stencil-lazy is a Stencil @Lazy decorator that allows you to call component method as the user scrolls component into the viewport. On supported browsers (Chrome and chrome based browsers, Firefox and Edge) stencil-lazy uses IntersectionObserver to accomplish this functionality. For Safari and IE it simply falls back to setTimeout unless you use polyfill.
If you want stencil-lazy to work everywhere (also on IE and Safari) use polyfill. You can pop this script tag:
<script src="https://polyfill.io/v3/polyfill.min.js?features=IntersectionObserver"></script>
in index.html and that's it:)
Polyfill is not included in stencil-lazy not to increase the bundle size and to leave the decision to you: either you go with setTimeout fallback or if you prefer, go with polyfill
In your Stencil project, add stencil-lazy to your package.json:
npm i stencil-lazy
It's very simple: you just need to anotate your method with @Lazy and it will be called when host component is scrolled to viewport. Method will be called once - the first time you scroll to component
import { Component } from '@stencil/core';
import { Lazy } from 'stencil-lazy';
@Component({ tag: 'lazy-component', shadow: true })
export class LazyComponent {
@Lazy()
someMethod() { console.log("someMethod was called because user scrolled to LazyComponent"); }
render() { return <div>Hello, World!</div>; }
}It may sometimes happen that you would like monitor for some HTMLElement that you render in component. This is also possible the API then is as follows:
import { Component } from '@stencil/core';
import { registerLazy } from 'stencil-lazy';
@Component({ tag: 'lazy-component', shadow: true })
export class LazyComponent {
someMethod() { console.log("someMethod was called because user scrolled to LazyComponent"); }
render() {
return (
<div
ref={divEl => registerLazy(this, divEl, () => this.someMethod())}>
Hello, World!
</div>;
)
}You can also set margin for @Lazy. It determines how far from the viewport lazy loading starts. Can have values similar to the CSS margin property, e.g. "10px 20px 30px 40px" (top, right, bottom, left). The values can be percentages.
@Lazy({ margin: "50%" })
someMethod() { console.log("someMethod was called because user scrolled to margin of LazyComponent extended by 50%"); }or if you want to have it dynamic (as web component @Prop)
@LazyMargin() @Prop() margin?: string;All web components here have optional margin prop.
Basically you can think of every action that you would normally do with the load of the page/component. Maybe some of those actions are time consuming, generating not needed network traffic and not giving any benefit to most of users? Good example is calling an API to get data to be presented by component. Maybe most of users are not even checking some forgotten carousel on the bottom of every page in your app? Or you need an easy way to implement a listing page with infinie scrolling?
Following component
import { Component, State, Element } from '@stencil/core';
import { Lazy } from 'stencil-lazy';
@Component({
tag: 'test-stencil-lazy'
})
export class TestStencilLazy {
@State() name: string;
@Lazy()
getName() {
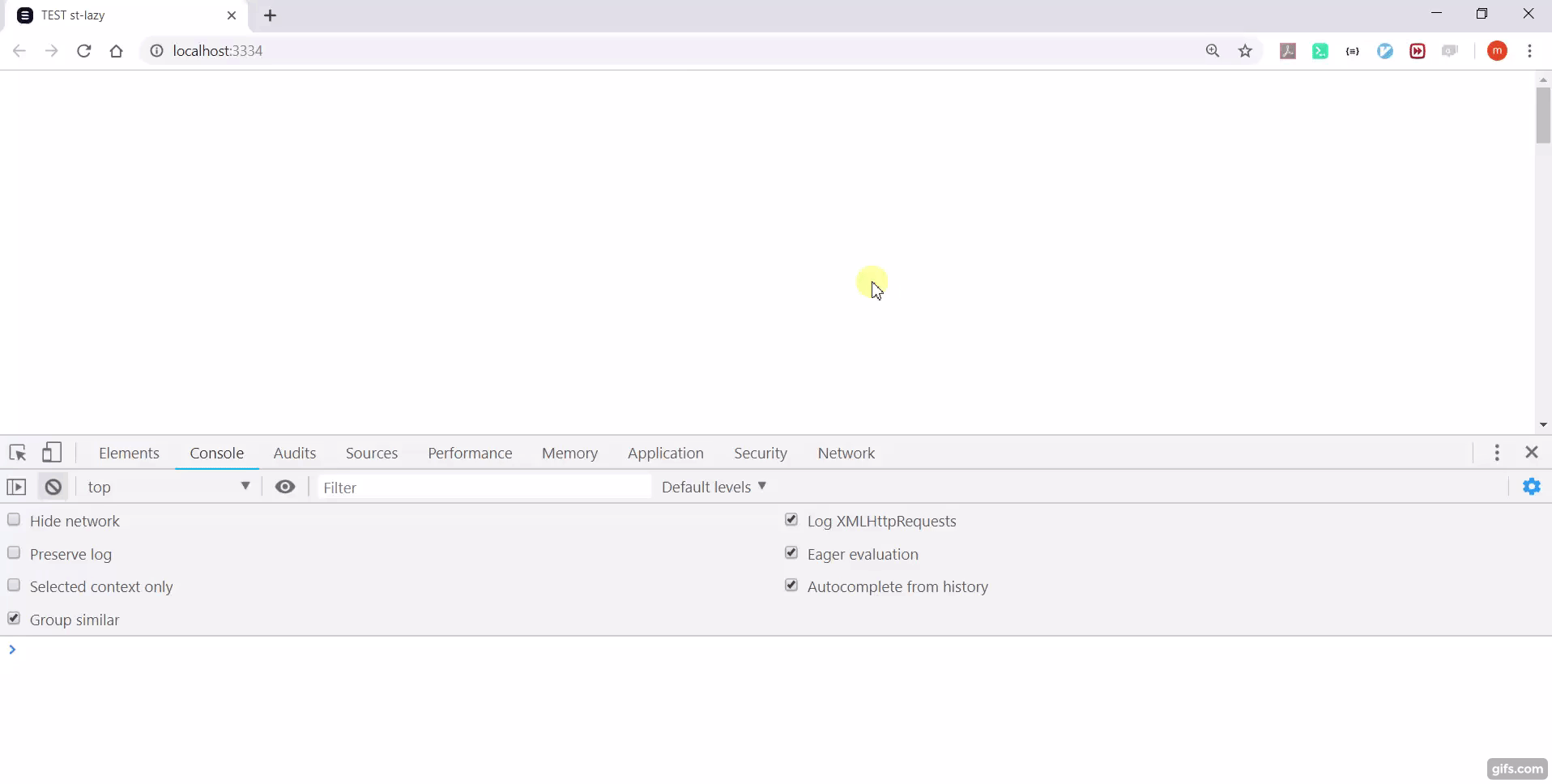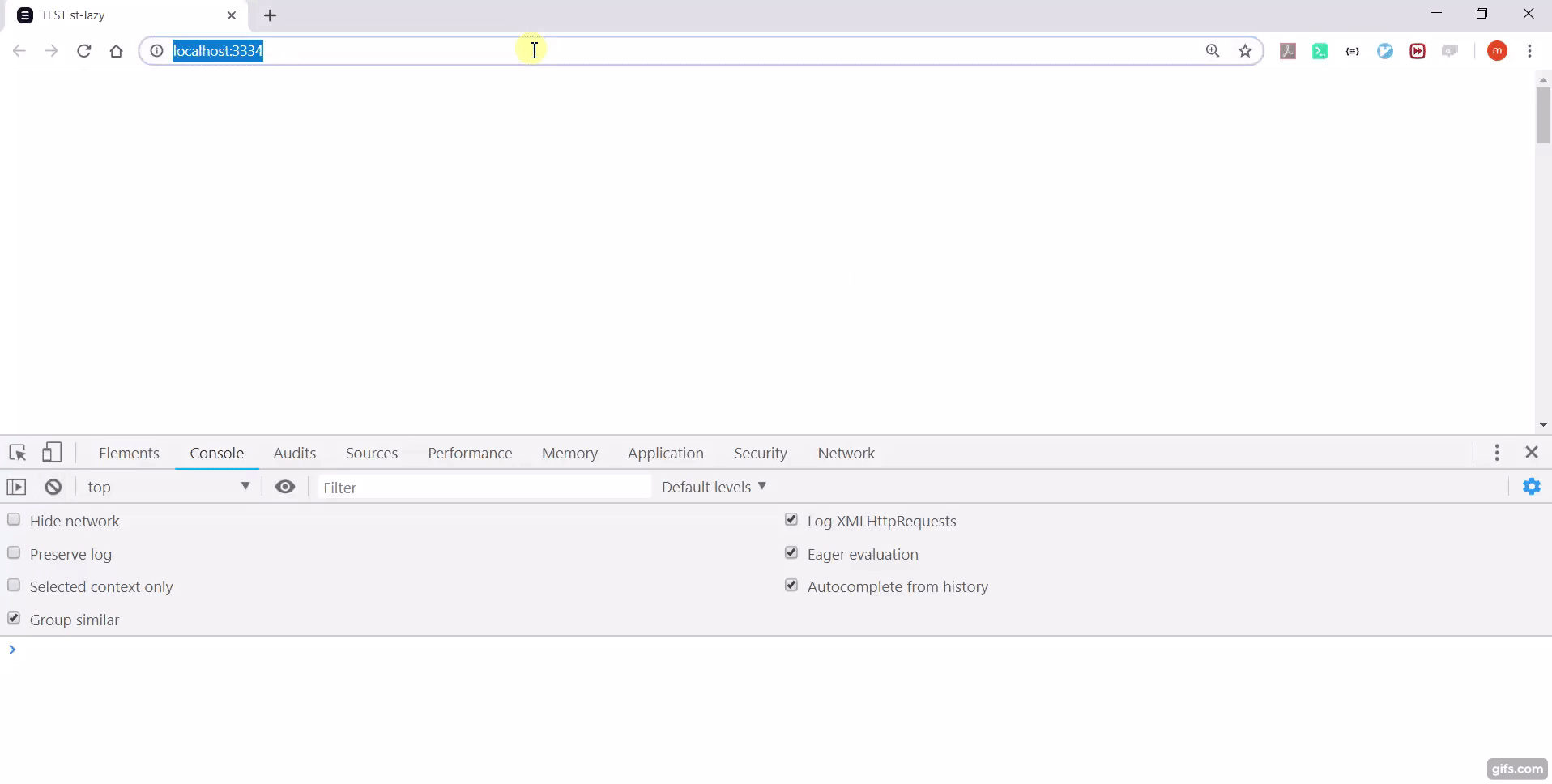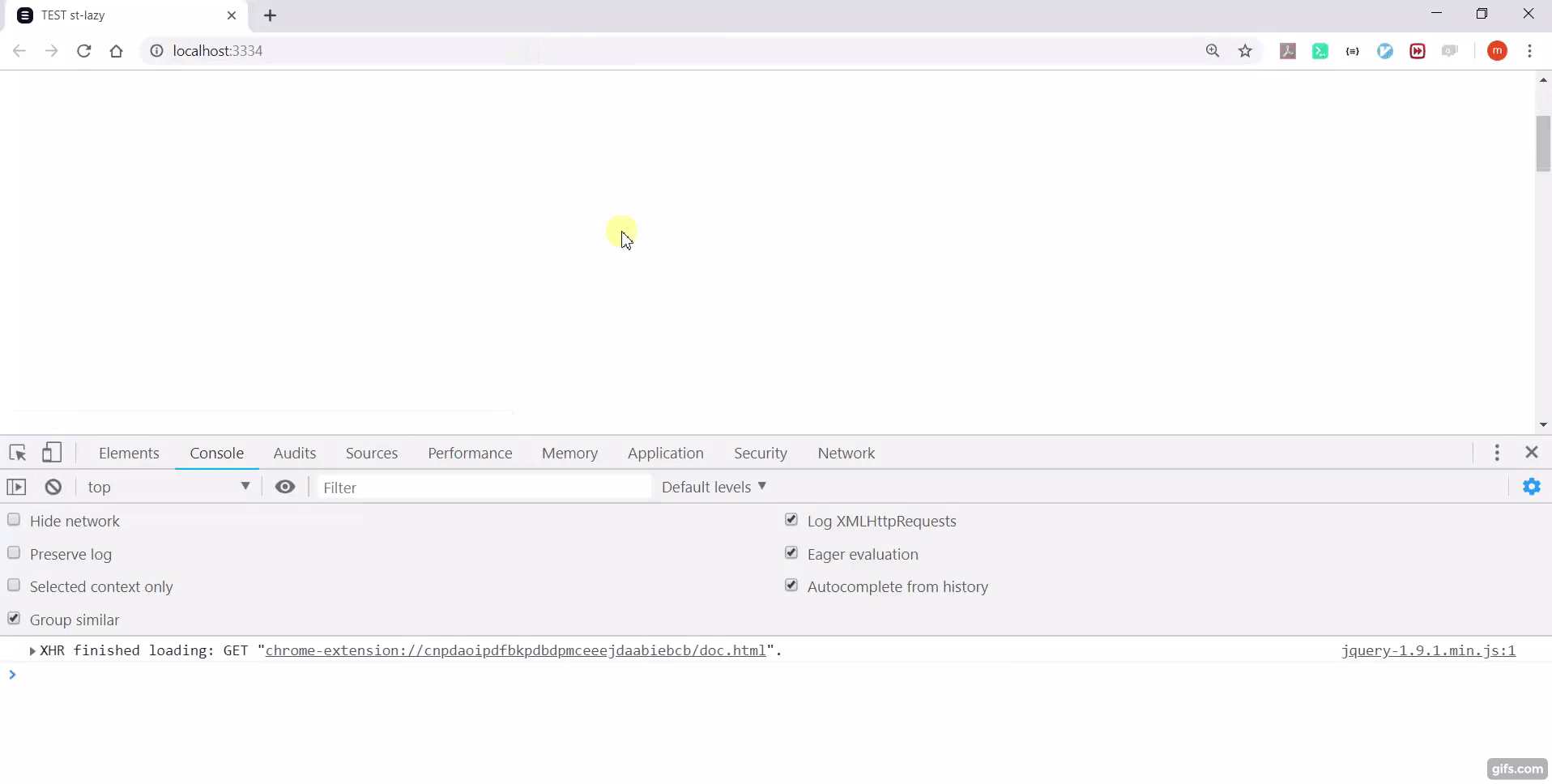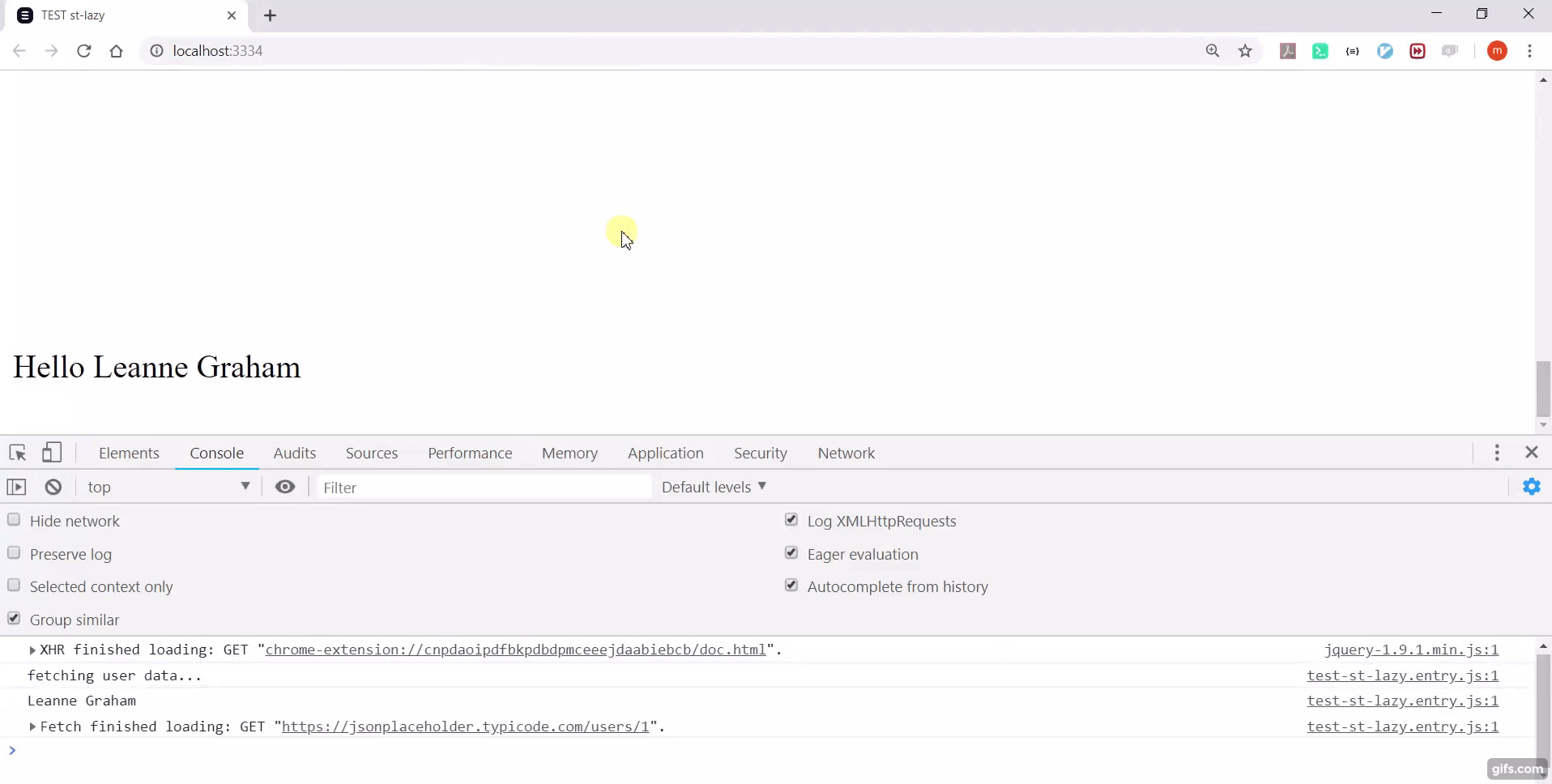
console.log("fetching user data...");
setTimeout(() => {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/1")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
this.name = data.name
console.log(this.name);
})
}, 300);
}
render() {
return (
<div><p>Hello {this.name}</p></div>
);
}
}...on the page
<body>
<div style="height: 1000px"></div>
<test-stencil-lazy></test-stencil-lazy>
</body>gives