SWAP was created so as to help non-English speaking natives to have a much easier understanding in Programming (i.e SWAHILI) in Tanzania . It is a programming Language that allows programmers to write codes in the Swahili Language construct
- Abdulbasit Rubeiyya- @ibnsultan
- node js
- jScript
Getting Started with Swap you need to have node runtime installed on your machine, After making sure that node runtime works on your machine run the following command
npm install -g swapro
After installation download run the command
swap -h
if your installation was successful the following result will show up
λ swap -h
Usage: cli [options] [file]
Options:
-v, --version output the version number
-h, --help output usage information
_________ _________ ________
/ / // // /
/ / // // / Swahili
/_________ / //________//________/ programming
// / // // Language
// / // // author: Abdulbasit Rubeiyya
________//____/_____// //
Examples:
$ swap file.sw
$ swap -h
$ swap -v
To program using swap we will be using vscode, so open the program and install the swap extension
-
Linux : no more configurations start right away
-
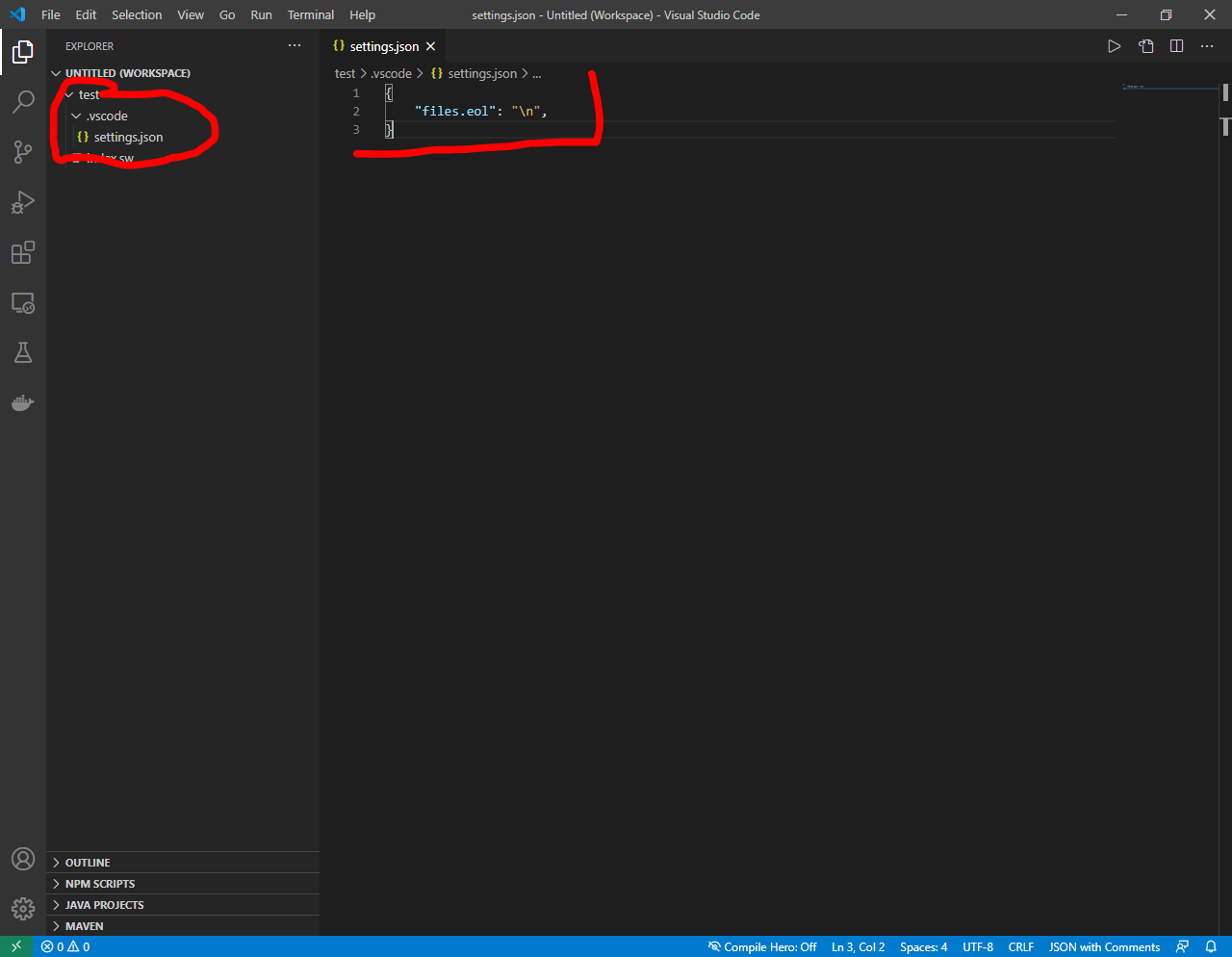
Windows: swap supports only LF (Line feed) end of line format while the default for windows is CRLF (Carrige Return and Line feed) EOL format so we have to change it In your project create a folder called .vscode, and inside it create a file settings.json and inside it add the following line.
{ "files.eol": "\n" }OR for windows you can use the notepad++ mod that provides a syntax highlighter for you code, click here to download it
NOTE: The file extension for a swap file is .sw and Swap does not use the WINDOWS (CRLF) EOL format, if you're not going to use the provided text editor on windows OS make sure it is set to use UNIX (LF) or MACINTOSH (CR) EOL format
First Program:
Swap does not use any preprocessors, It uses the constant andika to print out the desired content, andika literally means "write"
eg.1
andika "habari yako";
Result:
habari yako
Every line of code has and must be terminated by a delimiter which is a semicolon(;)
To run your program initiate a CMD in your project directory and run the command
swap file.sw
File should be replaced with the name of your file.
VARIABLE DECLARATION
Variables can only be declared in Swap using the keyword hifadhi which means to store something.
eg. 2
hifadhi a = 10;
hifadhi b = 20;
andika a + b;
Result
30
eg. 3
hifadhi jina= "juma";
hifadhi umri = 5 ;
andika jina + " " + "is" + " " + umri + " " + "years old" ;
Result
Juma is 5 years old
REQUESTING USER INPUT
Swap also supports the program interactive programming by requesting inputs from the user, the input request constant is dai which means "request".
eg. 4
hifadhi jina = dai("andika jina lako: ");
DISPLAYING USER INPUT
eg. 5
hifadhi jina = dai("andika jina lako: ");
andika "Habari " + jina;
assuming after running the program the user provided it with input "Abdulbasit"
then the Results will be
Habari AbdulbasitConditionals like if, else, else if and switch statements are also defined and used in Swap language
IF ELSE IF CONDITIONS:
if is denoted by kama
else is denoted by basi
else if as basi kama
eg. 6
hifadhi umri = 20;
kama ( umri < 18 ){
hifadhi makamo = "mtoto" ;}
basi kama ( umri > 18 && umri < 50){
hifadhi makamo = "kijana" ;}
basi {
hifadhi makamo = "mzee" ;}
andika "juma ni " + makamo ;
Result
juma ni kijana
**Explanation:**The above program is used to show from which age group does a person belong whether young, youth or an old person
SWITCH CASE:
Also, switch case expressions are included, The switch case is only evaluated Once, the value of each expression is always compared with the values of Each case. if there is a match, the associated code block is run and then escapes the sequence.
With exceptional to loops the use of break; which is presented by vunja; statement in Swap, to kill or escape a switch case sequence will result to a fatal error. In normal cases (without loops) the switch case automatically escapes the sequence after executing the true match of a case.
The switch case values are presented as follows;
switch - badilisha
case - chaguo
break - vunja
default - zaidi
eg. 7
andika "1. cct basic";
andika "2. cct ordinary";
hifadhi teule = dai("weka chaguo lako hapa: ");
wakati (teule > 0){
chagua (teule){
kesi 1 :
andika "chaguo lako ni: " + teule ;
vunja;
kesi 2 :
andika "chaguo lako ni: " + teule ;
vunja;
zaidi :
andika "umekosea tafadhali chagua tena";
}
hifadhi teule = dai("weka chagua lako hapa: ");
}
**Explanation:**The following program prompts a user to choose a tv package if a program chose is present and is matched with the associated case, the program will echo the user's input and exits else if the input value is not matched the program will continue to loop until a right input is given or the program is manually terminated.
INCREMENT and DECREMENTS
Increments and decrements like i++ or i-- are not valid and would throw out a fatal error when used, to declare an increment or decrement normal mathematical expressions are used
i.e.
hifadhi a = a + 1; for increment or
hifadhi a = a - 1; for decrement.
LOOPS
for Loop
In Swap, "for" loop in implemented by**hakika** statement and expressed as
hakika(hifadhi a = 0; a < 10; hifadhi a = a+1){
//statement
}
while - loop
In Swap, the while loop is represented by wakati() statement and is expressed as
wakati(hali/condition){
//statement;
}
eg. 8
hifadhi a = 10;
wakati(a!=0){
a = a-1;
}
Results
The program will continue to run until variable "a" decreases to 0 vunja; keyword can be used to escape loops when necessary
FUNCTIONS
A function is a code-block that performs a certain task, In Swap, a function can be a group of a procedure which performs a certain work or can be used to return a value.
Functions in Swap can be defined as independent modules of code blocks that perform certain work.
eg. 9
function keyword in held by njia
njia hesabu (a,b){
rejesha a+b;
}
hifadhi x = hesabu(12,6);
andika x;
or
njia hesabu (a,b){
andika a+b;
}
hesabu(12,6);
or
njia hesabu (a,b){
rejesha a+b;
}
andika = hesabu(12,6);
Result
18
in swap there is no pre-declaration of functional prototypes as in languages like C++, therefore the use of functions have to be fully declared before they are called.
IMPORT
The import keyword is supplemented by the constantlete which literally means "bring", the import(lete) constant is used to import other files in to the main program file.
The constant is followed by a string value which should contain the path to the imported file and this path must be provided as a suffix to the absolute path of the needed file
**eg. 10
** lete "file.swap"
the command will bring a file.swap into your program.
Suppose you want to import a file from another directory
lete "PATH/file.swap"
VARIABLE SCOPES
a variable scope is the settings within which the variable is declared, All the inner functions (njia) have access to the variables that are from the outer function, unlikely the inner functions the outer functions do not have access to their Inner functions.
eg. 11
hifadhi a=3;
njia namba(){
hifadhi a=a+10;
andika a;
}
andika a;
Result:
13
3
To adopt the changes of a variable in inner functions, a variable must be declared with ita, this will make all changes in the inner function to the outer function noticeable,
eg. 12
hifadhi a=3;
njia namba(){
ita a=a+10;
andika a;
}
andika a;
Result:
13 13
ARRAYS
An array is a data structure that stores multiple elements in a single variable. and in most cases these elements are all of the same types, like integer or string.
Swap supports two types of arrays,
- the one-dimensional array and
- the multi-dimensional array.
ONE DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
It is also known as the linear array, all elements stored can be accessed through a single subscript which either represents a row or a column,
eg. 13
hifadhi array = ["moja","mbili"];
andika array;
andika array[0]
Results
moja, mbili moja
MULTI-DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
It is an array that stores data with than one array level, a multi-dimensional array is used to store several data groups in one variable.
eg. 14
hifadhi array = [["macho","pua","mdomo","sikio"],[1, 2, 3]]
andika array;
andika array[0];
andika array[1][2];
Results:
'macho', 'pua', 'mdomo', 'sikio', 1, 2, 3 'macho', 'pua', 'mdomo', 'sikio' 3
Elements can be added to a swap array by the last position of an index empty
eg. 15
hifadhi array = [[1, 2, 3]];
andika array;
hifadhi array[]=4;
andika array;
Result:
1, 2, 3 1, 2, 3, 4
BUILT IN FUNCTIONS
Swap has several Helper functions, the following is a list of those helper functions.
BADILI:
BADILI constant is used to convert a string value of a variable into uppercase letters. The constant must be written in uppercase.
eg. 16
andika BADILI("herufi");
Result
HERUFI
badili:
badili this is an inverse of BADILI constant, it transforms a or converts a string value of a variable into lowercase letters. The constant must be written in lowercase.
eg. 17
andika BADILI("HerUFI");
Result
herufi
Kaunta:
kauntaThis is used to count the length of an array
eg. 18
andika kaunta([26,78,75,"mango"]);
Result
4
hariri:
hariri constant is used to edit a part of a string or substring of a string
eg. 19
andika hariri("wewe ni mbaya", "mbaya", "mzuri");
The function hariri takes in three arguments, assuming the parameters used by function hariri x, y and z then
x will be the initial input
y is the string to find and replace in the input of x
z is the string value to replace the input of y
Result
wewe ni mzuri
It has replaced string mbaya in a sentence with a string mzuri.
tafuta:
tafuta constant is used to find a substring in a string
eg. 20
andika tafuta ("wewe ni mbaya", "mbaya");
Result
boolean - kweli
if the substring does not exist in the main string then it would have returned
boolean - sikweli
Assuming we have two variable A and B where A=15 and B=20