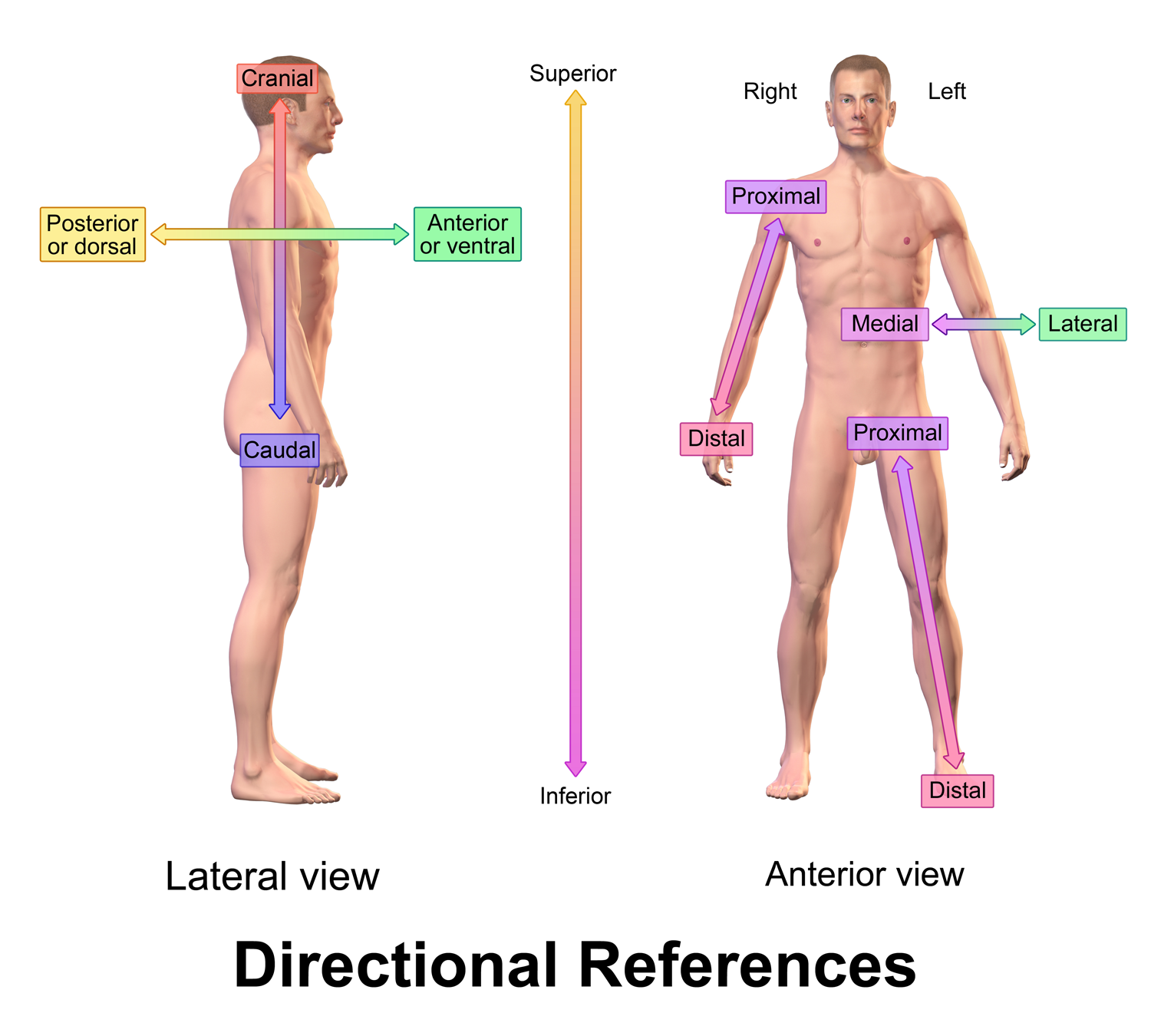
- Anatomical Directions
- Cybersickness
- Head-Mounted Display (HMD)
- Motion Sickness
- Postural Activity
- Postural Stability
- Simulator Sickness
- Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ)
- Somatosensory System
- Vection
- Vergence-Accommodation Conflict
- Vestibular System
- VR Sickness
- Anterior-Posterior Plane: Swaying forward and backward
- Anterior (Frontside)
- Posterior (Backside)
- Medial-Lateral Plane: Swaying left and right
Term to describe side effects from use of virtual environments. Often mentioned in studies using a variety of technologies including flat screen displays and HMDs.
See also: VR Sickness
Display device worn on the head with one or two small displays. Examples of head-mounted displays are modern VR headsets such as: Valve Index, HTC Vive, Oculus Rift.
Motion Sickness occurs due to difference between actual and expected motion. Main causes are:
- Motion that is felt but not seen (terrestrial motion sickness)
- Motion that is seen but not felt (space motion sickness)
- Motions felt and seen, that don't correspond to another
Postural Activity/Sway describes the horizontal movement of the center of gravity even when a person is standing still. It is essential and inevitable due to small pertubations within the body (e.g. breathing, shifting bodyweight between feet etc.). Postural Stability (balance) requires coordination of input from multiple sensory systems including the vestibular , somatosensory, and visual systems (reference to verticality of body , spacial relation to objects).
See also: Anatomical Directions
Term originating from early use of flight simulators in the military, and is still currently used in research using modern HMD technology. Simulator Sickness is a subset of motion sickness that is typically experienced by pilots who undergo training for extended periods of time in flight simulators. Symptoms include discomfort, apathy, drowsiness, disorientation, fatigue, vomiting.
Questionnaire intended for military personnel using flight simulators to asses simulation quality. Scores between 10-15 indicate significant symptoms; Scores between 15-20 are a concern; Scores over 20 indicate a problem simulator. Cut-off scores established from military personnel using flight simulators. Scores may differ for general population and tend to be higher in virtual environments compared to military grade flight simulators.
Part of the sensory nervous system, sensing proprioception/kinesthesia (self-movement and body position), as well as haptic perception (pressure, vibratory, and touch senses). Provides information about spatial position, movement relative to the support surface, and postition of body parts relative to each other.
Illusion of self-motion, occurs when there is perceived bodily motion despite no movement is taking place.
Vergence refers to the way the eyes move laterally to adjust to items moving toward and away from the eyes combined with the process of focusing (accomodation). These visual processes do not occur naturally in a stereoscopic display as accomodation occurs at a fixed screen depth.
Organs part of the inner ear, that regulate equilibrium. Provides directional information relative to head position (internal gravitational, linear, and angular acceleration).
Term typically used in studies using HMDs. Occurs when exposure to a virtual environment causes symptoms similar to simulator- or motion sickness. While simulator sickness tends to be characterized by oculomotor disturbances, VR sickness is characterized by disorientation.
See also: Cybersickness