The aim of this project is developing Machine Learning models to predict the precipitations in the city of Los Angeles based on meteorogical data. Microsoft Azure will be the platform to be used for the development and the deployment of the models. The idea is to benchmark models created using autoML and an optimized DecissionTree using Hyperdrive. The best model will be deployed and a sample data payload will be used to try out the created endpoint.
The dataset to be used is public and available on Kaggle.
The set up of our project is based on the environment provided by Udacity. No additional data science packages or add-ons are needed. A curated environment of Microsoft Azure will be enough to replicate our results
As mentioned earlier the data set is made up of meteorological data from different weather stations in Los Angeles. The data includes the following features:
- Name of the station
- Time stamp of the measurement
- Average daily wind speed
- Peak gust time
- Average temperature (empty column)
- Maximum temperature
- Minimum temperature
- Direction of fastest 2-minute wind
- Precipitation <----- goal feature
The data is available in tabular form on Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/varunnagpalspyz/precipitation-prediction-in-la
We will develop models using Microsoft Azure that will predict the precipitation on Los Angeles. From the data available we will use the following features for the training of the models:
- Average daily wind speed
- Average temperature (empty column)
- Maximum temperature
- Minimum temperature
- Direction of fastest 2-minute wind
We will not include time stamps as we will not be using models with time dependant abstractions nor we will use the name of the station.
The data will be accessed through a URL from github (copy of the dataset from Kaggle):
example_data = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RaikohGrass/ML_Azure_Capstone/main/precipitation_LA.csv'
dataset = Dataset.Tabular.from_delimited_files(example_data)
For our development we used the following configuration:
# TODO: Put your automl settings here
automl_settings = {
"experiment_timeout_minutes": 20,
"max_concurrent_iterations": 5,
"primary_metric" : 'normalized_root_mean_squared_error'
}
# TODO: Put your automl config here
automl_config = AutoMLConfig(compute_target='EduardoCluster',
task = "regression",
training_data=dataset,
label_column_name="PRCP",
enable_early_stopping= True,
featurization= 'auto',
debug_log = "automl_errors.log",
**automl_settings
)
As optimization metric we selected the normalized root mean squared error, a common metric for regression problems. Since we are dealing with a numeric prediction task, we selected "regression" on the "task" parameter of autoML. We enabled early stopping and used a timeout of 20 minutes for the training runs.
The resulting model was a Voting Ensemble made up of the following algorithms:
- 2'ExtremeRandomTrees',
- 2 'XGBoostRegressor'
- 'RandomForest
- 'DecisionTree
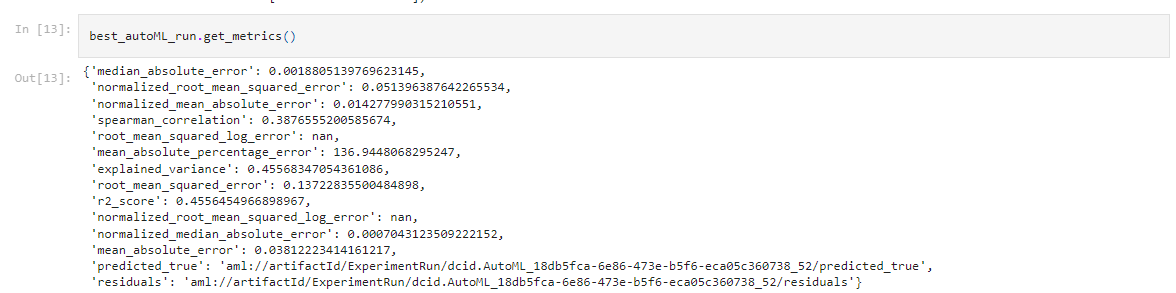
This Voting Ensemble resulted in the following metrics:
A way of improving the metrics would be to add more data to be used on the training or better yet to use deep learning together with the based time data that we ignored from the dataset. This way we would grant our models a feeling of the weather seasonal distributions in the year and of the consecutive days with rain.
We can see some details of the autoML run on the following screenshot:
The run and the model are shown in the following screenshot:
For the Hyperdrive experiment we selected a DecisionTreeRegressor from sklearn. This model was of interest as we have never used a DecisionTree for a regression problem before. We wanted to compare the performance of a simple tree with models created by autoML.
For the run we used the following Hyperdrive configuration:
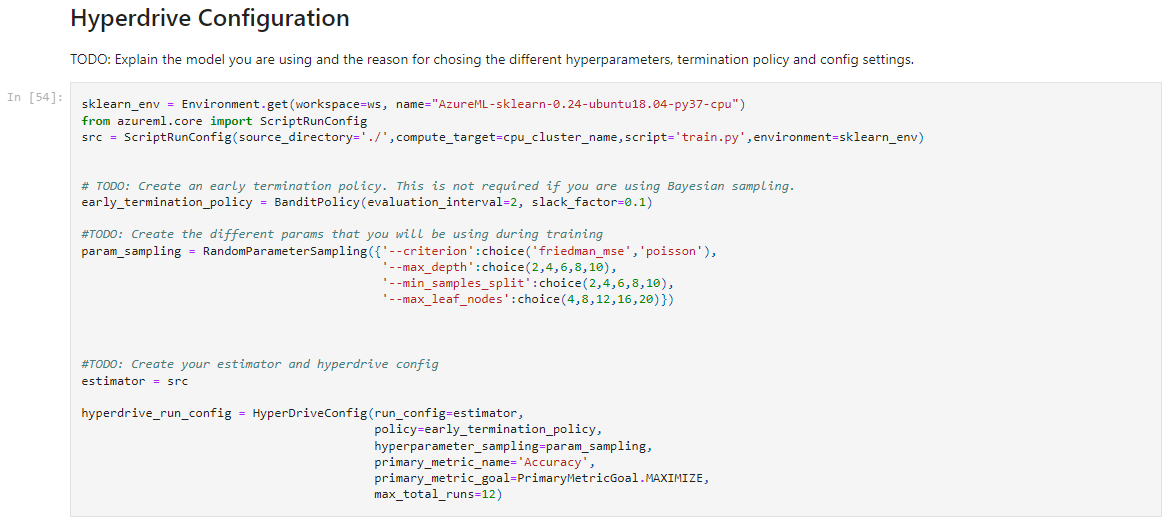
We wanted to iterate through four of the available parameters of sklearn for this model:
- Criterion: This will be the function used to decide the splits based on the features
- Max Depth: Maximum number of levels that our decision tree can reach
- Min Samples for Split: Minimum number of data samples that are to be used to make a split
- Max Leaf Nodes: Maximum number of leaf nodes of our tree
For the first parameter we sampled among two of the available options: 'friedman_mse' and 'poisson' The other parameters were integers that were to be sampled from five given values. The maximum depth was selected between 2 and 10 as we didn't want a really complex tree that splitted the whole samples The minimum samples was also selected between 2 and 10. Here we didnt expect that much of a change in the accuracy The maximum leaf nodes were selected between 4 and 20 also for the sake of keeping the complexity of the model at a basic level.
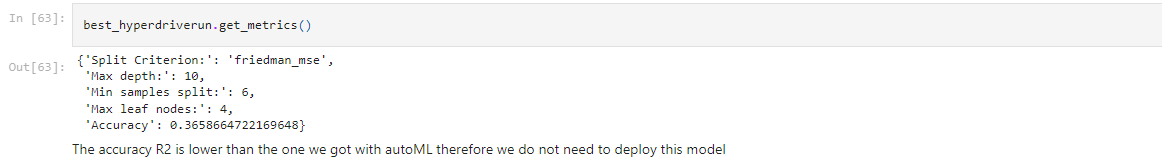
We got a model with the following parameters and metrics:
- Criterion: 'friedman_mse'
- Max Depth: 10
- Max Leaf Nodes: 4
- Min Samples for Split: 6
The model had a R2 score of 0.3658, which was a bit below our autoML model (0.4556) We could have improved the model by allowing a higher complexity, i.e., to increase the range of the Max Depth parameter. We can also increase dramatically the number of runs for the Hyperdrive optimization.
We can see some details of the run on the following screenshots:
The deployment of the model was pretty straight forward. We defined an environment based on the model provided by the autoML run.
The environment includes all the dependencies and libraries needed to handle the model created.
In order to interface and use the model for predictions we created an InferenceConfig that used the script created by autoML to make the predictions using the model.
The next step was to define a ACI instance and deploy the model:
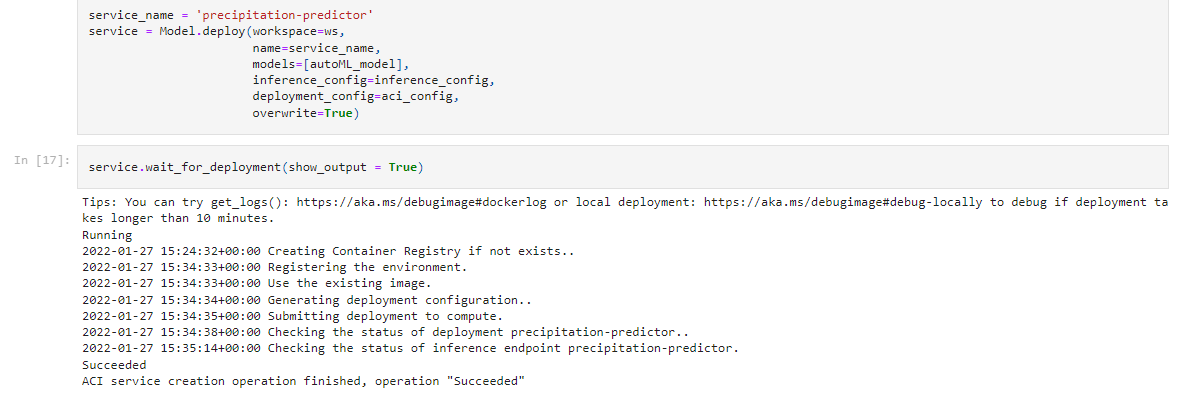
Having defined the InferenceConfig and the ACI instance we proceed to deploy the model as a web service:
We can check out the URI for the RESTapi and the Swagger documentation:

We can also look at the endpoint tab in Azure that the endpoint we created is "healty" and available:
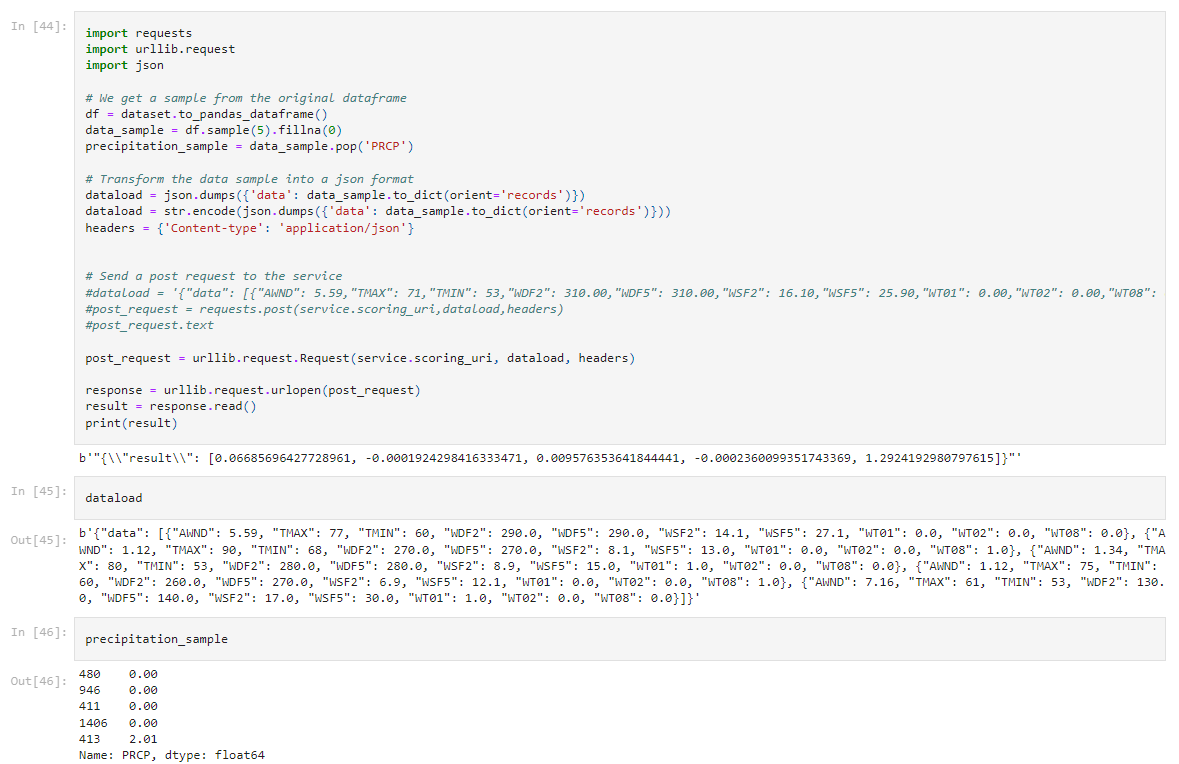
To use the deployed webservice we can select a datasample to be used as a data payload. This payload should be transformed into a JSON that follows the format of the needed POST request. Including the headers we can send the payload and get a response from the service:
Here is important to notice that we followed the instructions provided by the "consume" tab of the deployed model, as using the common "requests" library didn't work out.
Video of the project: https://youtu.be/m69ojRNL3Hg
TODO (Optional): This is where you can provide information about any standout suggestions that you have attempted.