Adapt Template.If CobiGen template jar not available then it download automatically.If CobiGen templates is already then it will override existing template in workspace and click on OK then imported template successfully message will come .If Template not available the it automatically
=== Wizard and WizardPages
The Wizard class from the org.eclipse.jface.wizard package provides the functionality to build custom wizards. This class controls the navigation between the different pages and provides the base user interface, for example, an area for error and information messages.
A wizard contains one or several pages of the type WizardPage. Such a page is added to a Wizard object via the addPage() method.
A WizardPage must create a new Composite in its createControl() method. This new Composite must use the Composite of the method parameter as parent. It also must call the setControl() method with this new Composite as parameter. If this is omitted, Eclipse will throw an error.
The WizardPage class defines the canFlipToNextPage() and setPageComplete() methods to control if the NEXT or the FINISH button in the wizard becomes active.
The Wizard class defines the canFinish() method in which you can define if the wizard can be completed. This last method is overrode at AbstractGenerateWizard.java.
In case that has been launched in batch mode, the wizard only will have the select increment and files page (initialized and configured at `SelectFilePage.java` from the package wizard.common)
In case of normal mode with an entity java class as input, the wizard will have an optional second page provided for `SelectAttributesPage.java` of the package wizard.generate.common for selecting attributes of the entity that will be used for the generation. The page is optional because the user can finish the wizard and perform the generation from the first page.
The pages of the CobiGen wizard is composed essentially for container. The containers have a CheckBoxTreeViewer object, a content provider object and a listener (that defines the behavior of the wizard when a check box is checked or unchecked)
The first page (`SelectFilesPage`) is composed by two containers:
-
Left container - Increment Selector
-
Created as a
CustomizedCheckBoxTreeViewer -
The content provider is a
SelectIncrementContentProvider -
Setting the input will upgrade the labels to show
-
Set
CheckStateListeneras listener
-
incrementSelector = new CustomizedCheckboxTreeViewer(containerLeft); incrementSelector.setContentProvider(new SelectIncrementContentProvider()); incrementSelector.setInput(cobigenWrapper.getAllIncrements()); gd = new GridData(GridData.FILL_BOTH); gd.grabExcessVerticalSpace = true; incrementSelector.getTree().setLayoutData(gd); CheckStateListener checkListener = new CheckStateListener(cobigenWrapper, this, batch); incrementSelector.addCheckStateListener(checkListener);incrementSelector.expandAll();
-
Right Container - Resources to be generated
-
Created as
SimulatedCheckBoxTreeViewerif the Customize button is not enabled or asCustomizedCheckBoxTreeViewerif it is. -
SelectFileContentProvideras content provider. -
SelectFileLabelProvideras label provider -
Generation target project as input
-
Set
CheckStateListeneras listener
-
|
Note
|
To know how a content provider works check the official documentation here. |
As previously explained, this page is optional, the user can press the Finish button at the previous page. Nevertheless, this page can only be accessed in case of a single entity file as input, never on batch mode.
The container is composed by a single CheckBoxTableViewer with a `SelectAttributesContentProvider` as content provider and a `SelectAttributesLabelProvider` as label provider.
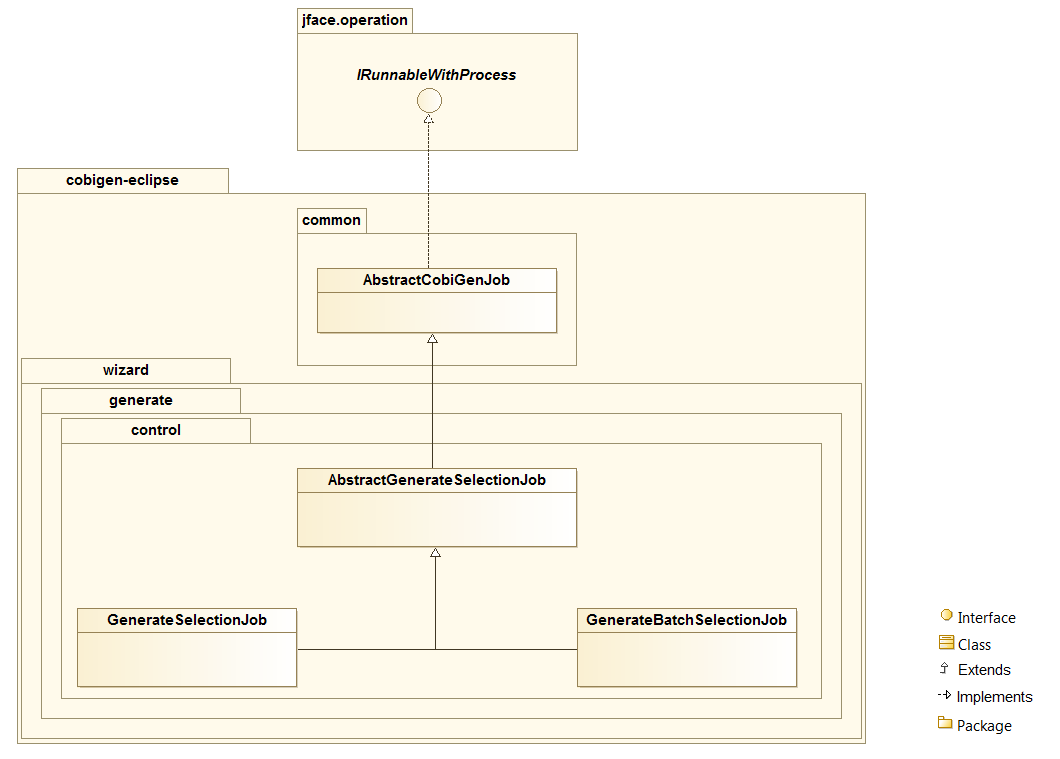
When the user press the Finish button, the generation process will begin. For that, a generation job will be created using as argument a list of templates to be generated retrieving them from the user selection of the first page (Select Files Page). The generate wizard will use the `GenerateSelectionJob.java` or the `GenerateBatchSelectionJob.java` for normal mode or batch mode respectively.
@Override
protected void generateContents(ProgressMonitorDialog dialog) {
if (cobigenWrapper instanceof JavaGeneratorWrapper) {
for (String attr : page2.getUncheckedAttributes()) {
((JavaGeneratorWrapper) cobigenWrapper).removeFieldFromModel(attr);
}
}
//Here are retrieved the templates to use for the generation selected at the first page
GenerateSelectionJob job = new GenerateSelectionJob(cobigenWrapper, page1.getTemplatesToBeGenerated());
try {
dialog.run(true, false, job);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
LOG.error("An internal error occurred while invoking the generation job.", e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("The working thread doing the generation job has been interrupted.", e);
}
}The dialog.run(true, false, job) method will call the performGeneration() method from `GenerateSelectionJob.java`
Calling the generate() method from the CobiGenWrapper will call the method with the same name from the core and the generation will begin.
At batch mode, the generation job will be instantiated depending if the selection was a container or a multiple files selection.
@Override
protected void generateContents(ProgressMonitorDialog dialog) {
List<TemplateTo> templatesToBeGenerated = page1.getTemplatesToBeGenerated();
List<String> templateIds = Lists.newLinkedList();
for (TemplateTo template : templatesToBeGenerated) {
templateIds.add(template.getId());
}
GenerateBatchSelectionJob job;
if (container == null) {
job = new GenerateBatchSelectionJob(cobigenWrapper, cobigenWrapper.getTemplates(templateIds),
inputTypes);
} else {
job = new GenerateBatchSelectionJob(cobigenWrapper, cobigenWrapper.getTemplates(templateIds),
container);
}
try {
dialog.run(true, false, job);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
LOG.error("An internal error occurred while invoking the generation batch job.", e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("The working thread doing the generation job has been interrupted.", e);
}
}The dialog.run(true, false, job) method will call the performGeneration() method from `GenerateBatchSelectionJob.java`
Disclaimer
If you discover any documentation bugs or would like to request new content, please raise them as an issue or create a pull request. Contributions to this wiki are done through the main repo under the folder documentation.
License
This documentation is licensed under the Creative Commons License (Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International)