You are given a 0-indexed integer array arr, and an m x n integer matrix mat. arr and mat both contain all the integers in the range [1, m * n].
Go through each index i in arr starting from index 0 and paint the cell in mat containing the integer arr[i].
Return the smallest index i at which either a row or a column will be completely painted in mat.
Example 1:
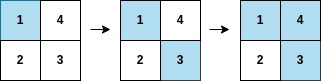
Input: arr = [1,3,4,2], mat = [[1,4],[2,3]] Output: 2 Explanation: The moves are shown in order, and both the first row and second column of the matrix become fully painted at arr[2].
Example 2:
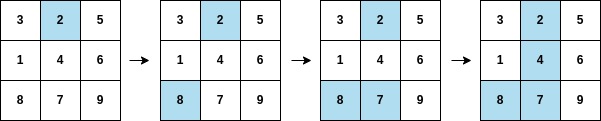
Input: arr = [2,8,7,4,1,3,5,6,9], mat = [[3,2,5],[1,4,6],[8,7,9]] Output: 3 Explanation: The second column becomes fully painted at arr[3].
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn = mat[i].lengtharr.length == m * n1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 1051 <= arr[i], mat[r][c] <= m * n- All the integers of
arrare unique. - All the integers of
matare unique.