Spring Boot provides different mechanisms to run a specific code at Application Startup.
Eine Möglichkeit ist der CommandLineRunner:
CommandLineRunner can be used to run code at application startup, provided it should be contained within SpringApplication.
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Application.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner demo(CustomerRepository repository) {
return (args) -> {
// save a couple of customers
};
}
}wobei (args) -> hier die args von main(args) sind
@Configuration kann man jeder Klasse geben, damit es von SpringBoot beim Startup gescannt wird.
Da @Configuration auch @Component einschließt , kann letzteres auch funktionieren, insb. wenn dessen Methoden auch noch mit @Bean markiert sind, muss aber nicht.
- enable color console, disable banner:
spring.main.banner-mode=off
spring.output.ansi.enabled=ALWAYS #or DETECT,NEVER
logging.config=/Users/<mylocation>/src/main/resources/mylogbackconfig.xml
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
spring.websecurity.debug=true # nur mit **WebSecurityCustomizer** in`@Configuration`@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ProjectConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Value("${spring.websecurity.debug:false}")
boolean webSecurityDebug;
@Bean
public WebSecurityCustomizer webSecurityCustomizer() {
return (web) -> web.debug(webSecurityDebug);
}
}add to application properities:
server.error.include-message=always
server.error.include-binding-errors=always
server.error.include-stacktrace=ON_PARAM # or always or never
server.error.include-exception=true- nur wenn man
logback-spring.xmlverwendet, klappt nicht mitlogback.xml! scanklappt nur von src-dir aus wenn man in application.properties:logging.config=/Users/me/myproj/src/main/resources/logback-spring.xmlsetzt.
<configuration debug="true" scan="true" scanPeriod="3 seconds">
<include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/defaults.xml"/>
<include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/console-appender.xml" />
<include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/file-appender.xml" />
<springProfile name="staging">
<!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active -->
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="dev | staging">
<!-- configuration to be enabled when the "dev" or "staging" profiles are active -->
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="!production">
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" />
</root>
<logger name="org.springframework.web" level="DEBUG"/>
</springProfile>
</configuration>- http://localhost:9090/h2-console/
- user/password: add to
src/main/resources/application.properties - add
security.headers.frame-options=disabletosrc/main/resources/application.properties;- because : This is because the H2 Database console is typically accessed within an iframe, and by default, the X-Frame-Options header is set to DENY or SAMEORIGIN, which prevents the console from being loaded within a frame.
The logback-access module, part of the standard logback distribution, integrates with Servlet containers such as Jetty or Tomcat to provide rich and powerful HTTP-access log functionality. more on logback-access
- in Intellij, to force spring debug logging use :

- or (even without Intellij), add
logging.level.root=DEBUGtosrc/test/resources/application.propertiesorsrc/main/resources/application.properties - open "View->Tools Windows->Service->Edit Configuration" in Intellij und setze "Enable debug output" (sets the -Ddebug switch)
- now spring shows during its startup what Beans/AutoConfiguration are configured
add to src/test/resources/application.properties or src/main/resources/application.properties
logging.level.org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping=trace
logging.level.org.springframework.test.web.servlet.TestDispatcherServlet=traceOR put it in logback-spring.xml:
<logger
name="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"
level="TRACE"/>
<logger name="org.springframework.test.web.servlet.TestDispatcherServlet" level="TRACE"/>
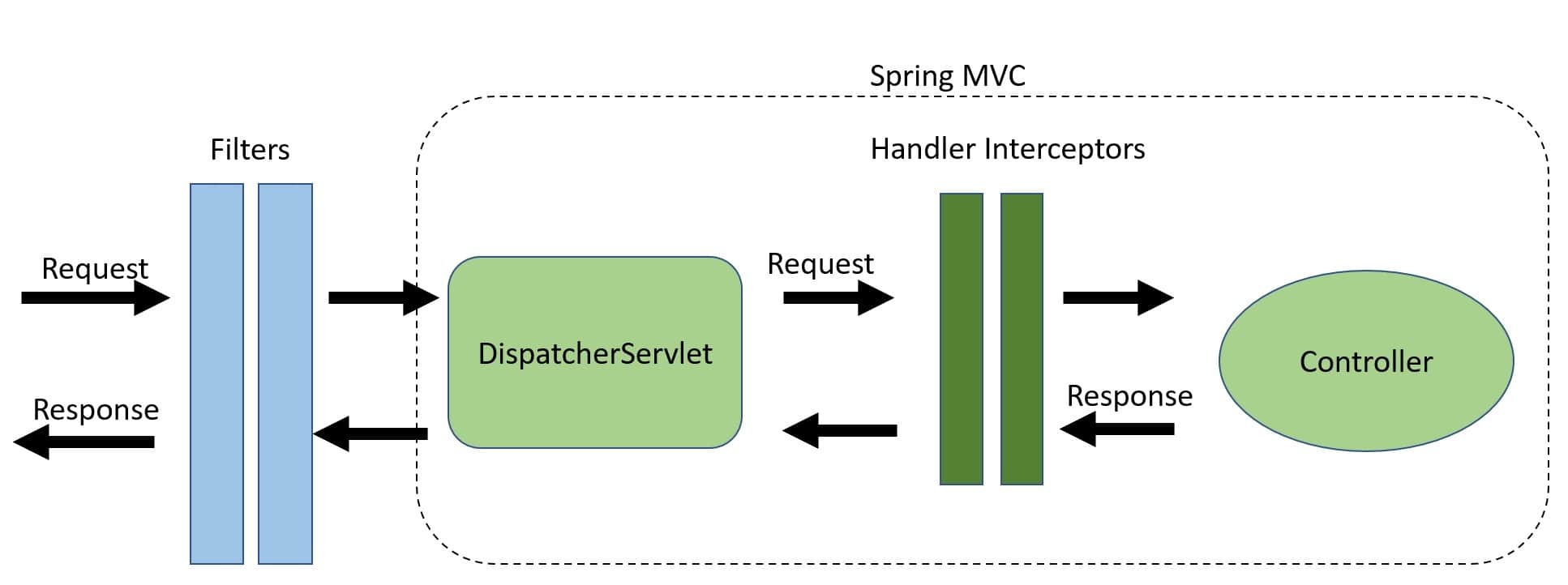
Filter vs Interceptors:
- Filter are part of Java Servlet Spec , Interceptors are not
- Interceptor are more powerful, have access to more details
- Interceptor can log the response IF it overwrites the
afterCompletion()method - however Interceptors does not log errors if a Filter in the securityFilterChain does deny a request, HandlerInterceptor's afterCompletion method is only called after successful completion of a request, not when an exception has been thrown.
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-mvc-handlerinterceptor-vs-filter
- org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor interface. This gives us the option to override three methods:
- preHandle() – Executed before the target handler is called
- postHandle() – Executed after the target handler but before the DispatcherServlet renders the view
- afterCompletion() – Callback after completion of request processing and view rendering*
@Component
public class LoggingInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("-------------- Request Data --------------");
System.out.println("Method: " + request.getMethod());
System.out.println("URL: " + request.getRequestURL().toString());
System.out.println("Headers: ");
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = headerNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(headerName + " = " + request.getHeader(headerName));
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("-------------- Response Data --------------");
System.out.println("Status: " + response.getStatus());
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
response.getHeaderNames().forEach(name -> headers.add(name, response.getHeader(name)));
System.out.println("Headers: " + headers);
}
}
//------
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ProjectConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final LoggingInterceptor loggingInterceptor;
@Autowired
public ProjectConfig(LoggingInterceptor loggingInterceptor) {
this.loggingInterceptor = loggingInterceptor;
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor);
}
}add this to the @Configuration:
@Bean
public HttpExchangeRepository httpExchangeRepository() {
// return new InMemoryHttpExchangeRepository(); //can be used for /actuator/httpexchanges
return new HttpExchangeRepository() {
@Override
public List<HttpExchange> findAll() {
return null; // only implement if you use /actuator/httpexchanges
}
@Override
public void add(HttpExchange httpExchange) {
StringBuffer out = new StringBuffer();
out.append("Request:\n");
httpExchange.getRequest().getHeaders().forEach((key, value) -> {
out.append(key + ": " + value + "\n");
});
if (httpExchange.getRequest().getMethod() != null && httpExchange.getRequest().getMethod().length() > 0) {
out.append(httpExchange.getRequest().getMethod());
out.append(" ");
out.append(httpExchange.getRequest().getUri());
}
out.append("\nResponse:\n");
httpExchange.getResponse().getHeaders().forEach((key, value) -> {
out.append(key + ": " + value + "\n");
});
out.append(String.format("Status: %s Time taken: %.6f sec",httpExchange.getResponse().getStatus(),
httpExchange.getTimeTaken().getNano()*0.0000000001));
log.info(out.toString());
MDC.clear();
}
};
}in pom.xml : add <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
#management.endpoints.enabled-by-default=true
management.endpoint.mappings.enabled=true
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=info, health, mappingscall http://localhost:9090/actuator/ oder direkt http://localhost:9090/actuator/mappings to show the REST (and other ) enpoints
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:build.properties", ignoreResourceNotFound = false)Spring MVC , Spring Basis Componenten die auf built on the Servlet API (ein offizieller Java Standard ) aufsetzt und letztlich das "HttpServlet" abstrahiert, vor dem Entwickler verbirgt und damit leichter benutzbar macht.
Letztlich ersetzt die @Controller die Notwendigkeit sich mit dem HttpServlet auseinandersetzten zu müssen.
Zum @Controller gehören weitere Annotations, die das ganze erst rund machen, z.B. :
@PostMapping("/meinpfad"), ebenso@GetMapping,@PutMapping,@DeleteMapping,@PatchMapping, mit 7 möglichen Parametern@RequestParam(required = false)
Simply put, the @RequestBody annotation on a method argument inside a @Controller class maps the HttpRequest body to a transfer or domain object, enabling automatic deserialization of the inbound HttpRequest body onto a Java object. Der Text im "request body" wird dann als JSON oder XML angesehen und es wird versucht davon direkt ein entsprechendes Java- Objekt zu erzeugen und zu bestücken.
- optinal:
@RequestBody(required = true)
das Gegenstück zu @RequestBody nur für die Rückgabe des Ergebnisses
@RestController’s source code shows that it actually is a @Controller, with the added @ResponseBody annotation. Which is equivalent to writing @Controllers which have @ResponseBody annotated on every single method.
ergänzt den @RequiredArgsConstructor um eine @Autowired Annotation
Passiert ja im RestController unter Umständen komplett implizit, daher hier nochmal zur Erinnerung , wie es explizit geht:
//create ObjectMapper instance
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//read json file and convert to customer object
Customer customer = objectMapper.readValue(new File("customer.json"), Customer.class);- in Intellij - maven see https://stackoverflow.com/a/36071308/3952407
- gradle: add
plugins{ id 'idea' }and
idea {
module {
downloadJavadoc = true
}
}pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.integration</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-integration-smb</artifactId>
<version>6.0.4</version>
</dependency> void integrationSpringtest() throws IOException {
var ssf = new SmbSessionFactory();
ssf.setHost(host);
// ssf.setHost(transfer);
ssf.setUsername(host + "\\" + username);
ssf.setPassword(password);
ssf.setShareAndDir("/SHAREName/mydir/");
var session = ssf.getSession();
var files = session.list(".");
for (var file : files) {
log.info("CanonicalPath {}", file.getCanonicalPath());
}
log.info("test.csv {}",session.isFile("test.csv"));
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
session.read("test.csv",outputStream);
byte[] fileContents = outputStream.toByteArray();
outputStream.close();
session.close();
log.info("File content: " + new String(fileContents));
}- use
OncePerRequestFilterand excend that. - consider using and implementing a
HandlerInterceptorAdapterinstead of a filter and implementing aWebMvcConfigurerthat adds thatHandlerInterceptorAdapter - However, a
OncePerRequestFiltermight be more suitable because:- It is at a lower level than
HandlerInterceptorAdapter, which means it is executed before any Spring-specific processing takes place. It ensures that your check is performed once and only once per request. It allows access to the raw request and response objects.
- It is at a lower level than
- On the other hand,
HandlerInterceptorAdaptercould be a better fit- if your custom filter logic is tightly integrated with your Spring MVC controllers, and you need to utilize Spring MVC specific features.
- define a OncePerRequestFilter :
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyOncePerRequestExceptionHandlingFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Process the request and catch exceptions from other filters , therefore avoid spring boots own
// exception handling which would reroute the request to "/error" page , which does not make much sense for
// REST requests
try {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (Exception ex){
log.error("exception: ",ex);
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST);
}
}
}- add this filter even before your other filters:
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.addFilterBefore(new MyOncePerRequestExceptionHandlingFilter(),
BasicAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterAfter(new MyRequestValidationFilter(),
MyOncePerRequestExceptionHandlingFilter.class)
.addFilterAfter(new AuthenticationLoggingFilter(),
BasicAuthenticationFilter.class).authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().permitAll();
return http.build();
}@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class ProjectConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Value("${spring.websecurity.debug:false}")
boolean webSecurityDebug;
@Bean
public WebSecurityCustomizer webSecurityCustomizer() {
return (web) -> web.debug(webSecurityDebug);
}
}