This is the tentative list of project ideas for the 2024 programme.
Relevant information about each of the projects are provided, and those interested can contact the mentors in case of any query.
Pre-requisites mentioned are not enforced in any way, and are just there to give you a sense of what skills are needed for the project, although it is a plus point if you have the pre-requisites :)
Note that this list is subject to change and not complete.
Current Project Count: 13
Check out our Amazing Projects below:
- Virtual Try On for Products
- Text To Speech
- GPT Reimagined: KANs vs MLPs
- Super MaRLo Bros
- ChromaSight
- Stock Transformers
- 2D Car Simulation with Genetic Algorithms
- SmartMailGuard: AI-Powered Email Classification
- Verbal to Visual : Text to Image Generation
- Deep Multiclass Audio Classification
- Lip Reading
- Xcelerate - Self Driving Car
- The Not So Generic Chatbot
Image visual try-on aims at transferring a target clothes image onto a reference person, and has become a hot topic in recent years. Prior works usually focus on preserving the character of a clothes image (e.g. texture, logo, embroidery) when warping it to arbitrary human pose. However, it remains a big challenge to generate photo-realistic try-on images when large occlusions and human poses are presented in the reference person.
This is a topic which will include Augmented Reality(AR) combined with Machine Learning(ML) to detect body movements. There are many ways to tackle this issue. One of them being:
-
A semantic layout generation module utilizes semantic segmentation of the reference image to progressively predict the desired semantic layout after try-on.
-
A clothes warping module warps clothes image according to the generated semantic layout, where a second-order difference constraint is introduced to stabilize the warping process during training.
-
An inpainting module for content fusion integrates all information (e.g. reference image, semantic layout, warped clothes) to adaptively produce each semantic part of human body.
This is one of the ways in which this problem can be tackled but not the only one. Applicants are encouraged to come up with your own solutions and steps to complete this project which could be more efficient and unique.
[1] Human Localization in Real-Time Video
[2] Virtual Try-On Implementation
Pre-requisites: C++ Programming, Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Computer Vision
Difficulty: Hard
Mentors: Mrudul Pawar
Domains: Computer Vision, Deep Learning, Augmented Reality
Text To Speech Synthesis is a machine learning task that involves converting written text into spoken words. The goal is to generate synthetic speech that sounds natural and resembles human speech as closely as possible.
Primitively, this was done by storing recorded clips of a person making various sounds like "ri-" or "-zz" and construct speech from this database by mapping sequences of alphabets to these sounds. However, with the rise of Deep Learning, many more efficient methods have emerged that perform much better at this task.
Normally, Deep Learning Models dealing with TTS comprise of a frontend and a backend, the frontend converts character sequences to spectrograms, and the backend(vocoder) converts spectrograms to audio. The frontend and backend used however differ widely across solutions.
This project will be exploring a wide number of these methods and implementing the ones that work best. Text To Speech has huge applications, some of which include, helping the blind browse websites, giving a voice to the mute(remember Stephen Hawking?), making announcements in public places(airports, train stations) and so, so much more.
Additionally, more research is ongoing to see how feasible it is to create a TTS model that mimics someone else voice(deepfakes) given audio clips of that person speaking.
The sky is the limit with this project, all you need is the hardwork and commitment to see it through.
[1] Understanding Text To Speech
[2] Understanding Audio Processing and Spectrograms
[3] A good overview of Text To Speech
[4] Some papers on Speech Synthesis
Pre-requisites: Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Difficulty: Hard
Mentors: Warren Jacinto, Veeransh Shah
Domains: Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Audio Processing
In this project, we aim to explore the effectiveness of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) as an alternative to traditional Multi Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) for implementing Generative Pretrained Transformers (GPTs). GPTs are a class of machine learning models known for their ability to generate natural language text and perform various natural language processing tasks. Traditionally, GPTs have been implemented using MLP architectures. However, KANs, a relatively new development, have shown promise in outperforming MLPs in certain tasks.
This project contributes to the ongoing research in machine learning architectures by providing empirical evidence on the efficacy of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks as an alternative to traditional MLPs for implementing state-of-the-art language models like GPTs. The findings of this study can inform future developments in neural network architectures and guide the design of more efficient and effective models for natural language processing tasks.
Objectives:
- Implement GPT using the traditional MLP approach.
- Implement GPT using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs).
- Compare the performance of GPT implemented with MLPs and KANs across various metrics, including but not limited to:
- Language generation quality
- Training speed
- Model size
- Resource utilization
- Provide a proof of principle for the performances of MLP-based GPTs versus KAN-based GPTs.
[1] MLP vs KAN
[2] KANs explained
[3] Original Research Paper proposing KANs
Pre-requisites: Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Machine Learning Algorithms and Neural Networks
Difficulty: Hard
Mentors: Param Thakkar, Mayank Palan
Domains: Deep Learning
Inspired by the classic game Super Mario Bros, Super MaRLo Bros is an exciting project that combines game development and artificial intelligence. You'll build the game from scratch using PyGame and then train the computer to navigate and succeed in it using Reinforcement Learning. You have to teach the computer to play the game you made. We'll experiment with different RL algorithms, learning how they work and which ones are most effective as we go along the project. This project is perfect for anyone interested in game development and artificial intelligence.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a machine learning technique that trains software to make optimal decisions through trial and error. RL algorithms use a reward-and-punishment system to process data. Actions that help achieve the goal are reinforced, while others are ignored.
By the end, you'll have a fully functional game and an AI-based smart computer player! No need to get overwhelmed, it only needs your interest!
[1] PyGame
[3] Basics of RL
Pre-requisites: Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Reinforcement Learning
Difficulty: Medium to Hard
Mentors: Vedant Mehra, Labhansh Naik
Domains: Game Development, Reinforcement Learning
ChromaSight is an innovative color correction tool designed to enhance visual experiences for individuals with color blindness. Our tool utilizes cutting-edge machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to provide personalized color correction solutions tailored to each user's specific color vision deficiencies.
The tool takes in images as input and processes them to enhance colors or apply color correction algorithms tailored for colorblindness. It analyzes the image and adjusts colors based on the type and severity of colorblindness. The tool provides an intuitive interface with options to upload images, select color correction modes, and view the corrected output.
Goals for this project are to:
- Incorporate accessibility features such as text-to-speech for navigation and colorblind-friendly UI design
- Utilize machine learning algorithms to automatically detect color blindness type and severity from user input or uploaded images.
The tool outputs corrected images that are optimized for colorblind individuals, ensuring better visibility and comprehension of visual content.
[1] A Color Guide for Color Blind People Using Image Processing and OpenCV
[2] Coloured Object Detection for Blind People Using CNN
Pre-requisites: Python Programming, Basic Understanding of CNNs and Image Processing
Difficulty: Medium
Mentors: Aditi Dhumal, Anoushka Ruikar
Domains: Deep Learning, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing
In the modern capital market, the price of a stock is often considered to be highly volatile and unpredictable because of various social, financial, political and other dynamic factors that can bring catastrophic financial loss to the investors. This project aims to predict stock prices using transformer architecture by utilising the concept of time series forecasting.
The transformer model has been widely leveraged for natural language processing and computer vision tasks,but is less frequently used for tasks like stock prices prediction. The introduction of time2vec encoding to represent the time series features has made it possible to employ the transformer model for the stock price prediction. We aim to leverage these two effective techniques to discover forecasting ability on volatile stock markets.
[2] Transformer Architecture Article
[3] Transformer Architecture 'Attention is all you need' paper
[4] Time2Vec from 8:00 to 12:00
Difficulty: Mediumto Hard
Mentors: Kindipsingh Malhi, Tvisha Vedant
Domains: Machine Learning, Deep Learning
Welcome to the exciting world of 2D car simulations powered by physics engines and genetic algorithms! 🎉 In this project, we'll explore how these powerful tools can be combined to create a virtual playground where cars evolve and adapt to their environment. Our simulation will take place in a highly realistic 2D world governed by the laws of physics, featuring mind-blowing elements like collision detection, contact callbacks, convex polygons and circles, multiple shapes per body, stable stacking, joints and constraints, and momentum and impulses, ensuring truly lifelike movements. Moreover, we'll implement our own physics engine, providing a deep understanding of the underlying mechanics and customization for our specific needs. Additionally, we'll harness the power of genetic algorithms (GAs) to create an intelligent and adaptive system that searches for the best car designs. GAs, inspired by natural selection and genetics, allow us to evolve solutions towards optimal performance. We'll start with a random initial population of car designs, evaluate their performance based on a fitness function (e.g., distance traveled, stability, etc.), and use genetic operations like crossover and mutation to create new generations. This iterative process continues until we find an optimal or satisfactory car design. By the end of this project, we will have a fully working simulation of 2D cars with all mentioned features and various parameters.
[1] Basics Of Genetic Algorithms
[2] Understanding Genetic Algorithms
[3] Physics Enginge
Pre-requisites: Basic Understanding of Web Development, Mechanics, Linear Algebra
Difficulty: Medium to Hard
Mentors: Manas Bavaskar, Sharan Poojari
Domains: Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning, Computer Graphics and Simulation, Game Development
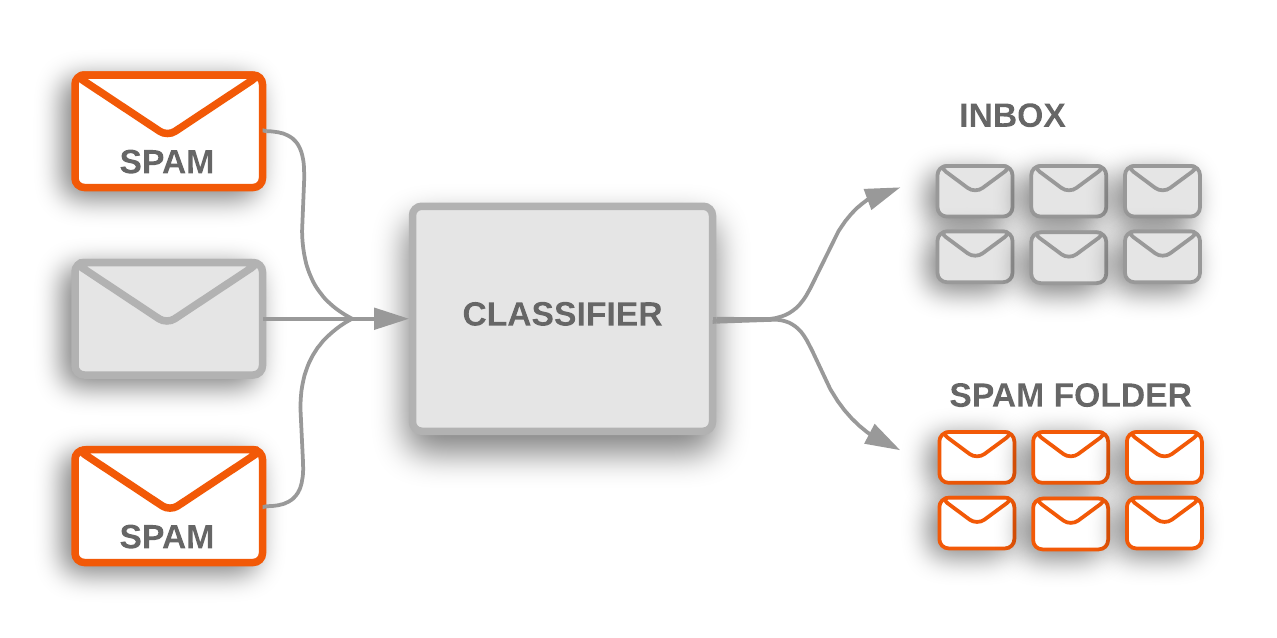
In today's fast-paced digital world, our inboxes are bombarded with a relentless stream of emails, making it increasingly challenging to separate the essential from the irrelevant. Spam emails not only clutter our inboxes but also waste valuable time and pose security risks.
Our mission is to develop an AI-powered tool that can accurately distinguish between spam and legitimate emails, revolutionizing productivity and enhancing security. We'll embark on an exciting journey into probabilistic programming, starting with the Naive Bayes Algorithm to build the foundation from scratch. Moreover we'll delve into the world of advanced neural networks, utilizing Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for their ability to understand the context of emails over time. To push the boundaries even further, we'll harness the power of state-of-the-art architectures like transformers, which have set new benchmarks in natural language processing.
[2] Introduction To Transformers
[4] Bayes Algorithm
Pre-requisites: Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Neural Networks and Bayesian Algorithms
Difficulty: Medium to Hard
Mentors: Druhi Phutane, Raya Chakravarty
Domains: Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Probabilistic Programming
Have you ever imagined a world where your words can instantly paint a picture? Verbal to Visual turns this imagination into reality.
Welcome to Verbal to Visual, an innovative project where deep learning breathes life into words, transforming textual descriptions into vivid, lifelike images. Harnessing the power of state-of-the-art neural networks, this project showcases a perfect fusion of natural language processing and computer vision to create stunning visual representations from mere text.
A very large dataset containing images and its text descriptions is used to train our model for it to extract features through encoder and create embeddings. A short text description is given as input. Our model predicts tokens for the image using trained data. Tokens are given input to the decoder to generate the image.
[1] Txt2Img-MHN
[3] Image Generation: Text to Image
[4] GAN Introduction
Pre-requisites: Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Difficulty: Medium to Hard
Mentors: Param Parekh, Rohan Parab
Domains: Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision
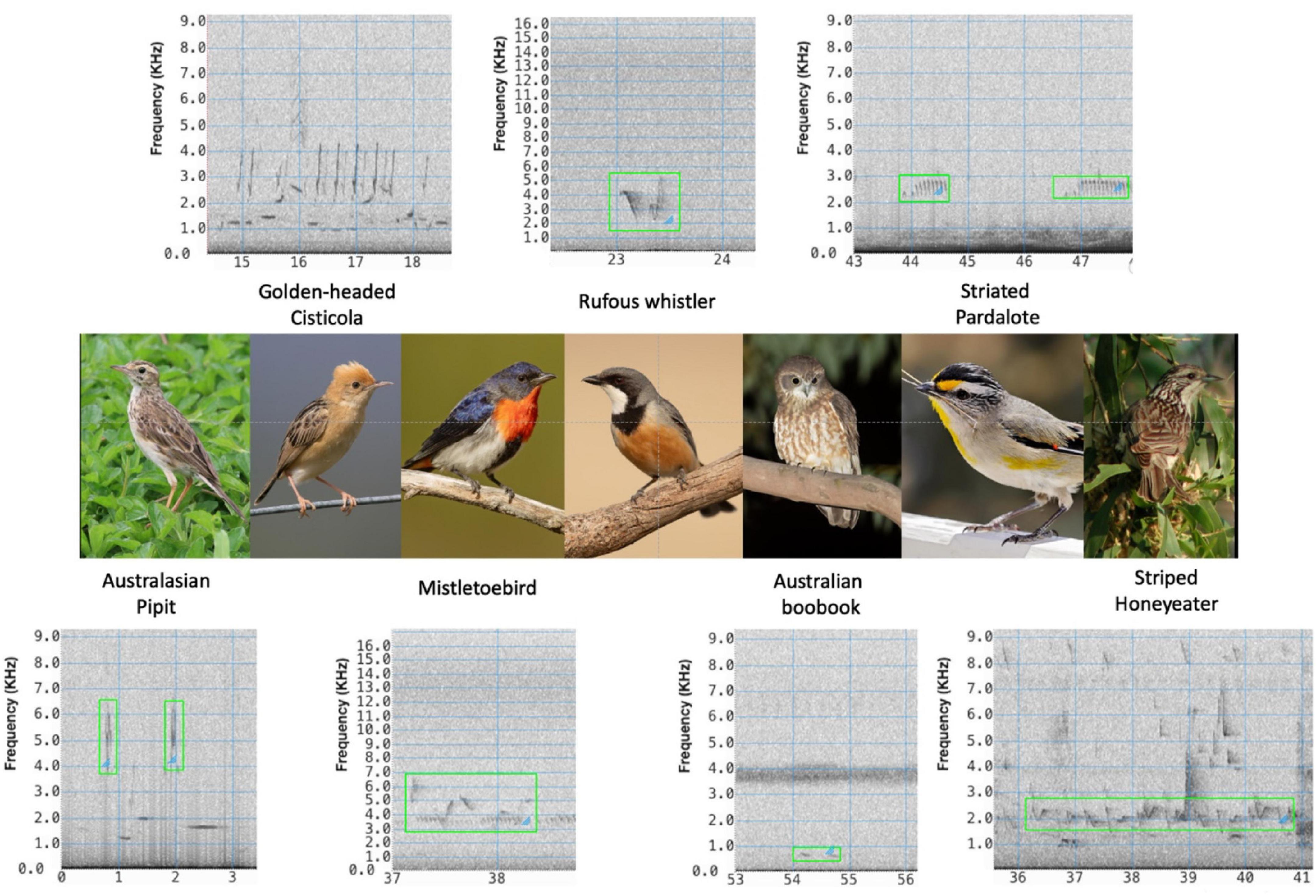
Our project focuses on classifying various audio recordings using CNNs. To achieve this, we will explore the basic architecture of CNNs in great detail. This includes a deep understanding of the underlying concepts of CNNs, such as convolutional layers (filters & kernels), batch normalization, different activation functions, loss functions, backpropagation, gradient descent, and more.
We would be providing our model multiple audio files based on which it would classify which audio corresponds to which bird. For this we would initially train the model on a dataset having all details of the birds and their corresponding sounds. Once it is trained we would test out the model results and try improve it's efficiency.
We will approach this project using two methodologies:
1.Building a Convolutional Neural Network from Scratch
2.Using Transfer Learning
Transfer learning involves leveraging pre-trained model weights for audio classification. Here, you will also fine-tune the pre-trained model on a specific dataset based on the project's requirements.
[2] Understanding Audio Processing and Spectrograms
It's often confusing for beginners to understand that, besides image processing, CNNs are also highly effective for processing audio data.
Pre-requisites: Proficiency in Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Neural Networks
Difficulty: Hard
Mentors: Kshitij Shah, Param Thakkar
Domains: Machine Learning, Deep Learning
A lip-reading model based on CNN and LSTM applies the power of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in combination with Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs) to decode speech from video sequences with lip movements. While the LSTM component captures the temporal dynamics of these motions for understanding spoken phrases or words, the CNN part extracts spatial features from consecutive frames showing lip movements. Hence, this combination can process both temporal and spatial information efficiently. When the model learns how lips move to produce particular sounds heard during speech it can accommodate itself to different accents including those of individual speakers. It is this adaptability that is particularly useful in noisy environments where audio quality varies greatly for example.
Pre-requisites: Proficiency in Python Programming, Basic Understanding of Natural Language Processing
Difficulty: Hard
Mentor: Veeransh Shah
Domains: Computer Vision, Natural Langauge Processing, Speech Recognition
videoplayback.4.1.1.mp4
The project uses a CNN to process the raw pixel data from the front-facing camera and map it directly to steering commands. This end-to-end approach eliminates the need for explicit feature extraction and path planning.
The Project focuses on training a convolutional neural network (CNN) to map raw pixels from a single front-facing camera directly to steering commands. This end-to-end approach is capable of navigating in various driving conditions, including local roads, highways, parking lots, and unpaved roads. The system learns necessary processing steps internally, detecting road features without explicit training for those features.
- Lane Detection
- Traffic Sign Recognition
- Vehicle Detection
- Path Planning
- Road Segmentation
Self driving car (Our Agent) has variable
- Speed
- Steering Angle
Sensor data is collected from the car and the car is controlled using the data collected.
There are 2 approaches to this project:
- Behavioral Cloning
- End-to-End Learning
Behavioral cloning is a method by which a neural network learns to map an input to an output by training on a dataset of input-output pairs. In the context of self-driving cars, the input is the image from the front-facing camera and the output is the steering angle. The network learns to predict the steering angle by training on the dataset of images and corresponding steering angles.
End-to-End learning is a method by which a neural network learns to map an input to an output by training on a dataset of input-output pairs. In the context of self-driving cars, the input is the image from the front-facing camera and the output is the steering angle. The network learns to predict the steering angle by training on the dataset of images and corresponding steering angles.
These are two of the ways in which this problem can be tackled but not the only one. Applicants are encouraged to come up with your own solutions and steps to complete this project which could be more efficient and unique
Pre-requisites: Gist of Neural Networks, Basic Understanding of Computer Vision, Proficiency in Python Programming
Difficulty: Medium to Hard
Mentors: Abhi Mehta , Aditya Yedurkar
Domains: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Computer Vision
Traditional LLMs have a limited Scope and their outputs just depend on the data it is originally trained on. If a user asks a query, the response of which depends on a specific chunk of information which might not be related to the general data llms are trained on then the output obtained is not reliable and may lead to false decisions. RAG is a great way to overcome this issue, also it is comparitively efficient than other techniques like fine-tuning. Due to the dawn of Multimodal LLMs, the limited scope of RAGs to utilise only text documents is expanding to include other media like images. In this project we aim to develop a topic specific chatbot that will havev additional context, using MultiModal RAG.It will be able to take text and image inputs and give reliable output based on the extra data it will be fed.
Difficulty: Medium
Mentors:Mohammed Bhadsorawala, Kshitij Shah , Tvisha Vedant
Domains: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, LLMs