-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 61
Photon Count calculation
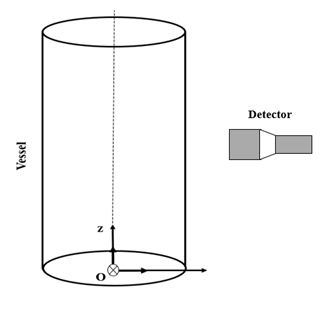
In this example, photon counts calculation for a single radioactive particle that emits gamma-ray has been performed. We perform the calculations for a set of given positions inside a cylindrical tank using a Monte-Carlo technique. The Monte-Carlo calculation generates the estimated counts with respect to a detector for each particle’s position inside the vessel. The geometry of the vessel and the detector is illustrated below:
In the subsection “rpt parameters”, we define a set of positions inside the reactor, the export filename, the number of Monte-Carlo iterations, the seed number and parameters values for the gamma-ray model. Common parameters for the RPT simulation are described in the RPT parameters subsection in the RPT Parameters documentation.
# --------------------------------------------------
# RPT Monte Carlo technique
#---------------------------------------------------
subsection rpt parameters
set particle positions file = positions.particle
set verbosity = verbose
set export counts = true
set counts file = counts.csv
set monte carlo iteration = 100000
set random number seed = 0
set reactor radius = 0.1
set peak-to-total ratio = 0.4
set sampling time = 1
set dead time = 1e-5
set activity = 2e6
set gamma-rays emitted = 2
set attenuation coefficient reactor = 10
set attenuation coefficient detector = 21.477
end
In the subsection “detector parameters”, we specify the file that contains the position of the detector face center and the position of a point inside the detector on its axis. In this example, the detector face center position is [0.15, 0, 0.08] and [0.17, 0, 0.08] is another point on the detector’s axis. The detector parameters are described in the RPT Parameters documentation.
#---------------------------------------------------
# Detector parameters
#---------------------------------------------------
set detector positions file = positions.detector
set radius = 0.0381
set length = 0.0762
end
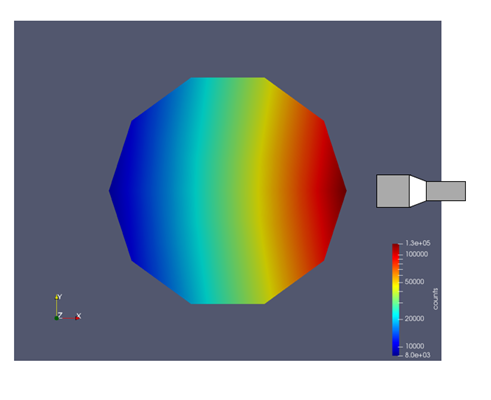
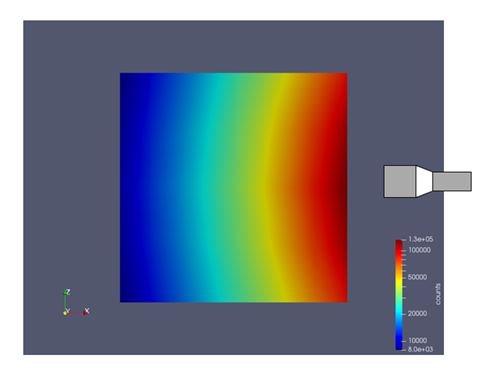
The plots below visualize the received photon counts by the detector from different positions inside the cylinder. The algorithm of RPT works based on a precise phenomenological model which relates the spatial coordinate of the radioactive particle and the number of photon counts received by the detector. The following plots are the top view (x-y plane) and front view (x-z plane) of the vessel. As it is shown, if the particle is placed in an area closer to the detector, the detector senses a higher amount of gamma-rays intensity compared to the areas further from the detector’s face.