diff --git a/README-JA.md b/README-JA.md
index f68518c8..b3d88859 100644
--- a/README-JA.md
+++ b/README-JA.md
@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@
## [MQTT Tutorials](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/category/mqtt-protocol)
Get to know the preferred protocol in IoT from beginner to master.
+- [MQTTクリーンスタートとセッション有効期限間隔の紹介 | MQTT 5機能](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/mqtt5-new-feature-clean-start-and-session-expiry-interval) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/ja/202410/mqtt5-new-feature-clean-start-and-session-expiry-interval.md))
- [MQTT 5.0:7つの新機能と移行チェックリスト](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/introduction-to-mqtt-5) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/ja/202409/introduction-to-mqtt-5.md))
- [MQTT vs HTTP: IoT向けどちらがより適していますか?](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/mqtt-vs-http) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/ja/202408/mqtt-vs-http.md))
- [User Properties - MQTT 5.0 の新機能](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/mqtt5-user-properties) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/ja/202312/mqtt5-user-properties.md))
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index b29fe8f4..658cc938 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -165,6 +165,7 @@ Best practice of MQTT in various clients.
## [MQTT Integration (Eco & Integration)](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/category/eco-and-integration)
Explore more with & via EMQ.
+- [Integrating STOMP with EMQX: A Comprehensive Guide](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/integrating-stomp-with-emqx) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/en/202410/integrating-stomp-with-emqx.md))
- [Database for MQTT Data Storage: A Selection Guide](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/database-for-mqtt-data-storage) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/en/202409/database-for-mqtt-data-storage.md))
- [MQTT and Snowflake: Creating a New Future for Distributed Renewable Energy](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/mqtt-and-snowflake-distributed-renewable-energy) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/en/202407/mqtt-and-snowflake-distributed-renewable-energy.md))
- [MQTT & micro-ROS: Building Efficient Robotics Applications](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/mqtt-and-micro-ros) ([Edit](https://github.com/emqx/blog/blob/main/en/202407/mqtt-and-micro-ros.md))
diff --git a/en/202410/integrating-stomp-with-emqx.md b/en/202410/integrating-stomp-with-emqx.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..710d3b4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/en/202410/integrating-stomp-with-emqx.md
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
+## Introduction to STOMP
+
+STOMP (Simple/Streaming Text-Oriented Messaging Protocol) is designed to provide a simple and transparent way for asynchronous message communication across different languages and platforms.
+
+As a text-based protocol, STOMP facilitates interoperable message exchange between clients and servers. It transmits data using frames, each containing a command, an optional header, and an optional body. STOMP defines standard commands like CONNECT, SEND, SUBSCRIBE, and DISCONNECT, which enable structured interaction between clients and servers.
+
+### **How It Works**
+
+The STOMP operates in an intuitive manner. First, a client establishes a connection with a server by sending a CONNECT frame. Once connected, the client can either send messages to a destination using the SEND frame or subscribe to receive messages from a specific destination using the SUBSCRIBE command. The server delivers messages to subscribed clients via a MESSAGE frame. Either party can close the connection by sending a DISCONNECT frame.
+
+### **Features and Benefits**
+
+Key features and benefits of STOMP include:
+
+- **Simplicity**: Its plain-text design is easy to understand and implement.
+- **Cross-Language**: Being a text-based protocol, it can be implemented in any programming language, promoting compatibility across environments.
+- **Interoperability**: Provides a standardized messaging method that works across different platforms and languages.
+- **Flexibility**: Supports customization and extensions through headers, allowing adaptation to various messaging scenarios.
+
+### **Comparison with Other IoT Protocols**
+
+Compared to other popular IoT protocols like [MQTT](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/the-easiest-guide-to-getting-started-with-mqtt) and [CoAP](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/coap-protocol), STOMP offers advantages in simplicity and flexibility. While MQTT excels in bandwidth-constrained environments due to its lightweight publish/subscribe model, its binary message format lacks the cross-language flexibility of STOMP. CoAP, designed for low-power devices, is ideal for constrained environments, whereas STOMP is more suitable for scenarios requiring greater flexibility and simple text messaging.
+
+In summary, the STOMP protocol, with its intuitive design and cross-language compatibility, is a powerful tool for building flexible and scalable IoT applications. When used appropriately, it can significantly enhance the efficiency and interoperability of messaging systems.
+
+## Accessing STOMP Devices with EMQX
+
+EMQX is a powerful, highly scalable distributed MQTT platform designed for IoT and real-time communication applications. In addition to fully supporting the MQTT protocol, EMQX manages connectivity, authentication, and messaging for various non-MQTT protocols, including STOMP, MQTT-SN, CoAP, and LwM2M, through a unified gateway interface for easier use.
+
+The STOMP gateway in EMQX is based on [STOMP v1.2](https://stomp.github.io/stomp-specification-1.2.html) and is compatible with versions v1.0 and v1.1. In the following steps, we’ll use EMQX’s STOMP gateway to connect to STOMP devices.
+
+### Preparation
+
+#### Installing EMQX 5.8.0
+
+EMQX offers download and installation guides for various platforms: [https://docs.emqx.com/en/emqx/latest/deploy/install-enterprise.html](https://docs.emqx.com/en/emqx/latest/deploy/install-enterprise.html).
+
+For this example, we will launch EMQX Enterprise 5.8.0 using Docker:
+
+```shell
+docker run -p 18083:18083 -p 1883:1883 -p 61613:61613 emqx/emqx-enterprise:5.8.0
+```
+
+#### Configuring the STOMP Gateway
+
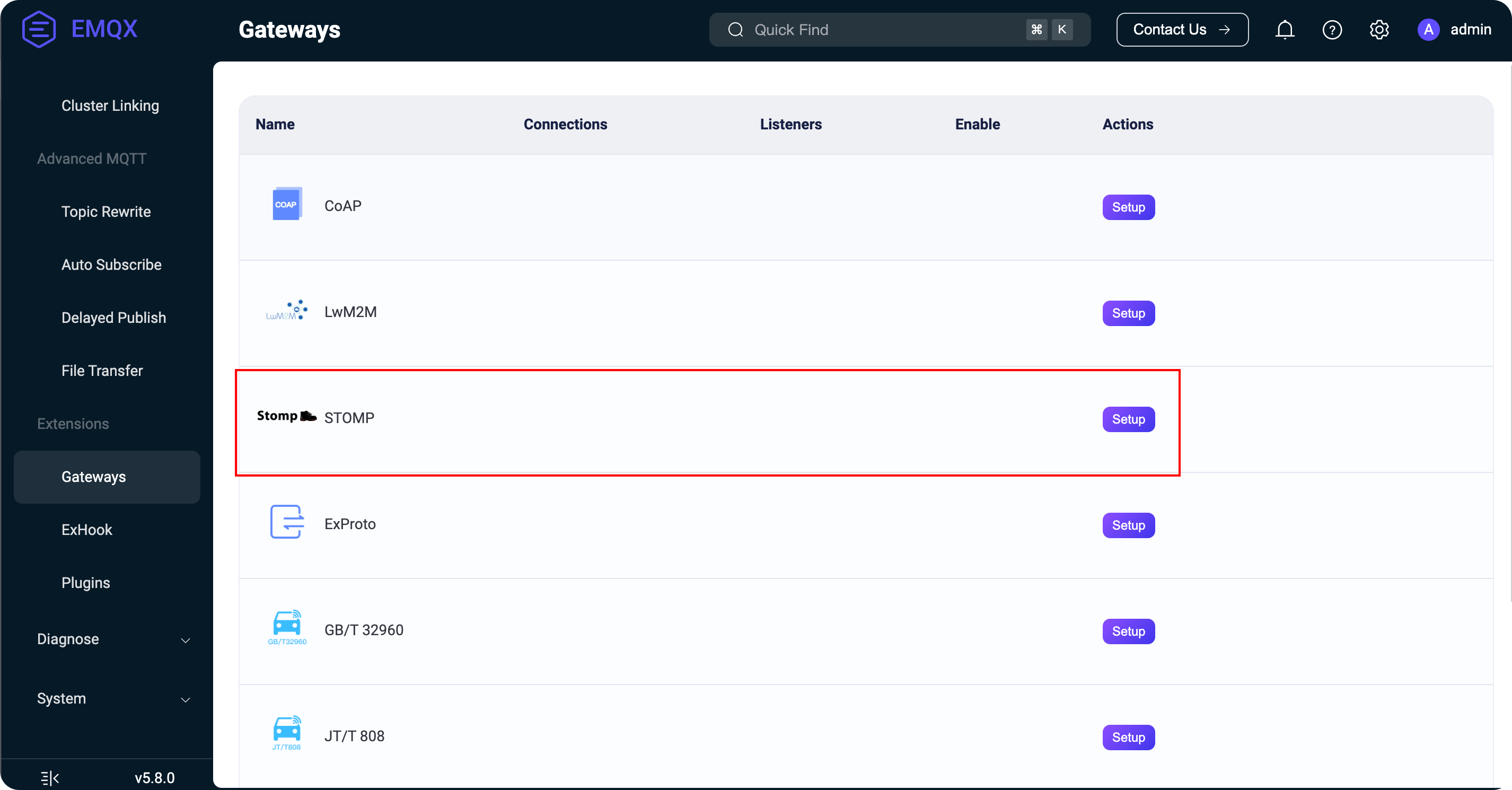
+Open the EMQX Dashboard at `http://127.0.0.1:18083` and log in with the default credentials: admin/public. Navigate to Management → Gateways to view the available gateways in the current version.
+
+
+
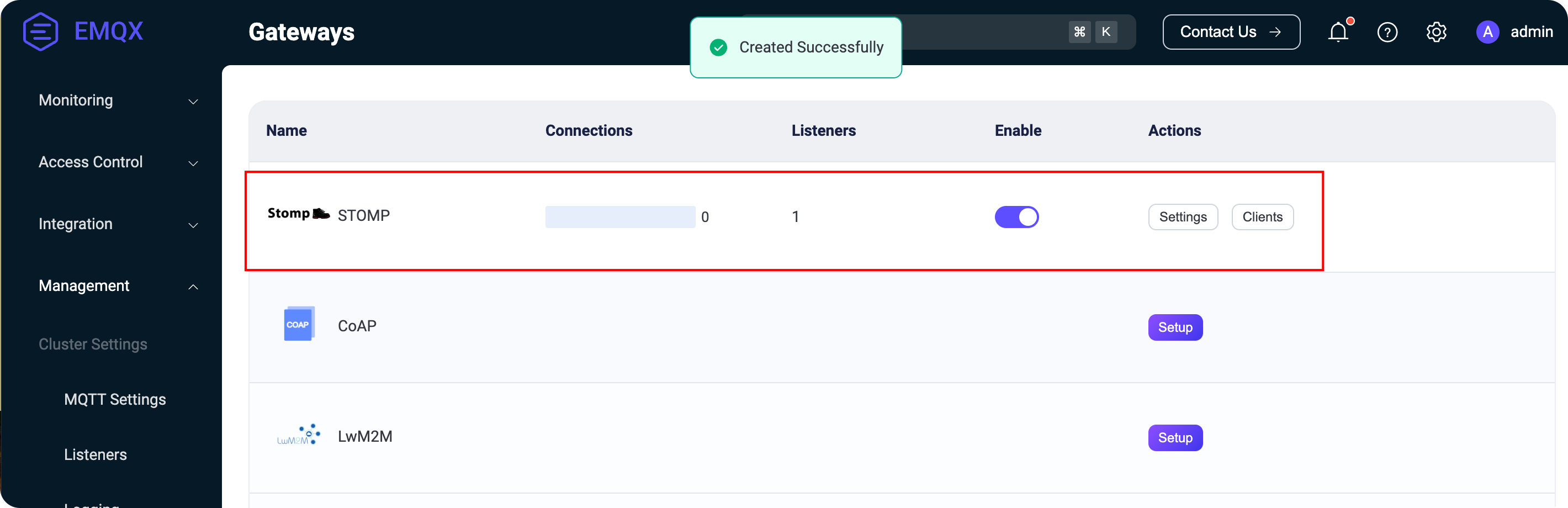
+Click the Configure button for the STOMP gateway to access the configuration page. Use the default settings and click Next several times until the configuration is complete. You will see that the gateway has started successfully.
+
+
+
+### Testing Connection
+
+The STOMP protocol is available in various programming languages. Here, we'll use [STOMPjs](https://www.npmjs.com/package/stompjs) in Node.js as an example to connect to the EMQX STOMP gateway.
+
+First, initialize the project and install STOMPjs:
+
+```shell
+mkdir STOMP-client-test
+cd STOMP-client-test
+
+npm install STOMPjs
+```
+
+Once installed, create a connect.js file:
+
+```javascript
+var STOMP = require('STOMPjs');
+
+var client = STOMP.overTCP('localhost', 61613);
+
+client.connect('username', 'password', function() {
+ console.log('connected to STOMP gateway');
+});
+```
+
+Run the connect.js file and check the output:
+
+```shell
+node connect.js
+```
+
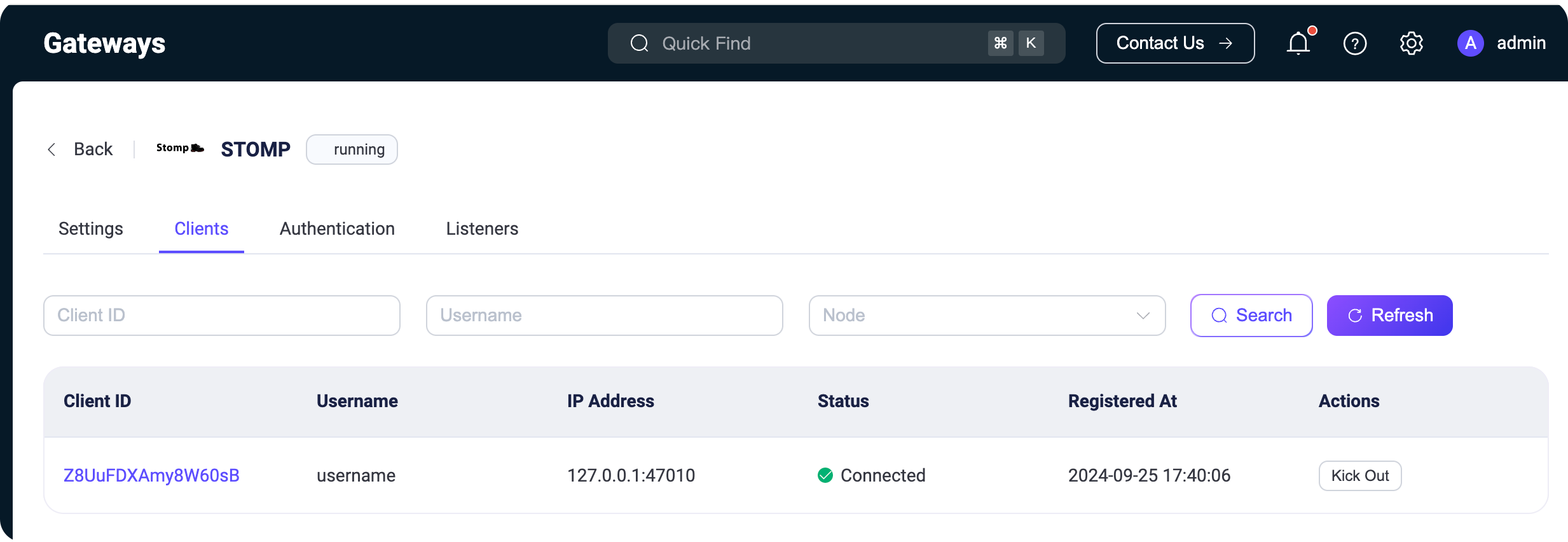
+After a successful connection, open the EMQX Dashboard and navigate to the Client List page of the STOMP gateway to see your client.
+
+
+
+### Testing Message Communication
+
+In the STOMP protocol, clients receive messages on a topic by subscribing to a specific topic, while publishers send messages by specifying the destination parameter, similar to the MQTT messaging model.
+
+To start a STOMP subscriber client, use the following code:
+
+```javascript
+var STOMP = require('STOMPjs');
+
+var client = STOMP.overTCP('localhost', 61613);
+
+client.connect('username', 'password', function() {
+ console.log('connected to STOMP gateway');
+ console.log('subscribing to /queue/test');
+ client.subscribe('/queue/test', function(message) {
+ console.log('received message: ' + message.body);
+ });
+});
+```
+
+Then, use MQTTX to publish a message to the topic /queue/test:
+
+```shell
+mqttx pub -t /queue/test -m 'Hi, STOMP Client'
+```
+
+You should see that the STOMP client successfully connects to EMQX and prints the received message:
+
+```shell
+connected to STOMP gateway
+subscribing to /queue/test
+received message: Hi, STOMP Client
+```
+
+Now, the STOMP client is successfully connected to EMQX and can send and receive messages with the MQTT client. You can also manage all STOMP clients through the EMQX Dashboard.
+
+## Advanced STOMP Gateway Applications
+
+### Enabling TLS Listening
+
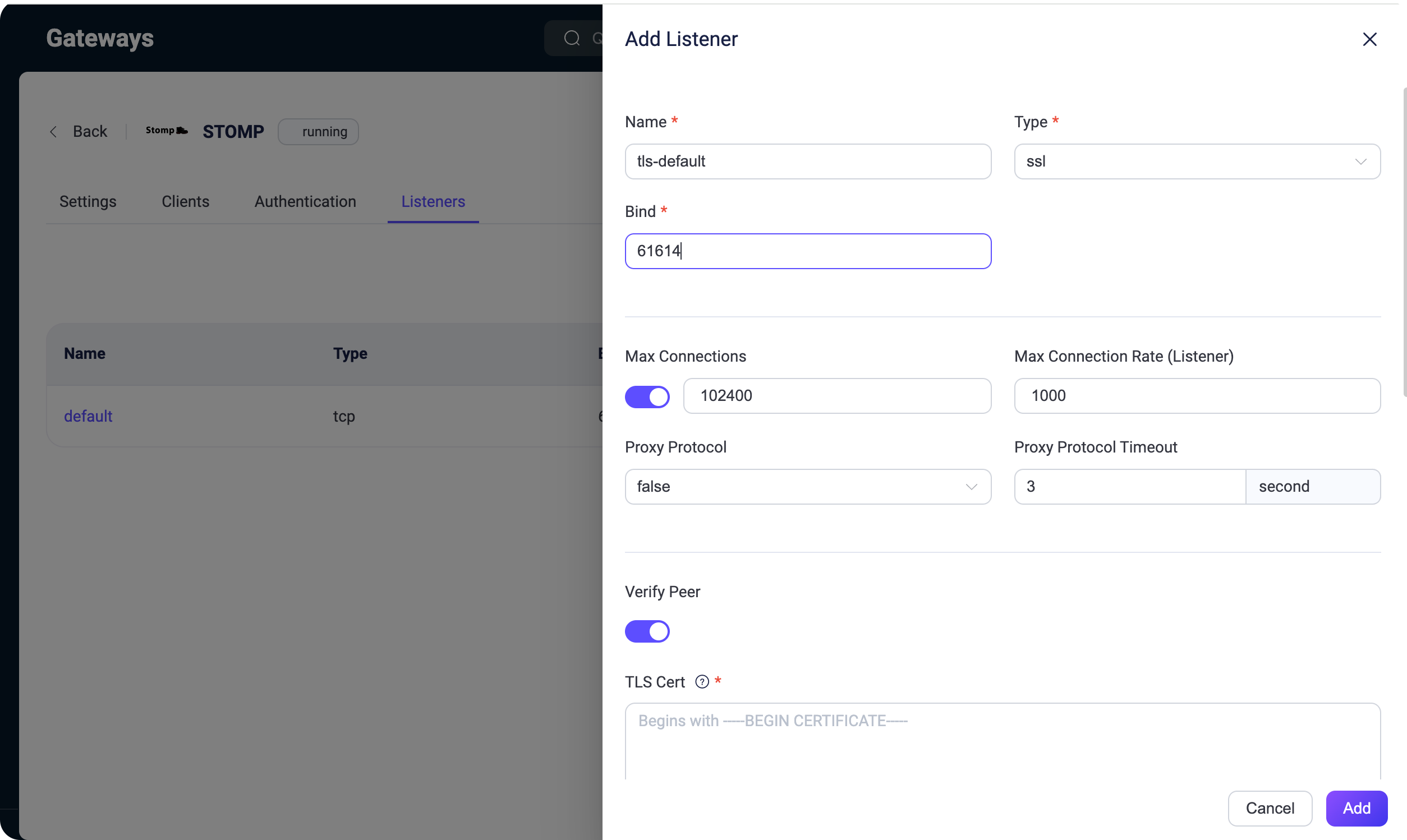
+The EMQX 5.0 STOMP gateway supports SSL connections. To enable this, open the EMQX Dashboard, navigate to Management → Gateways, select the Settings for the STOMP gateway, go to the Listener sub-page, and click Add.
+
+
+
+### Access Authentication
+
+The STOMP gateway also supports username and password authentication to verify client credentials during the connection process.
+
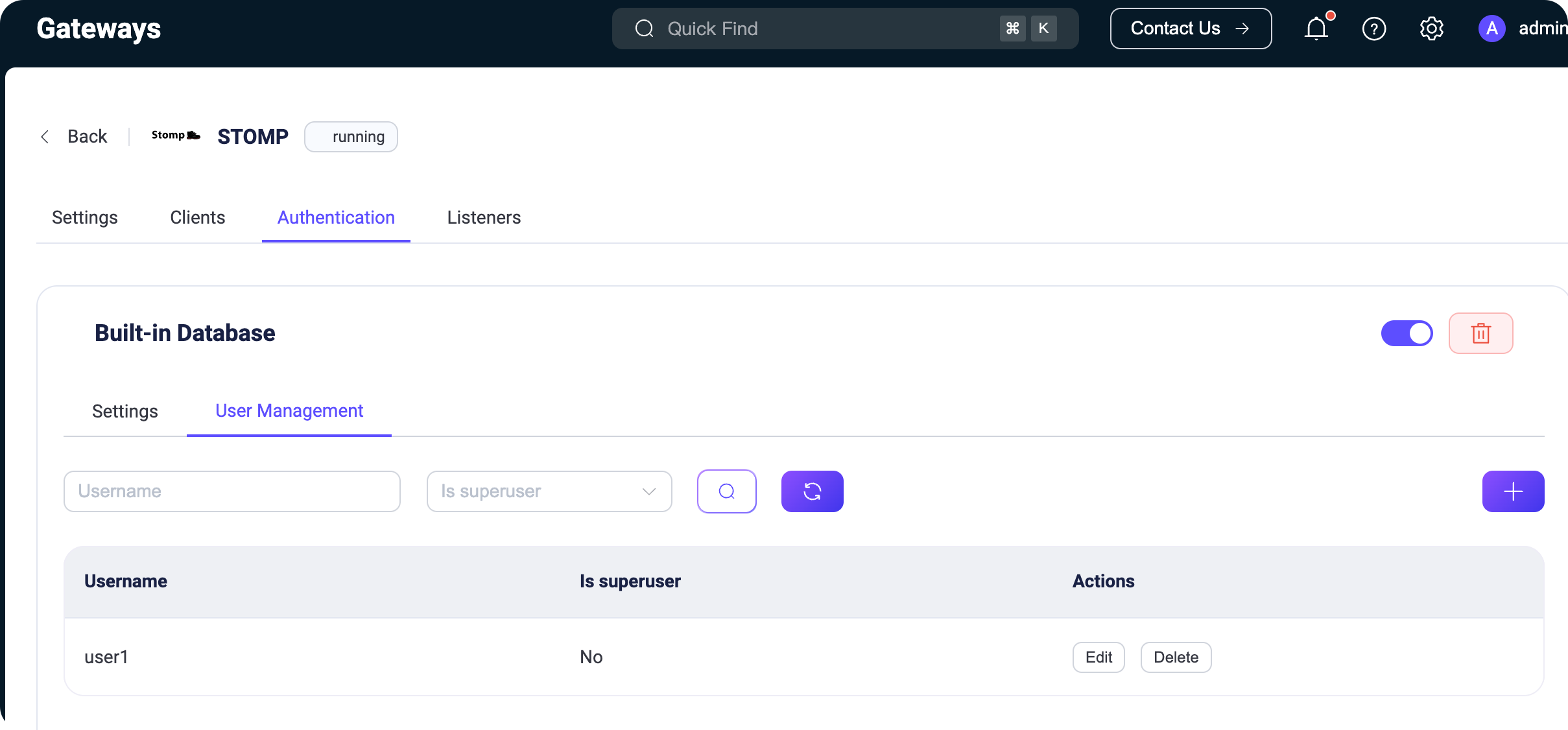
+To set this up, open the EMQX Dashboard, go to Management → Gateways, select the Settings for the STOMP gateway, then navigate to the Access Authentication sub-page and click Add to create built-in authentication based on username and password.
+
+
+
+## Conclusion
+
+This blog outlines the STOMP protocol and demonstrates how to establish STOMP connections through the EMQX Platform's STOMP gateway, enabling message forwarding and interoperability with MQTT messages.
+
+By integrating EMQX with STOMP, users can achieve efficient, unified, and multi-protocol client management and message processing in the same platform, simplifying system complexity.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/ja/202410/mqtt5-new-feature-clean-start-and-session-expiry-interval.md b/ja/202410/mqtt5-new-feature-clean-start-and-session-expiry-interval.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..fdc1f3b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ja/202410/mqtt5-new-feature-clean-start-and-session-expiry-interval.md
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+この記事では、[MQTTプロトコル](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/the-easiest-guide-to-getting-started-with-mqtt)のセッションメカニズムと、セッションライフサイクルを管理するために使用される2つの接続パラメータである**クリーンスタート**と**セッション有効期限間隔**について紹介します。
+
+> MQTT 5.0を初めてご利用ですか?ぜひご覧ください
+>
+> [MQTT 5.0:7つの新機能と移行チェックリスト](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/introduction-to-mqtt-5)
+
+## なぜMQTTはセッションメカニズムをサポートしているのか?
+
+IoTシナリオでは、ネットワークや電源の問題によりデバイスが頻繁に切断されることがあります。クライアントとサーバーが常に新しいコンテキストで接続を確立する場合、以下の問題が発生します:
+
+1. クライアントは再接続後にすべての関連トピックに再サブスクライブする必要があり、サーバーに追加のオーバーヘッドをもたらします。
+2. クライアントはオフライン期間中のメッセージを見逃します。
+3. QoS 1およびQoS 2のサービス品質が保証されません。
+
+これらの問題を回避するために、MQTTプロトコルはセッションメカニズムを設計しました。これがMQTT通信の基盤を形成しています。
+
+## MQTTセッションとは?
+
+[MQTTセッション](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/mqtt-session)は、本質的にはサーバーとクライアントによって追加のストレージが必要なコンテキストデータのセットです。一部のセッションはネットワーク接続が確立されている間のみ持続し、他のセッションは複数の連続するネットワーク接続にわたって存在することができます。クライアントとサーバーがこのセッションデータの助けを借りて通信を再開すると、ネットワークの中断はまるで発生しなかったかのようになります。
+
+サーバーを例に取ると、クライアントのサブスクリプションリストを保存する必要があります。クライアントが現在接続されているかどうかに関係なく、セッションが有効期限切れでない限り、サーバーはクライアントがサブスクライブしているメッセージを把握し、それらのメッセージをキャッシュすることができます。さらに、クライアントは再接続時にサブスクリプションを再初期化する必要がなくなり、サーバーのパフォーマンスオーバーヘッドも削減されます。
+
+MQTTは、サーバーレベルとクライアントレベルで保存する必要があるセッション状態を定義しています。
+
+**サーバーの場合、以下を保存する必要があります:**
+
+1. セッションの存在。
+2. クライアントのサブスクリプション。
+3. クライアントに送信されたが完全に確認されていないQoS 1およびQoS 2メッセージ。
+4. クライアントに送信が保留されているQoS 1およびQoS 2メッセージ、およびオプションでQoS 0メッセージ。
+5. クライアントから受信したが完全に確認されていないQoS 2メッセージ。
+6. [ウィルメッセージ](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/use-of-mqtt-will-message)とウィルディレイ間隔。
+7. セッションが現在接続されていない場合、セッションが終了しセッション状態が破棄される時刻。
+
+**クライアントの場合、以下を保存する必要があります:**
+
+1. サーバーに送信されたが完全に確認されていないQoS 1およびQoS 2メッセージ。
+2. サーバーから受信したが完全に確認されていないQoS 2メッセージ。
+
+これらのセッションデータをサーバーとクライアントに恒久的に保存させることは、多くの追加ストレージコストをもたらすだけでなく、多くのシナリオでは不要です。例えば、ネットワーク接続の一時的な中断によるメッセージの損失を避けたい場合、接続が切断された後にセッションデータを数分間保持するように設定するのが一般的です。
+
+さらに、クライアントとサーバーのセッション状態が一致しない場合、例えばクライアントデバイスが再起動によりセッションデータを失った場合、接続時にサーバーに元のセッションを破棄し新しいセッションを作成するように通知する必要があります。
+
+これらの2点に対して、[MQTT 5.0](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/introduction-to-mqtt-5)では、**クリーンスタート**と**セッション有効期限間隔**という2つの接続フィールドを提供し、セッションのライフサイクルを制御します。
+
+## クリーンスタートの紹介
+
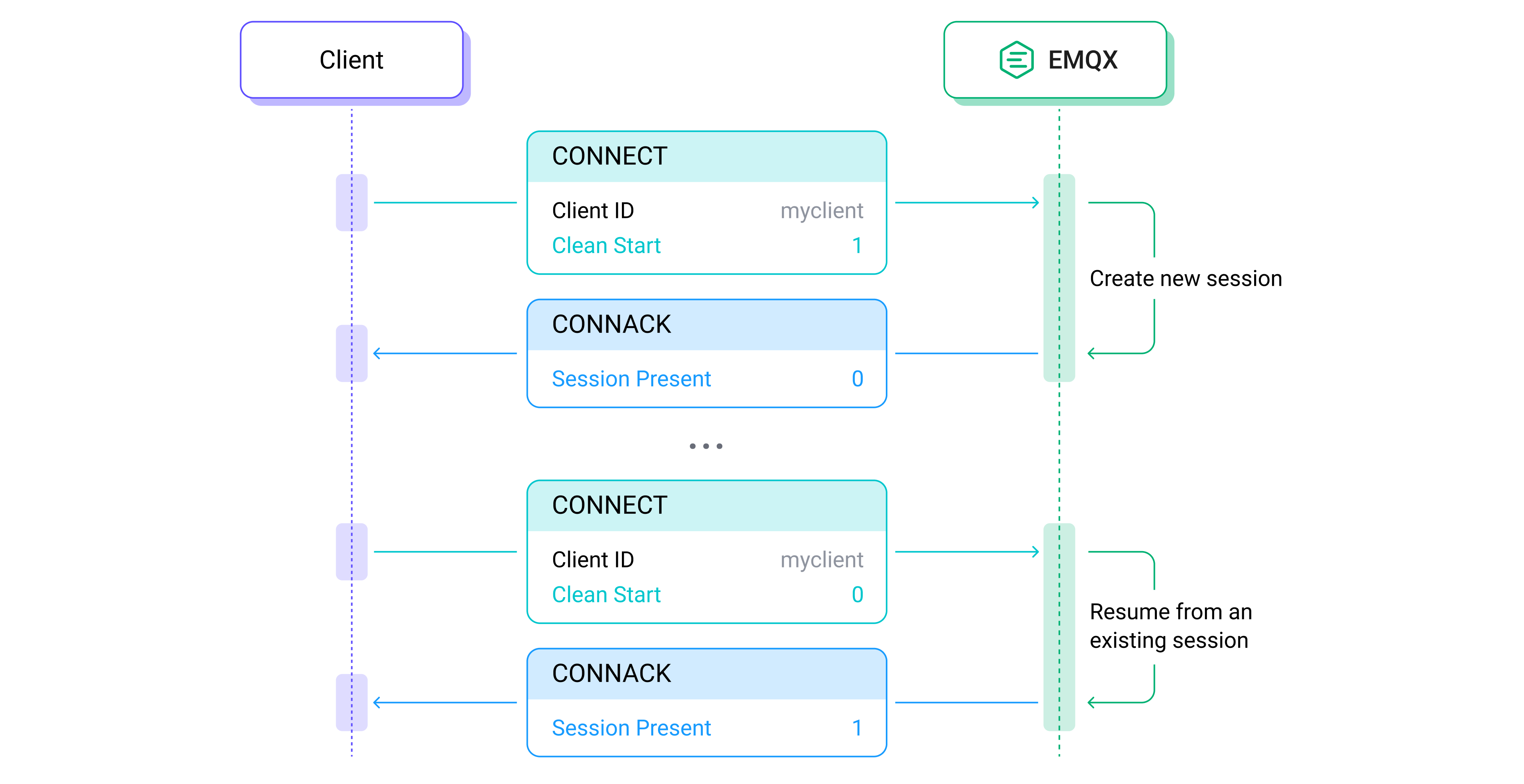
+**クリーンスタート**は、CONNECTパケットの[バリアブルヘッダー](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/introduction-to-mqtt-control-packets)に位置しています。クライアントは、接続時にこのフィールドを通じて既存のセッションを再利用するかどうかを指定します。値は0と1の2つだけです。
+
+**クリーンスタートが0に設定されている場合**、サーバーにクライアントが接続されているときに指定されたクライアントIDに関連付けられたセッションが存在する場合、サーバーはこのセッションを使用して通信を再開しなければなりません。
+
+クライアントIDに関連付けられたセッションが存在しない場合、サーバーは完全に新しいセッションを作成しなければなりません。この場合、クライアントは古いセッションを使用しており、サーバーは全く新しいセッションを使用しています。両者のセッション状態が不一致となります。したがって、サーバーはCONNACKパケットでSession Presentフラグを0に設定し、クライアントに期待していたセッションが存在しないことを知らせる必要があります。クライアントがこのネットワーク接続を続行したい場合、保存されているセッション状態を破棄しなければなりません。
+
+**クリーンスタートが1に設定されている場合**、クライアントとサーバーは既存のセッションをすべて破棄し、新しいセッションを開始しなければなりません。対応して、サーバーはCONNACKパケットでSession Presentフラグを0に設定します。
+
+
+
+## セッション有効期限間隔の紹介
+
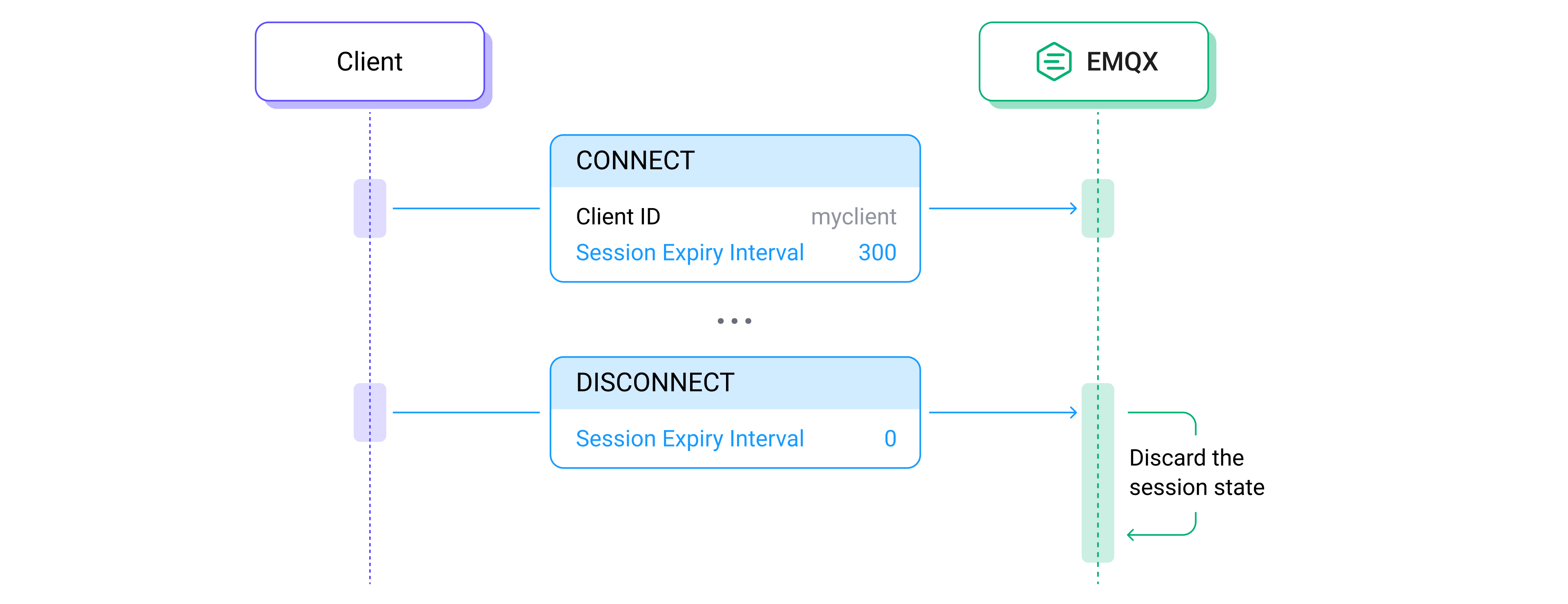
+**セッション有効期限間隔**もCONNECTパケットのバリアブルヘッダーに位置していますが、これはオプションの[プロパティ](https://www.emqx.com/en/blog/introduction-to-mqtt-control-packets)です。これは、ネットワークが切断された後、サーバー上でセッションが保持される最大時間を指定するために使用されます。期限が切れると、ネットワーク接続が回復していなくても、サーバーは対応するセッション状態を破棄します。典型的な値は以下の3つです:
+
+1. **このプロパティが指定されていないか0に設定されている場合**、ネットワーク接続が失われるとセッションは直ちに終了します。
+2. **0より大きい値に設定**されている場合、セッションが期限切れになる前にネットワーク接続が切断された後にセッションが持続できる秒数を示します。
+3. **0xFFFFFFFFに設定**されている場合、これは**セッション有効期限間隔**プロパティに設定できる最大値であり、セッションが決して期限切れにならないことを意味します。
+
+各[MQTTクライアント](https://www.emqx.com/ja/blog/mqtt-client-tools)は、独立して自身の**セッション有効期限間隔**を設定できます。実際のニーズに応じて、期限時間を柔軟に設定できます。例えば、永続的なセッションが不要なクライアントもあれば、ネットワークの変動の影響を避けるためにセッションを数分間保持するだけで十分なクライアント、さらにセッションを長期間保持する必要があるクライアントもあります。
+
+MQTTは、クライアントが切断時に**セッション有効期限間隔**を更新することも許可しています。これは主にDISCONNECTパケットの同名プロパティに依存します。一般的なアプリケーションシナリオとして、クライアントがオンライン時に**セッション有効期限間隔**を0より大きい値に設定し、ネットワークの中断が通常のビジネスに影響を与えないようにします。そして、クライアントがすべてのビジネスを完了し積極的にログオフすると、**セッション有効期限間隔**を0に更新し、サーバーがセッションをタイムリーに解放できるようにします。
+
+
+
+## セッションとクライアントID
+
+サーバーはクライアントIDを使用して各セッションを一意に識別します。クライアントが接続時に以前のセッションを再利用したい場合、以前と同じクライアントIDを使用しなければなりません。したがって、サーバーでクライアントIDを自動割り当てる機能を使用する場合、クライアントはCONNACKパケットで返される割り当てられたクライアント識別子を次回使用のために保存する必要があります。
+
+なお、MQTT 5.0以前のプロトコルバージョンでは、サーバーが自動的に割り当てたクライアントIDを返すことをサポートしていないため、サーバーによってクライアントIDが自動的に割り当てられるか、永続的なセッションを使用するかの選択をする必要があります。
+
+## MQTT 3.1.1におけるクリーンセッション
+
+MQTT 3.1.1のセッションメカニズムは、5.0に比べてはるかに柔軟性が低いです。3.1.1には**クリーンセッション**フィールドが1つしかなく、その値も0と1の2つだけです。
+
+MQTT 3.1.1で**クリーンセッション**を0に設定することは、MQTT 5.0で**クリーンスタート**を0に設定し、**セッション有効期限間隔**を0xFFFFFFFF(セッションが決して期限切れにならない)に設定することと同等です。
+
+MQTT 3.1.1で**クリーンセッション**を1に設定することは、MQTT 5.0で**クリーンスタート**を1に設定し、**セッション有効期限間隔**を0(セッションのライフサイクルがネットワーク接続と一致する)に設定することと同等です。
+
+
+
+ご覧の通り、MQTT 3.1.1ではセッションのライフサイクルに対して「期限切れなし」または「ネットワーク接続と一致」の2つのオプションしかありません。
+
+しかし、すべてのクライアントのセッションを恒久的に保存することは、間違いなくサーバーのリソースを無駄にします。これはMQTT 3.1.1のプロトコル設計における見落としのようです。したがって、EMQXは`mqtt.session_expiry_interval`設定項目を提供し、MQTT 3.1.1クライアントのグローバルなセッション有効期限間隔を設定できるようにし、サーバーのリソース消費を許容範囲内に制御できるようにしています。
+
+さらに、新しいセッションを作成するかどうかもセッションのライフサイクルに強制的に結びつけられます。MQTT 3.1.1では、新しい永続的なセッションをサーバーに作成させるために、**クリーンセッション**を1と0にそれぞれ指定して接続する必要があります。
+
+したがって、MQTT 3.1.1に比べて、MQTT 5.0はセッションにおいて大幅な改善を遂げています。
+
+## MQTT永続セッションの実践的な提案
+
+MQTTでは、ライフサイクルがネットワーク接続よりも長いセッションを通常、永続セッションと呼びます。しかし、永続セッションを使用する際にはいくつか注意すべき点があります。
+
+例えば、永続セッションがサーバーリソースに与える影響を正しく評価する必要があります。セッションの有効期限が長くなるほど、サーバーが必要とするストレージリソースが増える可能性があります。サーバーは通常、クライアントのメッセージを無制限にキャッシュしないため、[EMQX](https://github.com/emqx/emqx)を例に取ると、各クライアントセッションにキャッシュできるメッセージの最大数はデフォルトで1000ですが、クライアント数を考慮すると、これは客観的なストレージコストとなる可能性があります。サーバーのリソースが限られている場合、セッションの有効期限時間とセッションキャッシュの最大数の設定にもっと注意を払う必要があります。
+
+さらに、クライアントが長時間オフラインになった後に到着するメッセージを処理し続ける必要があるかどうかも評価する必要があります。もちろん、可能な限り多くのメッセージを保存するために大きなキャッシュを設定するか、最近到着したメッセージのみを処理できるように小さなキャッシュを設定するかは、実際のシナリオに依存します。
+
+## デモ
+
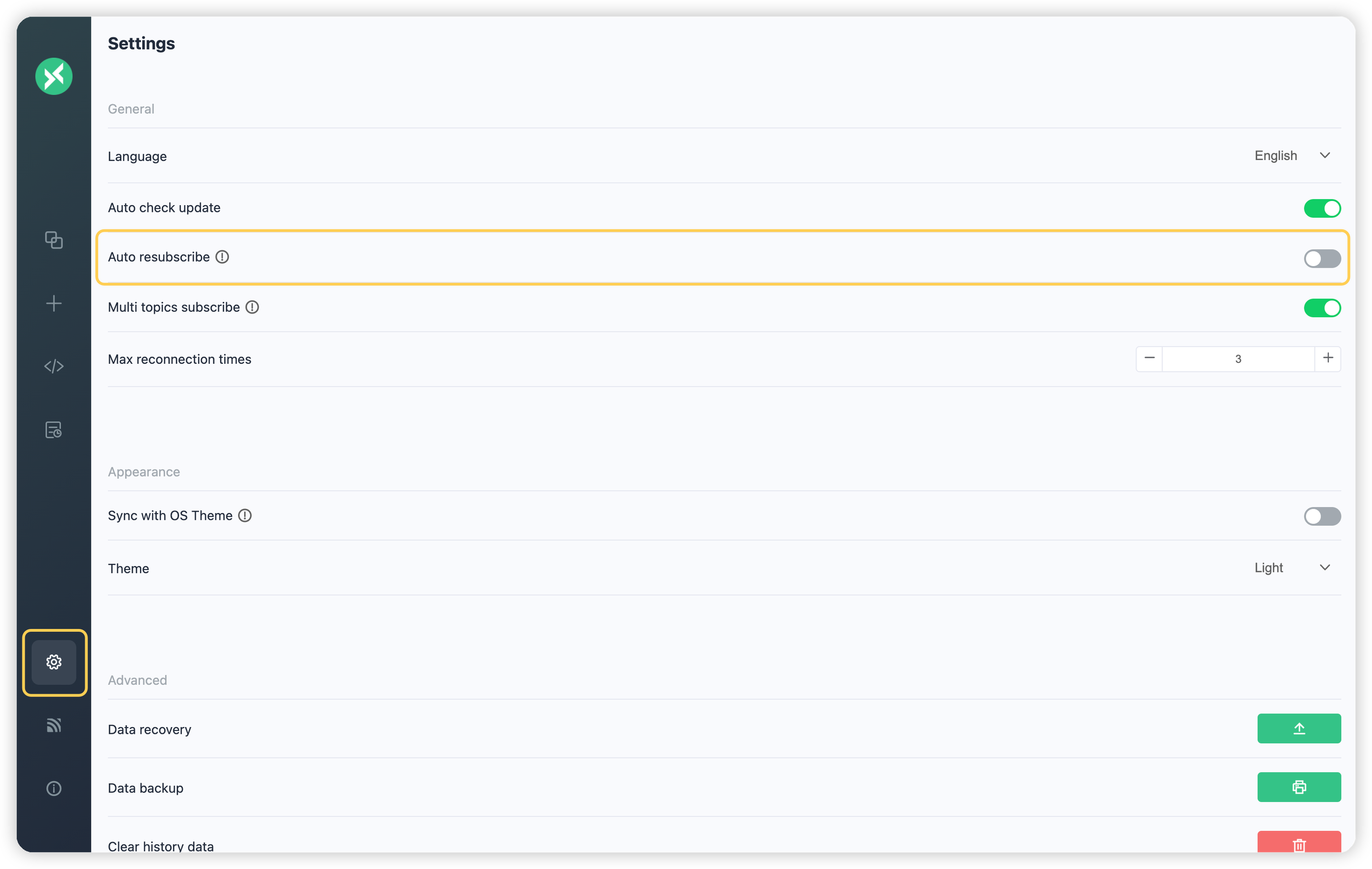
+1. [MQTTX](https://mqttx.app/ja)をインストールして開きます。MQTTのセッションメカニズムをよりよく示すために、まずMQTTXの設定ページに移動し、`Auto resubscribe`機能をオフにします:
+
+ 
+
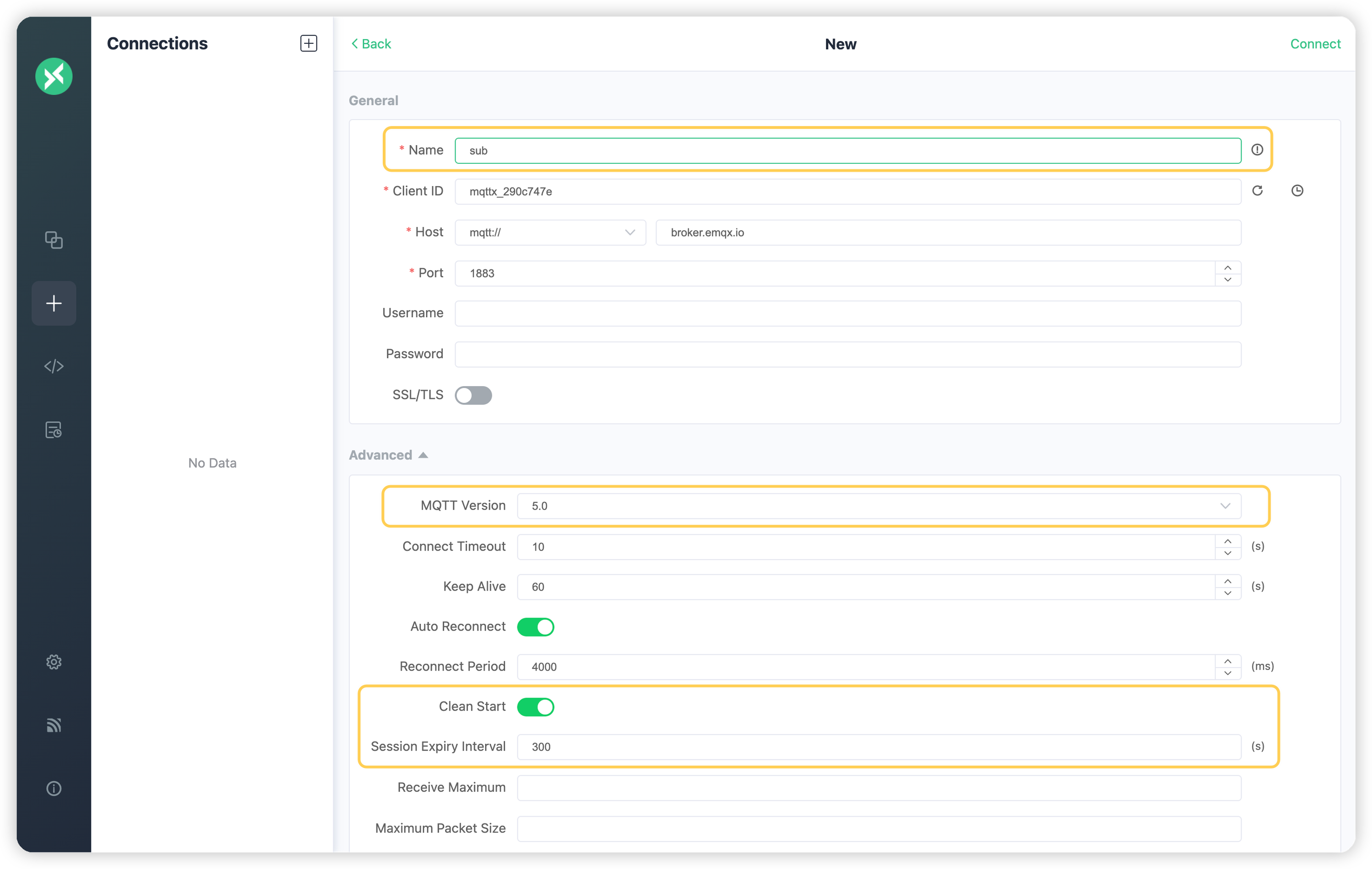
+2. `sub`という名前のクライアント接続を作成し、MQTTバージョンを5.0に設定、**クリーンスタート**を有効にし、**セッション有効期限間隔**を300秒に設定します。その後、[無料のパブリックMQTTサーバー](https://www.emqx.com/en/mqtt/public-mqtt5-broker)に接続し、トピック`mqttx_290c747e/test`にサブスクライブします:
+
+ 
+
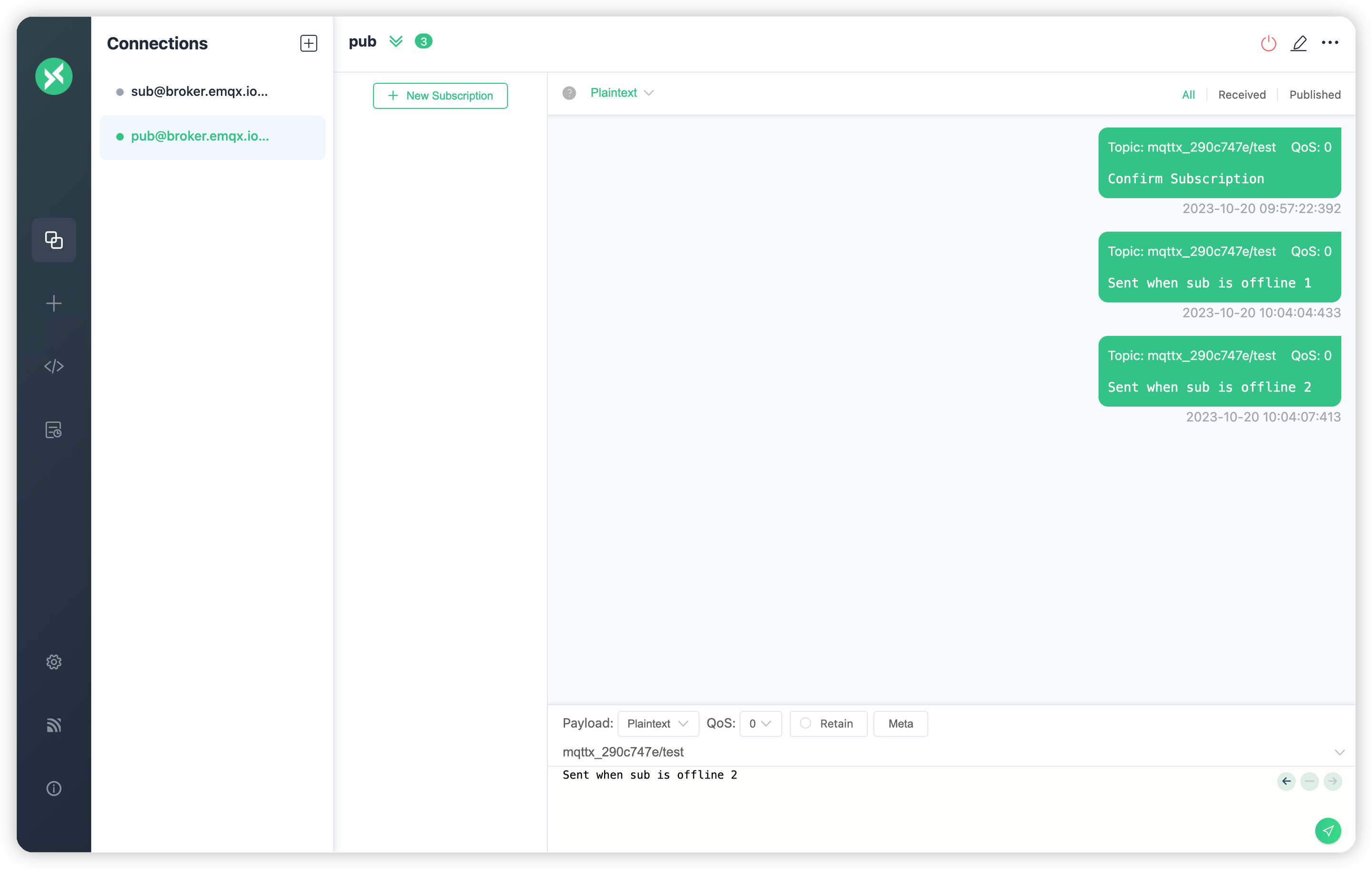
+3. `pub`という名前のクライアント接続を作成し、トピック`mqttx_290c747e/test`にメッセージを発行します。メッセージ内容は任意に設定できます。クライアント`sub`がこれらのメッセージを受信するのを確認します。その後、クライアント`sub`を切断し、クライアント`pub`を通じてメッセージの発行を続けます:
+
+ 
+
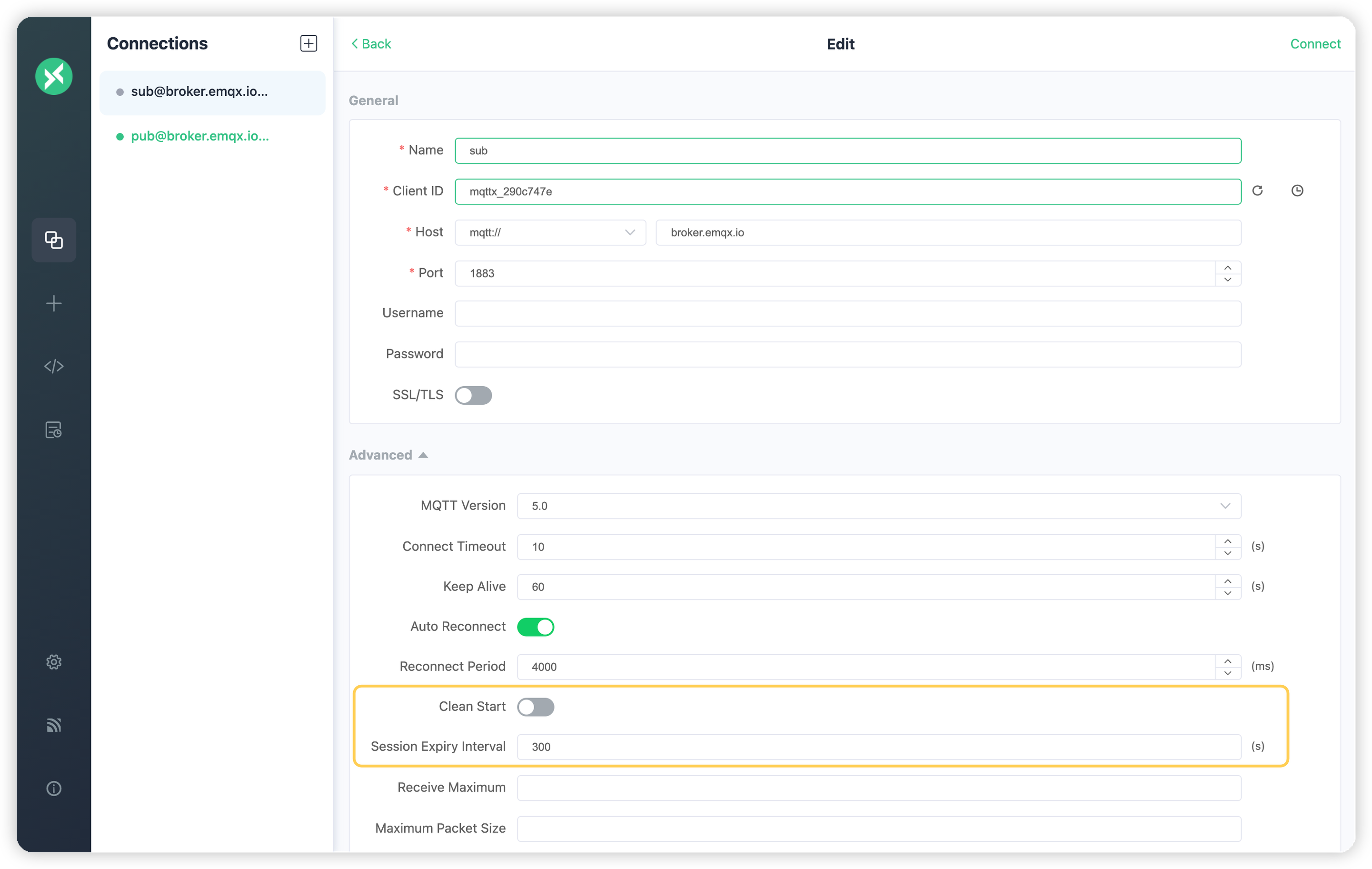
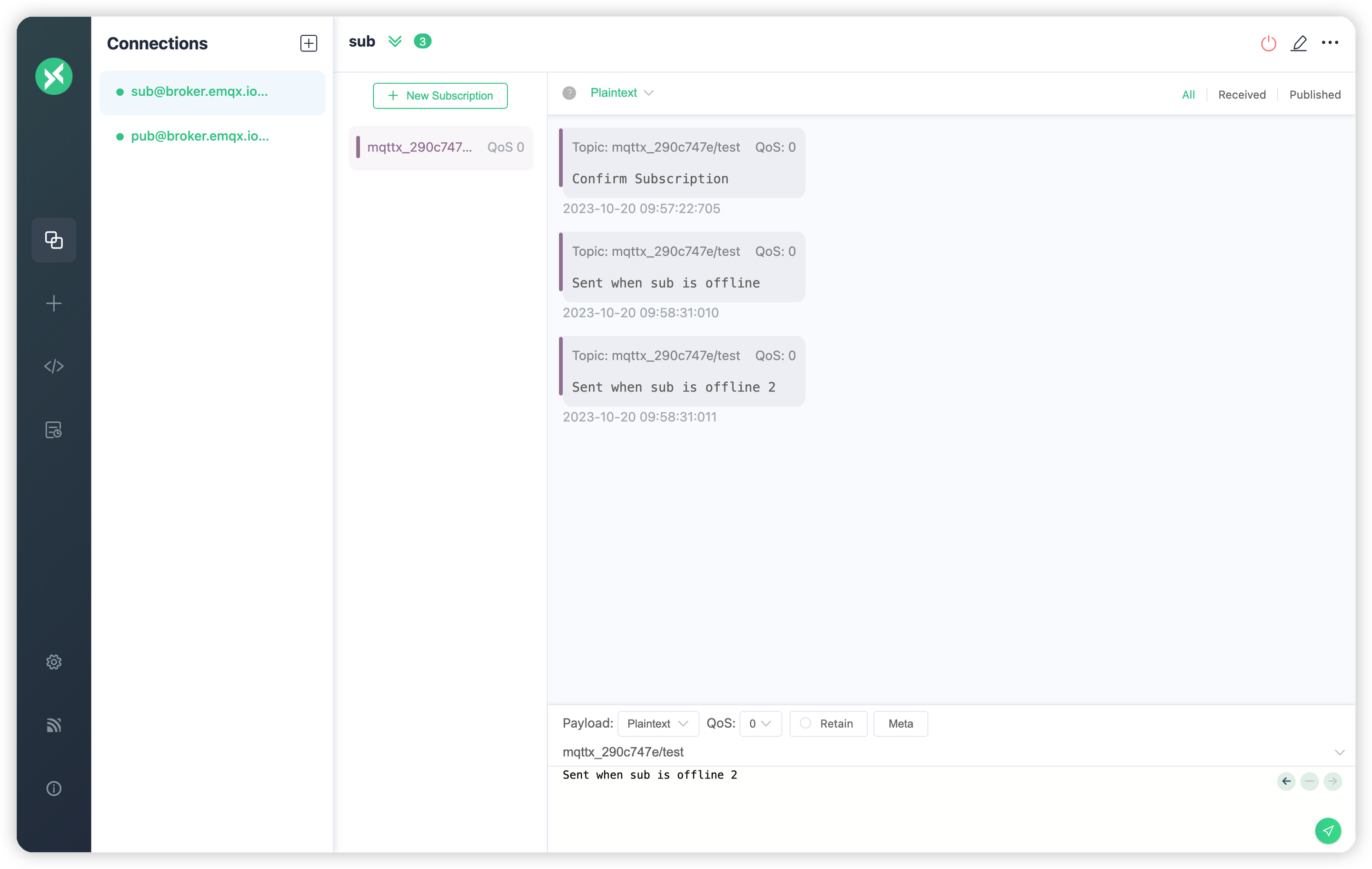
+4. 次に、クライアント`sub`の**クリーンスタート**オプションを無効にし、**セッション有効期限間隔**を300秒のままにして再接続します。クライアント`sub`がオフライン期間中に発行されたメッセージを受信するのを確認します:
+
+ 
+
+ 
+
+上記は、MQTTセッションがオフラインのクライアントのためにメッセージをキャッシュする能力です。ターミナルインターフェースでは、コマンドラインツールの[MQQTX CLI](https://mqttx.app/cli)を使用して上記の操作を完了することもできます。まず、以下のコマンドを使用してトピックにサブスクライブします。サブスクリプションが成功した後、ターミナルで`Ctrl+C`を入力してクライアントを切断します:
+
+```shell
+mqttx sub -h 'broker.emqx.io' --mqtt-version 5 --client-id mqttx_290c747e \
+--session-expiry-interval 300 --topic mqttx_290c747e/test
+… Connecting...
+✔ Connected
+… Subscribing to mqttx_290c747e/test...
+✔ Subscribed to mqttx_290c747e/test
+^C
+```
+
+次に、以下のコマンドを使用してトピック`mqttx_290c747e/test`にメッセージを発行します:
+
+```shell
+mqttx pub -h 'broker.emqx.io' --topic mqttx_290c747e/test --message "hello world"
+```
+
+発行が成功した後、サブスクライバーへの接続を復元します。以下のコマンドでは、以前と同じクライアントIDを維持し、`--no-clean`オプションを設定しています。これにより、サブスクライバーが接続前に発行されたメッセージを即座に受信するのが確認できます:
+
+```shell
+mqttx sub -h 'broker.emqx.io' --mqtt-version 5 --client-id mqttx_290c747e \
+--no-clean --session-expiry-interval 300 --topic mqttx_290c747e/test
+… Connecting...
+✔ Connected
+… Subscribing to mqttx_290c747e/test...
+payload: hello world
+
+✔ Subscribed to mqttx_290c747e/test
+```
+
+[MQTTX](https://mqttx.app/ja)や[MQTTX CLI](https://mqttx.app/ja/cli)などのMQTTクライアントツールは、主に誰もが迅速にMQTTを始められるようにすることを目的としているため、サーバーから返されるSession Presentの表示や、切断時に**セッション有効期限間隔**を更新するなどの不要な機能は提供していません。したがって、この部分に興味がある場合は、対応するPythonのサンプルコードを[こちら](https://github.com/emqx/MQTT-Feature-Examples)で入手し、詳細を学ぶことができます。
+
+
+
+